A wheel initially has an angular velocity of 18 rad/s but it is slowing at a rate of 2 rad/s2. By the time it stops it will have turned through:
81 rad
Four identical particles (mass of each = 0.4 kg) are placed at the vertices of a rectangle (2.5 m × 4.0 m) and held in those positions by four light rods which form the sides of the rectangle. What is the moment of inertia of this rigid body about an axis that passes through the mid-points of the shorter sides and is parallel to the longer sides?
2.5 kg⋅m2
A cylinder rotates with constant angular acceleration about a fixed axis. The cylinder’s moment of inertia about the axis is 4 kg·m2. At time t = 0 the cylinder is at rest. At time t = 2 seconds its angular velocity is 1 radian per second. What is the angular momentum of the cylinder at time t = 2 seconds?
4 kg·m/s
A scaffold of mass 60 kg and length 5.0 m is supported in a horizontal position by a vertical cable at each end. A window washer of mass 80 kg stands at a point 1.5 m from one end. What is the tension in the nearer cable?
840 N
An object is moving on a circular path of radius π meters at a constant speed of 4.0 m/s. The time required for one revolution is (in terms of π):
π 2/2
A particle is moving in a circle of radius 2 meters according to the relation θ = 3t2 + 2t, measured in radians and t is in seconds. The linear speed of the particle at t = 4 seconds is
52 m/s
A circular disk of radius 0.5 m and mass 3 kg has a force of 25 N exerted perpendicular to its edge, causing it to spin. What is the angular acceleration of the disk?
33.3 rad/s
A piece of space debris is travelling in an elliptical orbit around a planet. At its closest point to the planet, the debris is travelling at 18000 km/hr. When the debris is 10000 km from the planet, it travels at 5000 km/hr. How close does the debris get to the planet in its orbit?
2778 km
A uniform beam having a mass of 60 kg and a length of 2.8 m is held in place at its lower end by a pin. Its upper end leans against a vertical frictionless wall as shown in the figure. What is the magnitude of the force the pin exerts on the beam?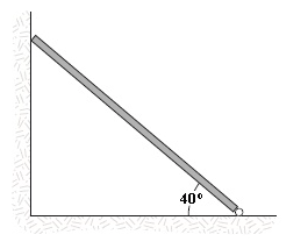
680 N
A particle moves along the x-axis with a non-constant acceleration described by a = 12t, where a is in m/s2 and t is in s. If the particle starts at rest from the origin at t = 0, where is it located at t = 2 s?
16 m
A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with an initial angular velocity of 20 rad/s. During a 5.0-s interval the angular velocity increases to 40 rad/s. Assume that the angular acceleration was constant during the 5.0-s interval. How many revolutions does the wheel turn through during the 5.0-s interval?
24 rev
A mass (M1 = 5.0 kg) is connected by a light cord to a mass (M2 = 4.0 kg) which slides on a smooth surface, as shown in the figure. The pulley (radius = 0.20 m) rotates about a frictionless axle. The acceleration of M2 is 3.5 m/s2. What is the moment of inertia of the pulley?
0.20 kg⋅m2
A thin rod of mass M and length L is struck at one end by a ball of clay of mass m, moving with speed v. The ball sticks to the rod. After the collision, the angular momentum of the clay-rod system about A, the midpoint of the rod, is
mvL/2
An 800-N billboard worker stands on a 4.0-m scaffold weighing 500 N and supported by vertical ropes at each end. How far would the worker stand from one of the supporting ropes to produce a tension of 550 N in that rope?
2.5 m
A weight lifter lifts a mass m at constant speed to a height h in time t. How much work is done by the weight lifter?
mgh
A wheel has eight equally spaced spokes and a radius of 30 cm. It is mounted on a fixed axle and is spinning at 2.5 rev/s. You want to shoot a 20-cm-long arrow parallel to this axle and through the wheel without hitting any of the spokes. Assume that the arrow and the spokes are very thin. What minimum speed must the arrow have?
4.0 m/s
A force F is applied to a cylindrical roll of paper of radius R and mass M by pulling on the paper as shown. The acceleration of the center of mass of the roll of paper (when it rolls without slipping) is
4F / 3M
A sanding disk with rotational inertia 1.2 × 10−3 kg·m2 is attached to an electric drill whose motor delivers a torque of magnitude 16 N·m about the central axis of the disk. About that axis and with the torque applied for 33 ms, what is the magnitude of the angular momentum of the disk
0.53 kg·m2/s
An 80-kg man is one fourth of the way up a 10-m ladder that is resting against a smooth, frictionless wall. If the ladder has a mass of 20 kg and it makes an angle of 60 degrees with the ground, find the force of friction of the ground on the foot of the ladder
170 N
An object weighing 4 newtons swings on the end of a string as a simple pendulum. At the bottom of the swing, the tension in the string is 6 newtons. What is the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the object at the bottom of the swing?
0.5g
In the figure, two particles, each with mass m1 = 0.85 kg, are fastened to each other, and to a rotation axis at O, by two thin rods, each with length d = 5.6 cm and mass M = 1.2 kg. The combination rotates around the rotation axis with angular speed of 0.3 rad/s. Measured about O, what is the combination's kinetic energy?
1 x 10-3 J
A pulley, with a rotational inertia of 0.001 kg·m2 about its axle and a radius of 10 cm, is acted on by a force applied tangentially at its rim. The force magnitude varies in time as F = 0.5t + 0.3t2, with F in newtons and t in seconds. The pulley is initially at rest. At t = 3 s what is its angular acceleration?
420 rad/s2
A wheel is rotating freely at angular speed 800 rev/min on a shaft whose rotational inertia is negligible. A second wheel, initially at rest and with twice the rotational inertia of the first, is suddenly coupled to the same shaft. What is the angular speed (in rev/min) of the resultant combination of the shaft and two wheels?
267 rev/min
In the figure, block A (mass 10 kg) is in equilibrium, but it would slip if block B (mass 5.0 kg) were any heavier. For angle θ = 30 degrees, what is the coefficient of static friction between block A and the surface below it?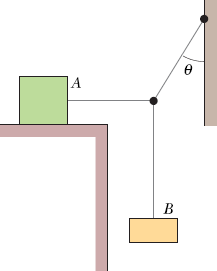
0.29
An object of mass m is moving with speed v0 to the right on a horizontal frictionless surface, as shown above, when it explodes into two pieces. Subsequently, one piece of mass 2/5 m moves with a speed v0/2 to the left. The speed of the other piece of the object is
2v0