Binds to the hemoglobin in red blood cells
Oxygen
Supports the skull and trunk and allows for their movement
Spine
Stroke Volume x Heart Rate
Cardiac Output
7.35-7.45
Normal pH of blood
60-100 bpm
Normal Heart Rate
Used to drain air, fluid, or blood from the pleural space and reestablish negative pressure
Chest tube
Decreased bone density, cartilage degeneration, decreased ROM, slowed movement, decreased strength
Changes associated with aging
Volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole
Preload
Caused by the retention of too much acid
pH <7.35
Acidosis
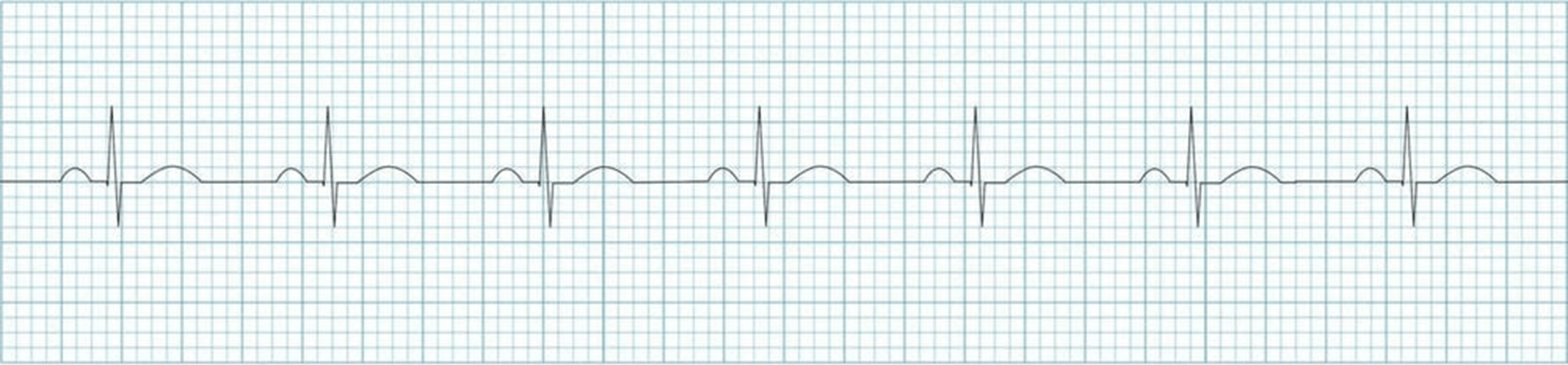
Normal Sinus Rhythm
Low-pitched wheezing sound caused by secretions in the large airways
Rhonchi
Infection of the bone, bone marrow, or surrounding soft tissue
Osteomyelitis
Inflammation of the heart muscle
Myocarditis
Caused by the retention of too much base
pH > 7.45
Alkalosis
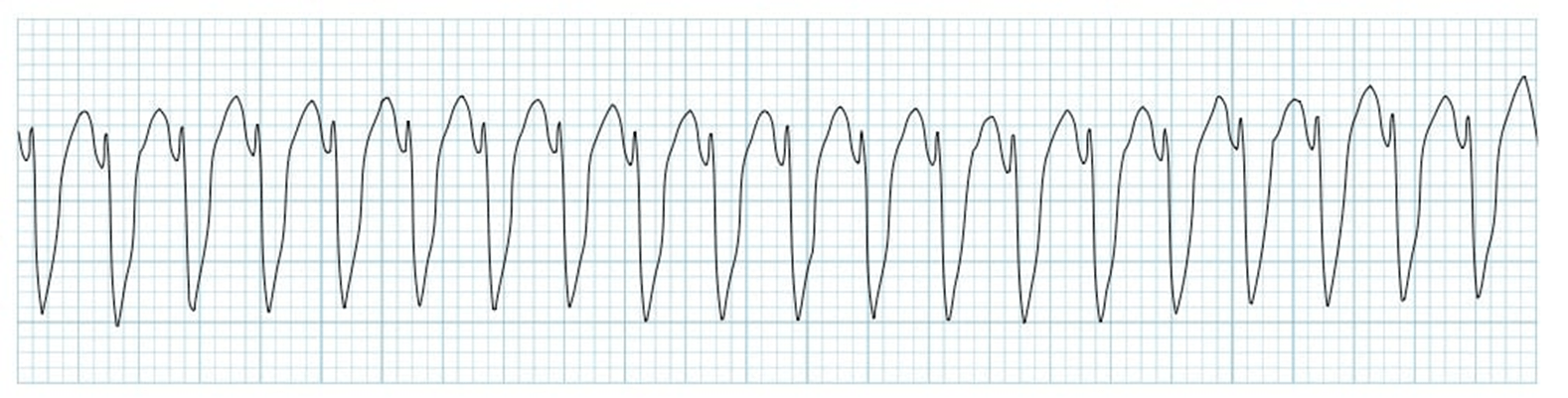
Ventricular Tachycardia
Symptoms include SOB on exertion, barrel chest, clubbing of fingers, wheezing
COPD
Traction used for uncomplicated femur fractures
Buck Traction
Dyspnea, pulmonary congestion, hypoxia
Left sided heart failure
pH- 7.49
PaCO2- 27
HCO3- 24
Respiratory Alkalosis
Very fast atrial rate, but ventricular rate is normal or slow
Irregular rhythm
Atrial fibrillation (a-fib)
Symptoms include cough, chest pain, tachycardia, petechiae over the chest and axillae
Pulmonary Emboli (PE)
Pain out of proportion, pressure, paresthesia, pallor, paralysis, pulseless
Compartment Syndrome
Weakness in a section of a dilated artery that causes a widening or ballooning of the arterial wall
Aneurysm
pH- 7.31
PaCO2- 36
HCO3- 18
Metabolic acidosis

ST Elevation MI