What (3) blood vessels supply to the rotator cuff muscles?
2. Suprascapular
3. Humeral circumflex arteries
Tendons of which muscles make up the conjoint tendon?
1. coracobrachialis
2. short head of the biceps
The figure depicted by the asterisk derives its innervation from what nerve on the brachial plexus?
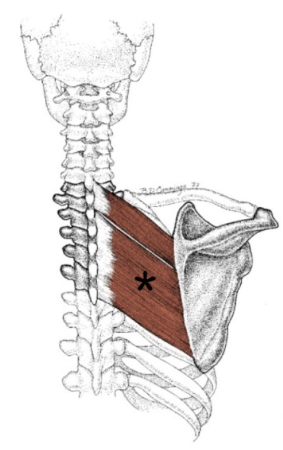
Dorsal scapular nerve
The image shows the rhomboid major, innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve derived from the C5 nerve root.
What is the internervous plane of the posterior approach (interval and nerves)
What are the contents of the carpal tunnel?
Bonus: what are the borders
FPL
FDL (4)
FDS (4)
median nerve
roof - flexor retinaculum
floor - carpal groove
medial/ulnar - hamate
radial/lateral - scaphoid/trapezium
What are the boarders of the quadrangular space?
superior: teres minor
inferior: teres major
lateral: humerus
medial: long head of triceps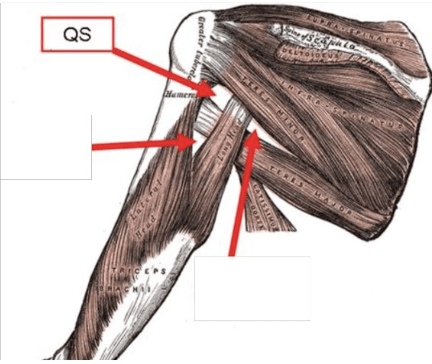
Damage to what peripheral nerve(s) would impair external rotation at the glenohumeral joint? Name the nerve AND the muscle
1. suprascapular nerve (infraspinatus)
2. axillary nerve (teres minor)
Which elbow extensor originates inferior to the radial groove on the humerus?
Medial head of the triceps brachii
Anconeus also contributes to elbow extension and is technically inferior to the radial groove as well - Technically should accept this answer as well.
Origins
Long head: infraglenoid tubercle of scapula;
Lateral head: posterior surface of humerus, superior to radial groove;
Medial head: posterior surface of humerus, inferior to radial groove
What nerve roots are involved in patients who present with medial scapular winging?
C5, C6, C7
Loss of serratus anterior (long thoracic nerve) leads to medial winging (inferior border goes medial).
C5, C6, C7 nerve roots contribute branches to the long thoracic nerve.
What is the distal dissection plane of the anterolateral approach? (interval and nerves)
brachialis (musculocutaneous nerve + radial nerve)
brachioradialis (radial nerve)
What is the difference between the classic Henry approach and modified Henry approach? (interval and what to do with the radial artery)
Classic: approach between brachioradialis and radial artery, have to ligate vessels of radial artery
Modified: FCR and radial artery, do not ligate vessels but have to watch for radial artery proximally
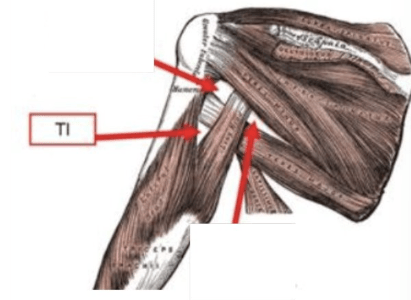
What are the borders of the triangular interval?
superior: teres major
lateral: lateral head of triceps
medial: long head of triceps
A cyst at the spinoglenoid notch can result in compression of what nerve and atrophy of what muscle(s)?
1. suprascapular nerve
2. infraspinatus muscle
Name two muscles of the upper extremity with dual innervation (4 total)
Bonus - name the nerve attached with them
1) Pectoralis Major
a) Sternocostal head, which receives it’s innervation from Medial pectoral nerve (C8, T1) arising from the medial cord of brachial plexus.
b) Clavicular head, which receives it’s innervation from Lateral pectoral nerve (C5,6,7) arising from the lateral cord of brachial plexus.
2) Subscapularis muscle supplied by the Upper & Lower Subscapular nerve (C5,6) arising from the posterior cord of brachial plexus.
3) Brachialis muscle, which acts as the flexor of elbow, receives its innervation from the Musculocutaneous nerve (C5,6,7) in its medial part and Radial nerve (C5,6,7,8, T1) in its lateral part.
