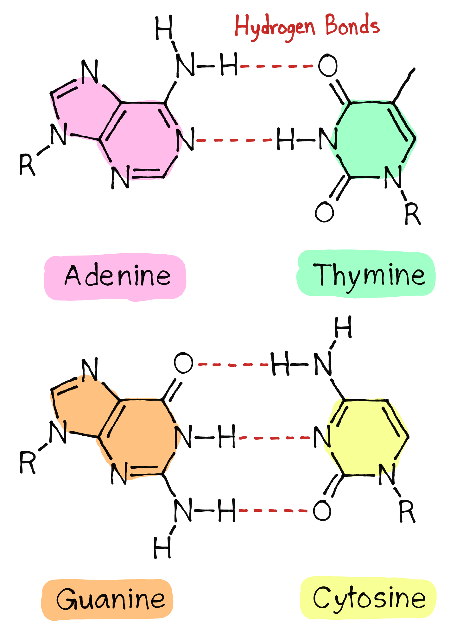
What are the pairing rules (which letters go together) in DNA?
A-T and C-G
True or false: we have learned everything about DNA.
When does DNA replication occur?
Before cell division.
What is the purpose of protein synthesis?
To make proteins
What is a mutation?
A change in the DNA.
What are the monomers of DNA?
Nucleotides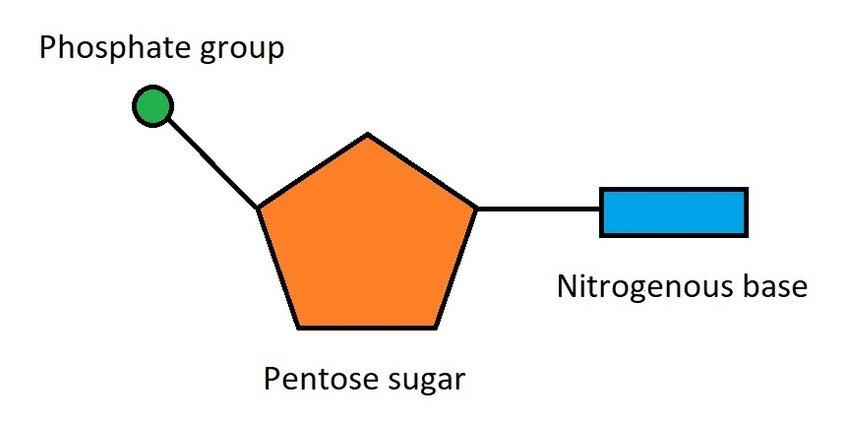
We learned about DNA discovery. From this example, explain something you can learn about how scientists discover new things.
Scientists build on the work of the people who came before them. 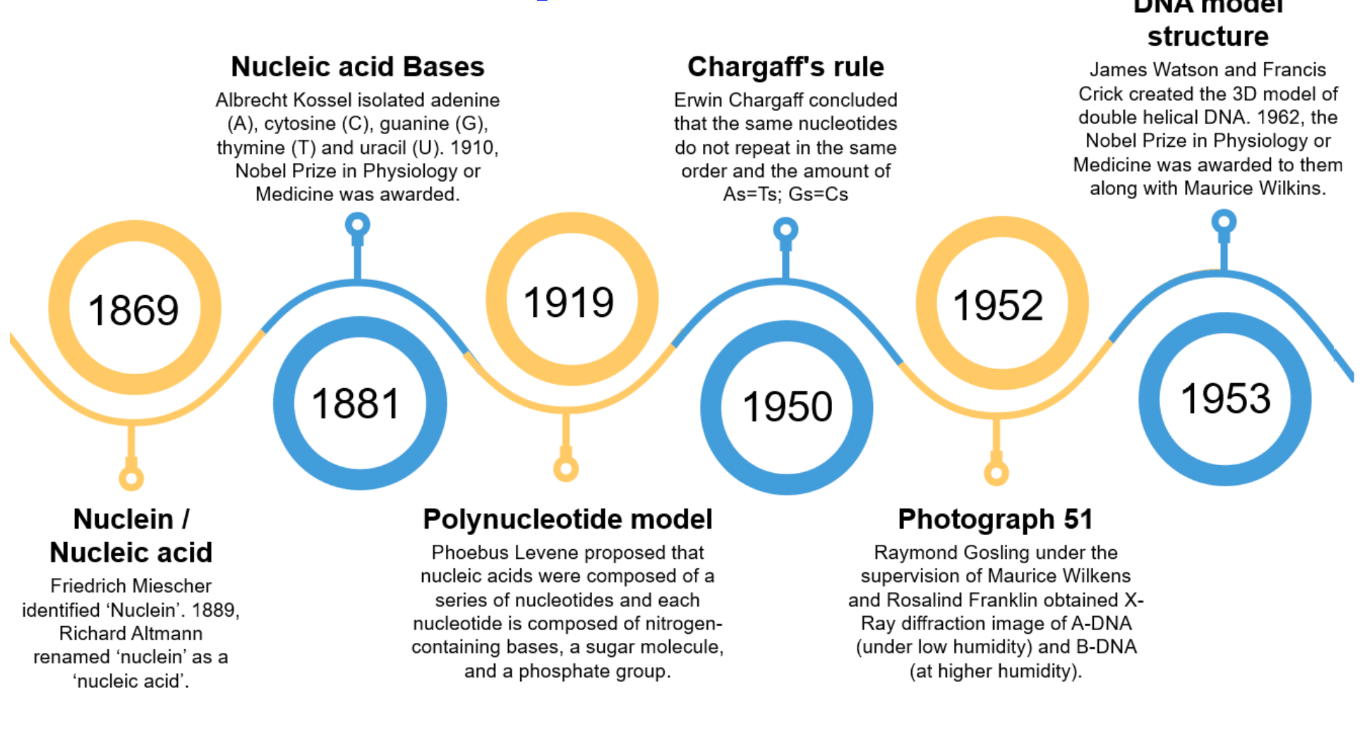
What two enzymes are used in DNA replication, and what does each one do?
