What are the 4 states of matter in order from the LEAST to MOST amount of energy of the particles?
What are solid, liquid, gas, plasma?
The term for when a liquid turns into a gas?
Evaporation.
What happens when heat is added to matter?
Adding heat makes the particles move faster.
What are Joules (or kilojoules)
Name the following states of matter in order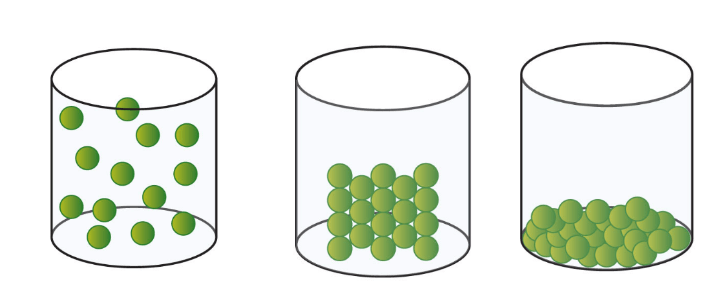
Gas, Solid, Liquid
Liquids have a fixed shape, but not a fixed volume. True or False?
False. Liquids have no fixed shape, but have a fixed volume.
What is the term called for when a gas turns into a liquid?
Condensation.
What happens to the spaces between the particles when a solid is heated and why?
The spaces between the particles in the solid increases because they are vibrating faster and need more room to move.
The SI unit for pressure.
What are Pascals?
The two equations used to calculate heat required for phase transitions.
What are Q=mC(delta)T
and Q=mHf/v
Name two properties of a solid.
Definite shape, incompressibility (definite volume), high density
The phase change that occurs when dry ice turns into vapors.
What is sublimation?
When we add heat, what are we adding to the molecules?
Energy.
The significant temperature (including the scale/unit) at which all molecules theoretically cease movement (have no kinetic energy).
What is absolute zero (Kelvin)?
Heat of vaporization is used when...
A substance reaches evaporation/condensation point
Which states of matter cannot be compressed?
Solids and Liquids.
The phase transition that occurs when frost forms on glass.
What is deposition?
With kinetic molecular theory, it is assumed that all collisions between molecules are elastic/inelastic energy is partially/fully transferred.
Elastic, fully
A physical property that distinguishes a molecular solid from an ionic solid.
What is melting/boiling point (ionic is higher)
Heat of fusion is used when...
The two phases that exist at equilibrium at a substance's boiling point.
What are liquid and gas?
The phases of the graph at stage A to B and E to F.
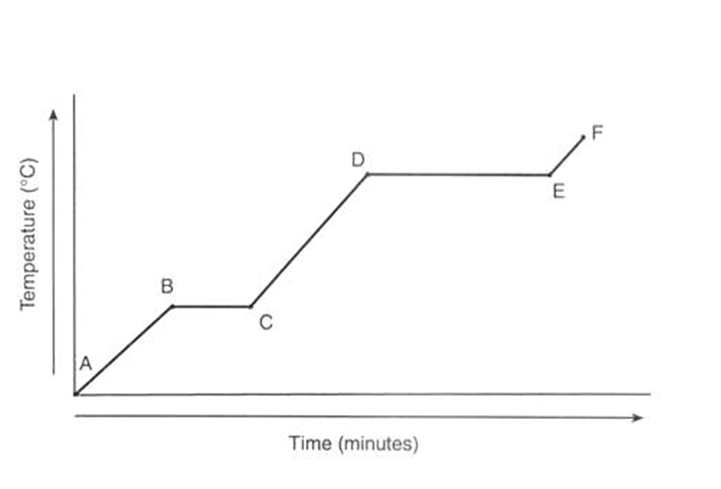
What is solid and gas?
How evaporation cools a liquid.
The units of heat capacity.
J/g˚C. (energy/mass•temperature)
How many times steps (total number of equations) will be used when calculating the energy required to bring water from -10˚C to 3˚C?
What is 3: solid, heat of fusion, liquid
How a liquid evaporates in terms of kinetic energy.
The liquid molecules obtain energy to have enough kinetic energy to escape the surface of the liquid and turn into gas.
In this heating curve of ice, what state/s is the water in during:
stage B to C and stage D to E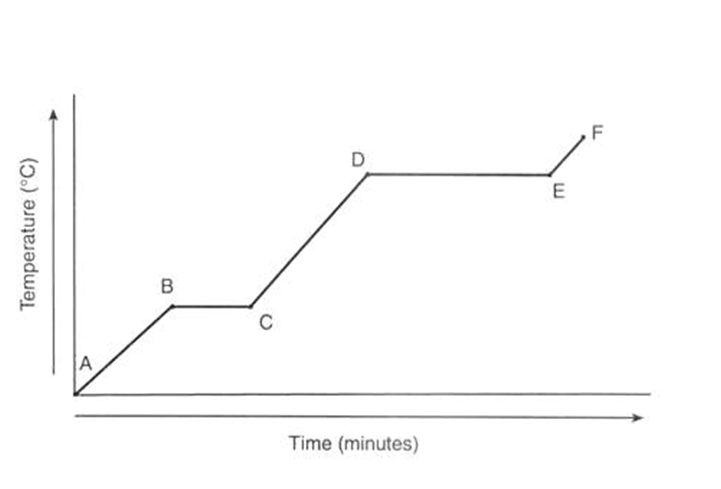
B and C -a mixture of solid ice and water
D and E - a mixture of water and steam (gas)
One of the five properties of an ideal gas.
1. many molecules
2. volume of molecules negligible
3. elastic collisions
4. no electrical forces of attraction/repulsion
5. average KE proportional to temperature
The definition of a unit of pressure.
What is force per unit of area?
The equation used for calculating energy for water sitting at 100˚C.
What is Q=mHv