The formula for work when force and displacement are in the same direction.
W= Fd
Energy of Motion
Kinetic energy
This states that net work is equal to change in kinetic energy.
Work-Energy Theorem
The unit of power
Watt
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a given mass of a substance by 1 degree C / 1 K
Specific heat capacity
A force where work is independent of path (example gravity).
Conservative force
The type of work that occurs when a force opposes motion.
Negative work
Energy stored in a stretched spring
Elastic potential energy
In the absence of non-conservative forces, this quantity remains unchanged.
Total mechanical energy
To calculate power, you need one of these two pairs of values.
Work and time OR force and speed
"Heat Lost = Heat Gained" is an expression of this law specific to heat transfer.
Law of Conservation of Energy
The ratio of output force to input force for a machine
Actual mechanical advantage (AMA)
A 60. N force is applied at 30.° to move an object 5.0 m. How much work is done?
260J
A 1.0kg ball is dropped from 10.0m. If it loses 10% of its initial energy due to air resistance, it will hit the ground at this speed.
13m/s
A crane lifts a 1250kg load to a height of 25m in 35s. What is the power output of the crane?
8800W (8.8kW)
0.50kg of aluminum (c=900.J/kg°C) cools from 85°C to 35°C. How much heat did it release?
23kJ (23000J)
The rate at which work is done or energy is transferred
Power
0J (Force is perpendicular to displacement).
A 5.0kg mass is lifted from the top of a desk 0.85m above the floor to a shelf 2.5m above the floor. How much gravitational potential energy did it gain?
81J
A block slides down a ramp with friction. The relationship between work by friction and energy change is...
Wfriction=ΔKE+ΔPE (i.e. work due to friction is equal to change in total mechanical energy)
An 850kg elevator is lifted at a constant 1.2m/s. If the motor lifting the elevator is rated at 18hp, what is its efficiency?
74%
0.750kg of an unknown substance originally at -15.0°C is placed in 2.00kg of water originally at 20.0°C. If the final temperature of the substance and water is 18.8ºC, what is the likely identity of the unknown substance?
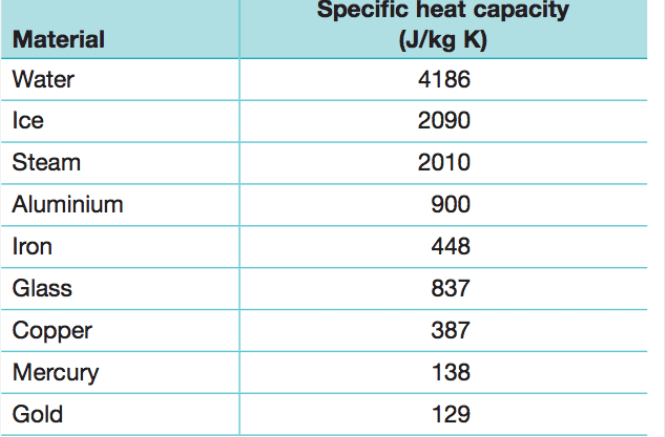
Copper
When objects in contact reach the same temperature and stop exchanging heat.
Thermal equilibrium
A delivery person pushes a 30.0kg crate with 100.N horizontally against 20.N of friction over a distance of 10.0m. If the crate starts from rest, what is the final speed of the crate?
7.3m/s
A 0.40kg ball is thrown upwards from 1.2m above the ground. If its initial upwards speed is 15m/s, what is the total mechanical energy of the ball?
50.J
A pendulum swings from 0.80m height to its lowest point. If 10.0% of its initial energy is lost to air resistance, its speed at its lowest point will be this many percent of the maximum speed without air resistance.
95%
If a ramp is 8.0m long and 2.0m high with 75% efficiency, what is the average force of friction acting when pushing a 15kg object up this ramp at constant speed?
49N
125 grams of gold (c=127J/kg°C) at 145°C is placed in 0.25L of water (density of water 0.9998g/mL) initially at 25°C. What is the final temperature?
27°C
A device used to measure heat exchange in physical or chemical processes.
Calorimeter