Helicase divides the DNA and DNA polymerase builds a new molecule by adding nucleotides.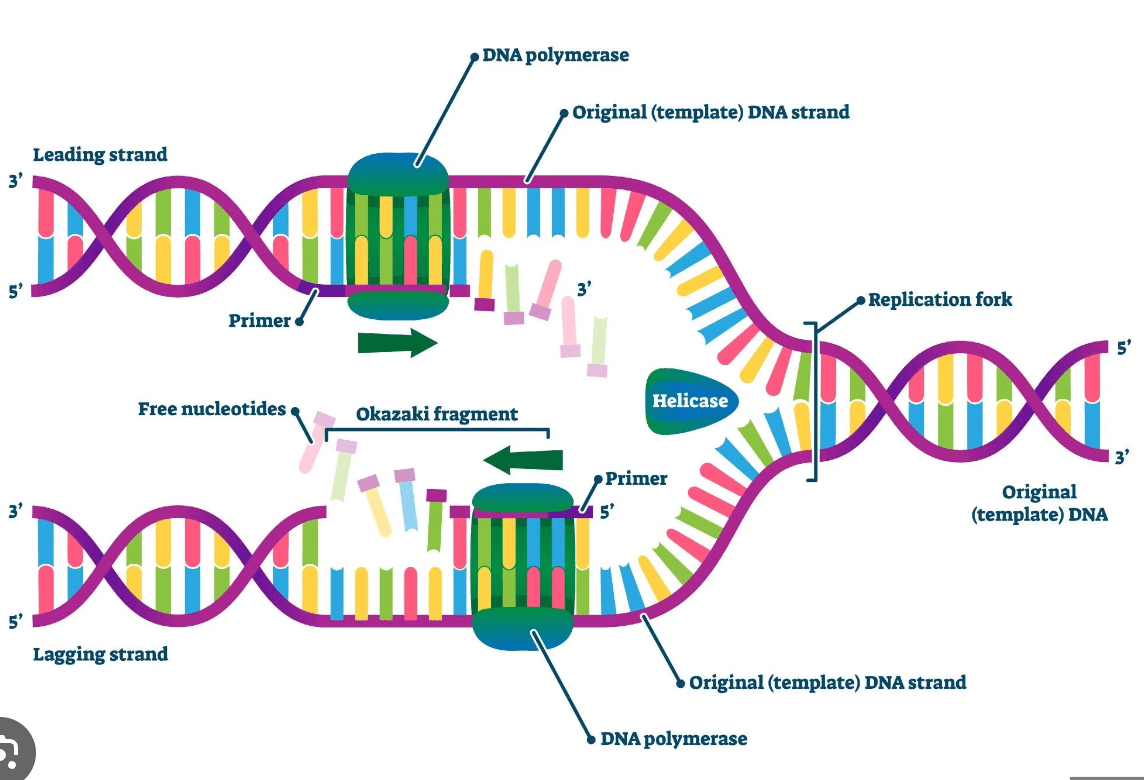
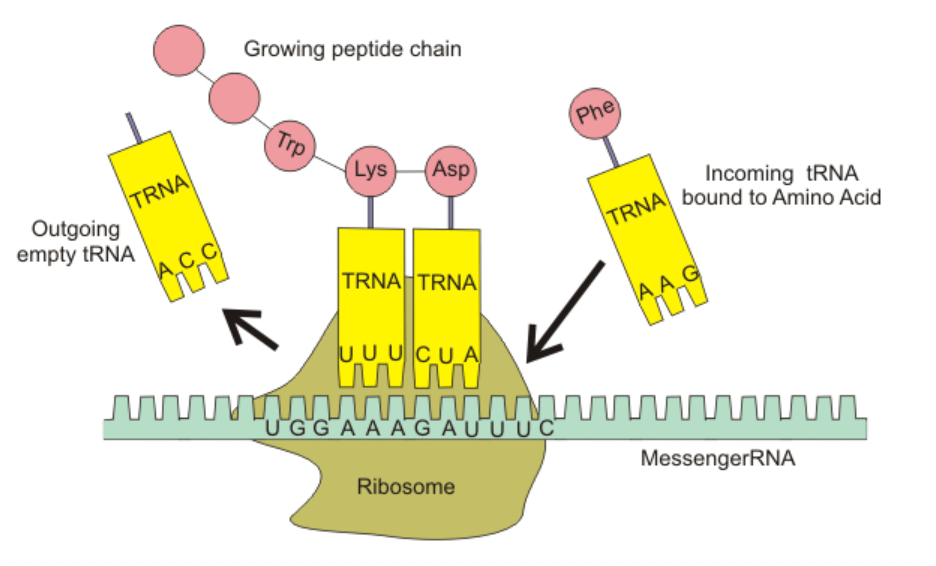
What is the name of this process? 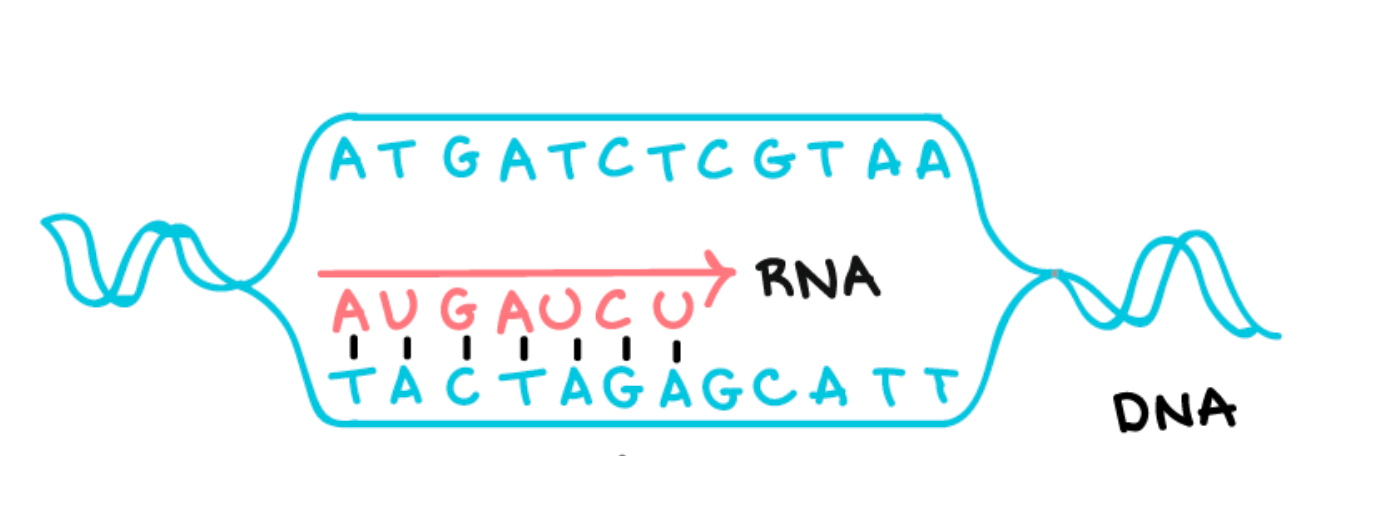
Transcription
Correct this sentence: Mutations start with a mistake in the amino acid.
