What is the difference between distance and displacement?
(¿Cuál es la diferencia entre distancia y desplazamiento?)
distance (distancia): total length traveled (longitud total recorrida)
displacement (desplazamiento): difference between ending point and starting point (diferencia entre punto final y punto inicial)
Define force.
(Definir fuerza.)
A push or pull on an object
(Empujar o tirar de un objeto.)
How long ago did the universe form?
(¿Hace cuánto tiempo se formó el universo?)
13.7 billion years ago
(Hace 13.7 mil millones de años)
Define galaxy.
(Defina galaxia.)
A system of millions or billions of stars, gas, and dust that is held together by gravity
(Un sistema de millones o miles de millones de estrellas, gas y polvo que se mantiene unido por la gravedad.)
Define star.
(Definir estrella.)
A huge sphere of gas that emits light
(Una enorme esfera de gas que emite luz.)
What is the equation for speed or velocity?
(¿Cuál es la ecuación para la rapidez o la velocidad?)
s = d/t
v = d/t
Explain the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces.
(Explica la diferencia entre fuerzas equilibradas y desequilibradas.)
Balanced forces: cancel each other out and the object won't move.
(Fuerzas equilibradas: se cancelan entre sí y el objeto no se mueve.)
Unbalanced forces: cause an object to move in the same direction as the stronger force.
(Fuerzas desequilibradas: hacen que un objeto se mueva en la misma dirección que la fuerza más fuerte.)
True or False: The Big Bang Theory states that there was an explosion that formed the universe
(Verdadero o Falso: La Teoría del Big Bang afirma que hubo una explosión que formó el universo)
False
(Falso)
List the 2 ways that different shaped galaxies can form from elliptical galaxies.
(Enumera las 2 formas en que se pueden formar galaxias de diferentes formas a partir de galaxias elípticas.)
close encounters and collisions
(Encuentros cercanos y colisiones.)
What gases can be found in the core of stars and what is the reaction called that takes place?
(¿Qué gases se pueden encontrar en el núcleo de las estrellas y cómo se llama la reacción que se produce?)
Hydrogen and helium, nuclear fusion
(Hidrógeno y helio, fusión nuclear.)
Define acceleration and state its equation.
(Defina la aceleración y enuncie su ecuación.)
The change in velocity over time, a = v/t
(El cambio de velocidad en el tiempo, a = v/t)
State all 3 of Newton's Laws.
(Enuncie las 3 leyes de Newton.)
1: An object in motion stays in motion and an object at rest stays at rest unless an outside force acts on it. (Un objeto en movimiento permanece en movimiento y un objeto en reposo permanece en reposo a menos que una fuerza externa actúe sobre él.)
2: F = ma
3: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction (Para cada acción hay una reacción igual y opuesta.)
How long ago did our solar system form?
(¿Hace cuánto tiempo se formó nuestro sistema solar?)
4.6 billion years ago
(Hace 4.6 millones de años)
Name the 3 main shapes of galaxies.
(Nombra las 3 formas principales de las galaxias.)
spiral, elliptical, irregular
(Espiral, elíptica, irregular)
Name the life stage of a star shown in this picture.
(Nombra la etapa de vida de una estrella que se muestra en esta imagen.)

nebula/planetary nebula
(nebulosa/nebulosa planetaria)
What is the distance and displacement of someone that runs 3 laps around a 400 meter track?
(¿Cuál es la distancia y el desplazamiento de alguien que corre 3 vueltas alrededor de una pista de 400 metros?)
d = 1200 m
x = 0 m
Define friction and list the 3 types of friction.
(Defina fricción y enumere los 3 tipos de fricción.)
Resistance to motion when 2 objects come in contact with each other. (Resistencia al movimiento cuando 2 objetos entran en contacto entre sí.)
Static, sliding, rolling (Estático, deslizante, rodante.)
Name the first 2 elements that were created early on in the universe.
(Nombra los primeros 2 elementos que se crearon en las primeras etapas del universo.)
Hydrogen and helium
(Hidrógeno y helio)
What is the name of our galaxy and what shape is it?
(¿Cómo se llama nuestra galaxia y qué forma tiene?)
Milky Way Galaxy, barred spiral
(Vía Láctea, espiral barrada)
Name the life stages of an average star from beginning to end.
(Nombra las etapas de la vida de una estrella promedio de principio a fin.)
nebula -> protostar -> main sequence -> red giant -> planetary nebula -> white dwarf -> black dwarf
(nebulosa -> protoestrella -> secuencia principal -> gigante roja -> nebulosa planetaria -> enana blanca -> enana negra)
Describe the motion in the velocity vs time graph below at every point.
(Describe el movimiento en el gráfico de velocidad versus tiempo a continuación en cada punto.)
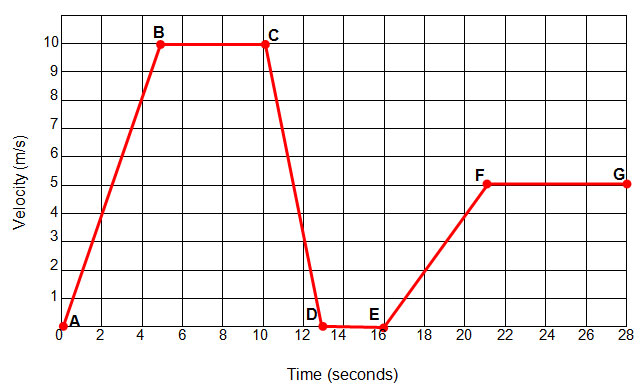
A-B: constant acceleration (aceleración constante)
B-C: constant speed (velocidad constante)
C-D: constant deceleration (desaceleración constante)
D-E: not moving (no moverse)
E-F: constant acceleration (aceleración constante)
F-G: constant speed (velocidad constante)
Define air resistance and gravity, then state what the number for gravity is.
(Defina la resistencia del aire y la gravedad, luego indique cuál es el número de la gravedad.)
Air resistance: resistance when traveling through air
(Resistencia del aire: resistencia al viajar por el aire.)
Gravity: the attraction 2 objects have on each other, 9.8m/s2
(Gravedad: la atracción que tienen 2 objetos entre sí, 9.8m/s2)
List at least 4 examples of evidence that support the Big Bang Theory.
(Enumere al menos 4 ejemplos de evidencia que respalden la teoría del Big Bang.)
1. universal expansion (expansión universal)
2. background radiation (radiación de fondo)
3. quasars (cuásares)
4. radioactive decay (desintegración radiactiva)
5. stellar formation/evolution (formación/evolución estelar)
6. speed of light (velocidad de la luz)
State the shape of this galaxy and the location/color of the older stars and younger stars.
(Indique la forma de esta galaxia y la ubicación/color de las estrellas más viejas y más jóvenes.)

spiral, red older stars in the middle, blue younger stars on the edges
(espiral, estrellas rojas más viejas en el medio, estrellas azules más jóvenes en los bordes)
Name the life stages of a massive star from beginning to end.
(Nombra las etapas de la vida de una estrella masiva de principio a fin.)
nebula -> protostar -> main sequence -> red supergiant -> supernova -> black hole/neutron star
(nebulosa -> protoestrella -> secuencia principal -> supergigante roja -> supernova -> agujero negro/estrella de neutrones)