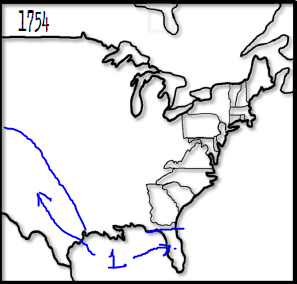
 Who did the following territory belong too?
Who did the following territory belong too?
The Spanish
The French
The British
The Spanish
What were some of the reasons why slavery spread to the southern colonies?
- The Southern colonies were more dependent on manual labor of others due to the large number of plantations in the south.
- The Southern colonies were lazy and lacked the motivation to work their own plantations, so they required slaves to work for them.
- All of the above.
- The Southern colonies were more dependent on manual labor of others due to the large number of plantations in the south.
What year did the French and Indian War begin?
a. 1656
b. 1700
c. 1754
d. 1800
c. 1754
Who were the people that were responsible for the first Thanksgiving?
a. The Puritans c. The Pilgrims
b. The Scotts d. The Scotts
c. The Pilgrims
Define Colony:
a. give up or hand over (a person, right, or possession), typically on compulsion or demand.
b. is people allowing other people to think or practice other religions and beliefs.
c. The science or practice of farming.
d. a country or area under the full or partial political control of another country, typically a distant one, and occupied by settlers from that country.
d. a country or area under the full or partial political control of another country, typically a distant one, and occupied by settlers from that country.
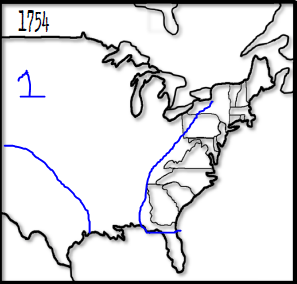
Who did the following territory belong too?
The Spanish
The French
The British
The French
What are the characteristics of the Middle colonies?
- Strict, hardworking, friendly.
- Diversity, religious tolerance, rapid growth.
- Unfriendly, one religion, strict laws
- All of the above.
- Diversity, religious tolerance, rapid growth.
What countries were involved in the French and Indian war?
a. Spain, Mexico, Britain and France.
b. Netherlands, Britain and Scotland.
c. France and Netherlands.
d. France and Britain.
d. France and Britain.
Who was the first explorer sent by the Spanish that landed in the Americas?
a. Cortes
b. Columbus
c. Pizarro
d. de Gama
b. Columbus
Define Surrender:
a. give up or hand over (a person, right, or possession), typically on compulsion or demand
b. is people allowing other people to think or practice other religions and beliefs.
c. The science or practice of farming.
d. a country or area under the full or partial political control of another country, typically a distant one, and occupied by settlers from that country.
a. give up or hand over (a person, right, or possession), typically on compulsion or demand
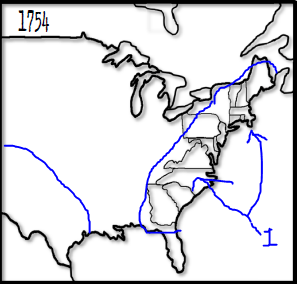
Who did the following territory belong too?
The Spanish
The French
The British
The British
What colonies were known as the “Breadbasket” colonies because of the crops they produced?
- The New England colonies
- The Southern colonies
- The Spanish colonies
- The Middle colonies
- The Middle colonies
What document ended the French and Indian War?
a. The Treaty of Versailles.
b. The Treaty of Commerce.
c. The Treaty of America.
d. The Treaty of Paris.
d. The Treaty of Paris.
Who were the people that settled the New England Colonies?
a. The Puritans c. The Pilgrims
b. The Scotts d. The Scotts
a. The Puritans
Define Agriculture:
a. give up or hand over (a person, right, or possession), typically on compulsion or demand
b. is people allowing other people to think or practice other religions and beliefs.
c. The science or practice of farming.
d. a country or area under the full or partial political control of another country, typically a distant one, and occupied by settlers from that country.
c. The science or practice of farming.
Where did the fighting in the French and Indian War start in the Americas?
New York
Amsterdam
The Ohio Valley
The Appalachian Mountains
The Ohio Valley
What were the main cash crops of the Southern colonies?
a. Cotton, tobacco, rice and indigo.
b. Oranges, apples, rice and sugar.
c. Sugar, corn, tomatoes and grapes.
d. Wheat, rye, barley, grain
d. Wheat, rye, barley, grain
What was the outcome of the French and Indian war?
a. Britain won control of the Americas and France lost all its colonies.
b. Britain lost and was forced to leave the Americas.
c. France and Britain maintained a presence and lived peacefully together.
d. The colonies gained control of America and forced Britain and France out of America.
a. Britain won control of the Americas and France lost all its colonies.
What was the name of the man that settled the New England colonies first?
a. Christopher Columbus
b. Montezuma
c. John Winthrop
d. John Smith
c. John Winthrop
Define Plantation:
a. Something, typically money, that is owed or due.
b. an estate on which crops such as coffee, sugar, and tobacco are cultivated by resident labor.
c. a financial gain, especially the difference between the amount earned and the amount spent in buying.
d. give up or hand over (a person, right, or possession), typically on compulsion or demand.
b. an estate on which crops such as coffee, sugar, and tobacco are cultivated by resident labor.
How many continents was the French and Indian War fought in?
2
5
6
4
4
What was the main economic industry for the New England colonies?
a. Textile, grain and cotton gin.
b. Sugar, bananas and molasses.
c. Lumber, ship building, fishing and whaling.
c. Lumber, ship building, fishing and whaling.
How many continents was the French and Indian War fought in?
a. 2
b. 3
c. 4
d. 6
c. 4
What were two main reasons settlers came to the New World?
a. Fur and Land
b. Money and trade
c. Lumber and fishing
d. Freedom to practice religion and wealth
d. Freedom to practice religion and wealth
Define debt:
a. Something, typically money, that is owed or due.
b. an estate on which crops such as coffee, sugar, and tobacco are cultivated by resident labor.
c. a financial gain, especially the difference between the amount earned and the amount spent in buying.
d. give up or hand over (a person, right, or possession), typically on compulsion or demand.
a. Something, typically money, that is owed or due.