Mutations start with a mistake in the DNA. 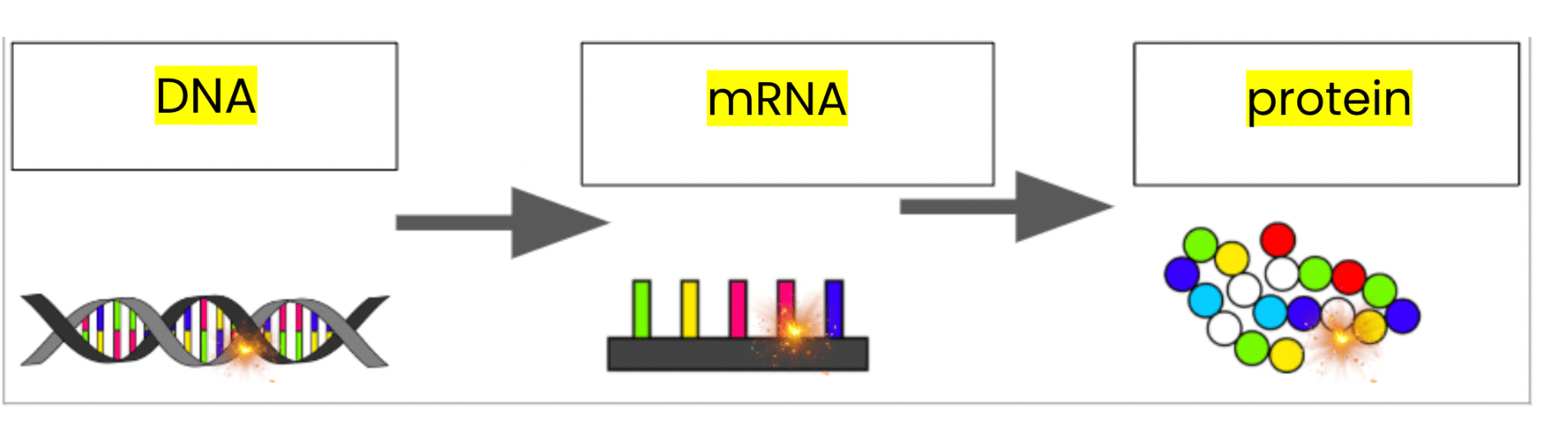
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
Sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base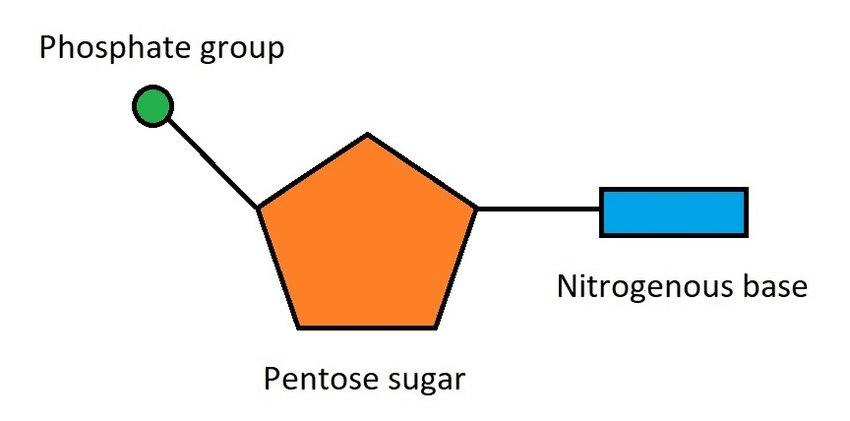
Complete the complementary DNA strand for this DNA:
TAC. AGG. GAC. CCC. TTT. TAT. CTA. GAC.
