What are the four major vital signs?
Blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, body temperature.
What are the types of cells that help our bodies fight infection?
White blood cells
What is the function of the respiratory system?
Takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
What is the basic unit of communication in the nervous system?
The neuron
What is the major function of the heart?
To pump blood
Which organ helps the immune system remove pathogens from the bloodstream?
The liver
Which structure is responsible for gas exchange?
Alveoli
_______________ are clusters of neurons grouped together.
Nerves
The diagram of the heart below includes directional arrows that indicate the direction of blood flow. The structure labeled ‘X’ is called the _________________. 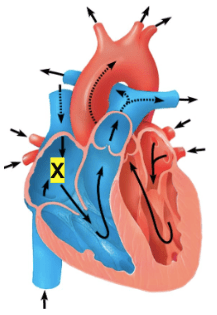
Right Atrium
How does the liver play a role in the digestive system?
It creates bile, which helps break down fats.
What is one function of the mouth in the digestive system?
Mechanical breakdown - Chews food and breaks it down further so we can swallow.
Chemical breakdown - Produces saliva, which has enzymes that help break down macromolecules.
What are the two MAIN divisions of the nervous system?
Central and Peripheral
Part A: List, in order, the pathway that food moves through the body (6 structures/organs).
Part B: Pick 1 structure/organ and explain the function.
Part A -- Mouth, pharynx (throat), esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine.
Part B -- Mouth: Mechanical breakdown (chewing) and chemical breakdown (saliva). Pharynx: acts as a tunnel. Esophagus: tube that connects back of throat to stomach. Stomach: holds food/fluid and breaks down food using acid. Small Intestine: absorbs nutrients and sends them to the rest of the body. Large Intestine: absorbs water, collects waste and moves it out of the body.
What is an example of negative feedback?
1) Body Temperature
2) Insulin/Glucagon Response
What are the two main function of the kidneys?
To maintain water and electrolyte levels in the body.
Remove waste in the form of urine.
Which structure is responsible for absorbing nutrients from the food we eat?
Small intestine
When you walk by a restaurant and smell food cooking, a signal gets sent to your brain and you immediately recognize the it. This is an example of ______________ neuron function.
Sensory
Part A: List, in order, the pathway that oxygen moves through the body (7 structures).
Part B: Pick 1 structures/organs and explain the function.
Part A -- Mouth/nasal cavity (nose), pharynx (throat), larynx (voicebox), trachea (windpipe), bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli.
Part B -- Mouth/nasal cavity: filters other gasses out of the air so we only inhale oxygen.
Pharynx, larynx, trachea: carry oxygen down to the lungs.
Bronchi and bronchioles: bring oxygen into the lungs
Alveoli: Where gas exchange happens (CO2 and O2).
Define systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Systolic - the force against the walls of your arteries when the heart is beating.
Diastolic - the force against the walls of your arteries when your heart is at rest (filling up with blood).
Both the skin and the mucus lining the inside of the nose are considered parts of the immune system. This is because they:
act as barriers, preventing pathogens from entering the body
Which disease is characterized by fluid in the air sacs of the lungs?
Pneumonia
What is the pathway that blood travels through the circulatory system?
Blood starts at the right side of the heart, then travels to the lungs to pick up oxygen, after the lungs the oxygenated blood travels to the left side of the heart. When oxygenated blood leaves the left side of the heart it travels to the rest of the body so we can function properly.