AUG. TCC. CTG. GGG. AAA. ATA. GAT. CTG.
Why do we say DNA replication is semi-conservative?
Each new strand is half old and half new.

What is the name of this process?
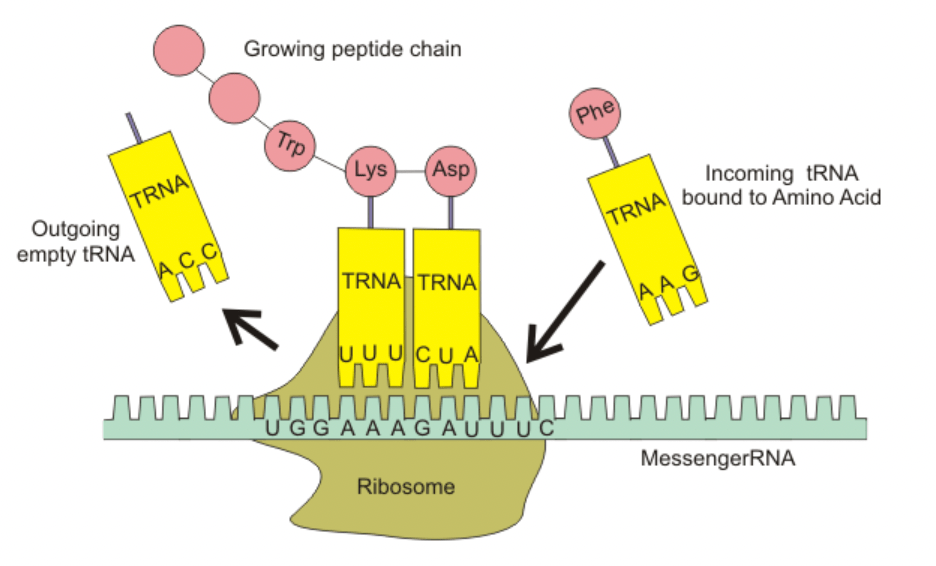
Translation
What is the main cause of mutations?
Mistakes in replication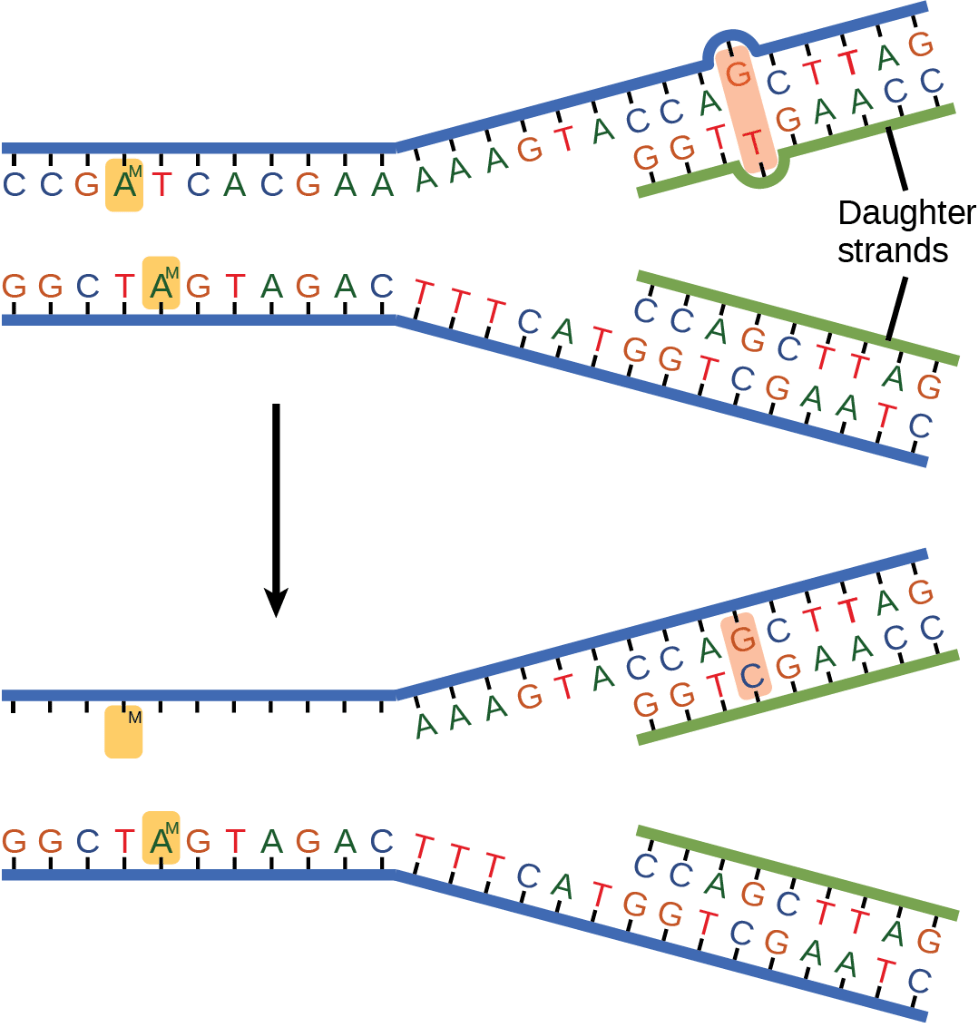
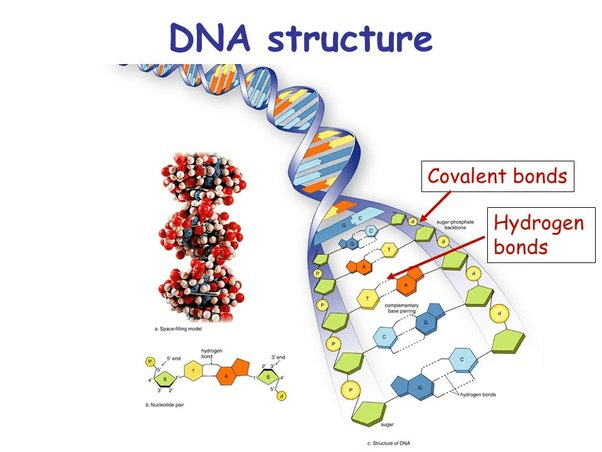
This bond connects nitrogen bases in DNA.
Hydrogen bond.
Tell at least THREE people who helped discover DNA and what they each contributed.
Watson and Crick discovered the DOUBLE HELIX. Rosalind Franklin took the X-Ray photo.
How do the new DNA strands compare to the original?
The new strands are identical to the original strand.
Describe TRANSCRIPTION in your own words.
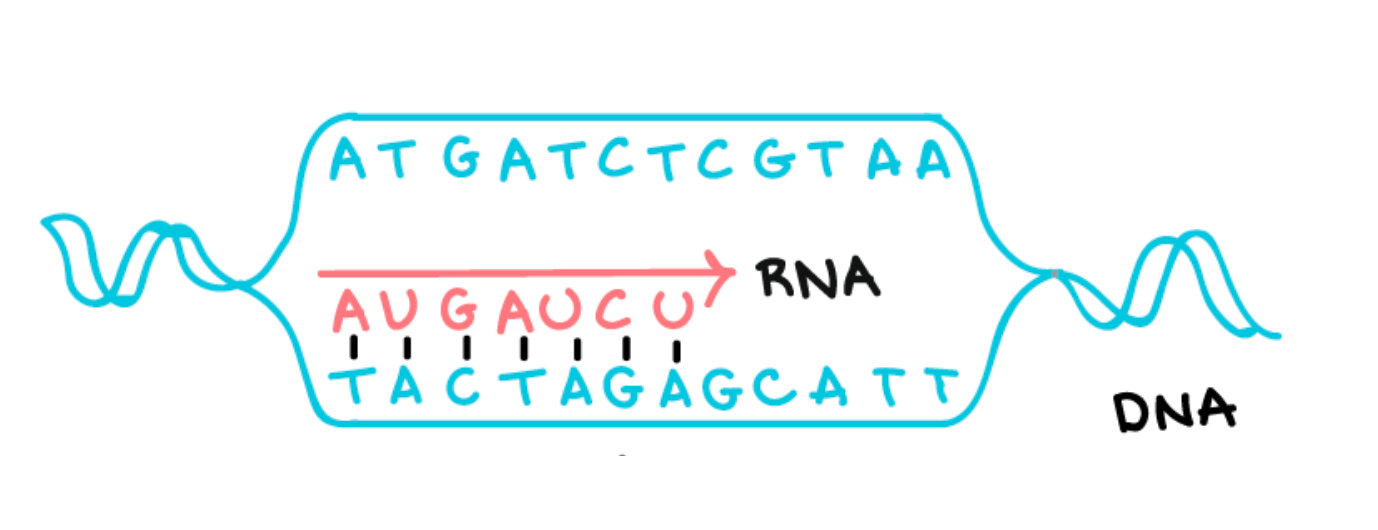 DNA polymerase unzips the DNA and adds nucleotides to make mRNA.
DNA polymerase unzips the DNA and adds nucleotides to make mRNA.
Give an example of a deleterious mutation.
Cystic fibrosis or sickle-cell anemia
This bond connects sugar and phosphate bases.
Covalent bond.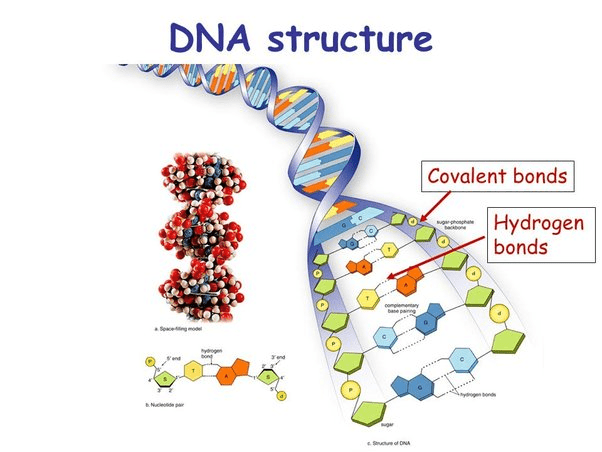
Tell two important applications of the Human Genome Project.
Easier to test for genetic diseases, helped us understand the role of human genes, made forensics easier, helped us understand human evolutionary relationships, made it easier to sequence genomes of other organisms
Why is DNA replication important?
So that each new cell has ALL of the genetic information.
Describe TRANSLATION in your own words.
Three nitrogen bases (codon) on the mRNA match to three bases (anticodon) on tRNA. The tRNA carries an amino acid that matches for each codon. The amino acids join to make a protein.