4) Flexor Digitorum Profundus (FDP) muscle, which acts as the strong flexor of fingers, is supplied by the anterior interroseus branch of Median nerve (C8,T1) in its lateral part and Ulnar nerve (C8, T1) in its medial part.
An abnormal histamine test is suggestive of what injury?
Post-ganglionic
Abnormal histamine test = only redness and wheal, but NO flare, which suggests post-ganglionic injury as the continuity between the skin and dorsal root ganglion will have been interrupted. A response with a flare in an insensate area of skin suggest that the reflex arc is intact and that the lesion has to be proximal to the dorsal root ganglion (i.e. pre-ganglionic injury).
In the anterolateral approach, what interval is the lateral cutaneous nerve of the found in?
Bonus: what is the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm a branch from
biceps and mobile wad (brachioradialis)
musculocutaneous nerve
The PIN enters the supinator muscle beneath a fibrous arch known as:
Arcade of Frohse
what are the borders and contents of the triangular space
superior: teres minor
inferior: teres major
lateral: long head of triceps
contents: scapular circumflex artery
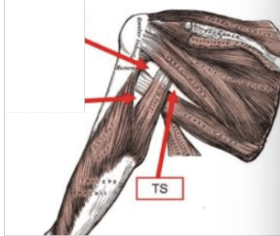
Name the nerve(s) that innervates the subscapular muscle and what branch from on the brachial plexus does it arise from?
1. upper and lower subscapular nerve
2. posterior cord
Patient is a 58M who underwent ORIF of a right proximal radial shaft fracture via a dorsal Thomson approach. Post-operatively, the patient demonstrates the finding pictured when he is asked to extend his thumb and index finger bilaterally. Careful handling of which muscle during the case could have prevented this finding
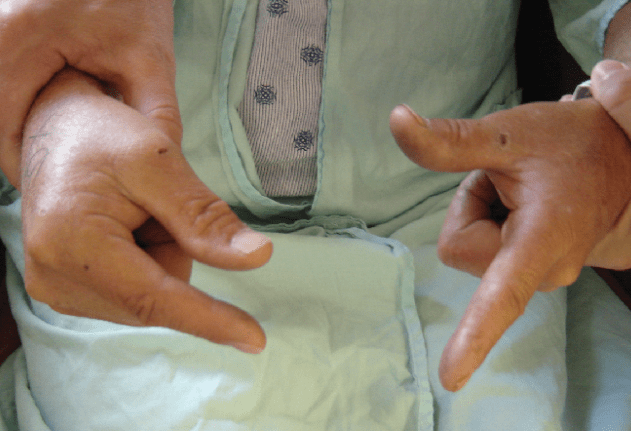
Supinator (PIN)
Fully supinating will also help protect the nerve.
Identify the insertion of supinator by turning arm into full supination
Supination moves the PIN away from area of deep dissection
Incise insertion of supinator along radius and subperiosteally strip supinator off bone to expose proximal third of radius
for more proximal exposures, two deep approaches exist to protect PIN:
dissecting proximal to distal:
- detach origin of ECRB and ECRL from lateral epicondyle and identify and dissect PIN as it enters supinator muscle
dissecting distal to proximal:
- identify nerve as it exits supinator and dissect it proximally out of supinator substance
A 36-year-old male presents to the ED with right arm pain after a fall off a ladder found to have a distal 1/3 spiral humeral shaft fracture. He is found to have a nerve palsy on physical exam depicted by the arrow in the diagram. What is the third muscle expected to recover?
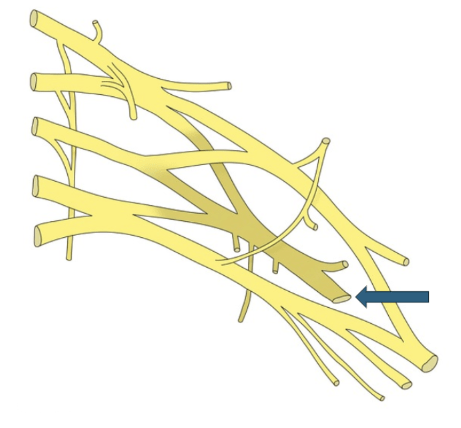
Supinator
Order of muscle recovery from radial nerve palsy: brachioradialis, ECRL, supinator, ECRB, EDC, ECU, EDQ, APL, EPL, EPB, and EIP.
In the anterolateral approach, what interval is the radial nerve found in?
brachial and brachioradialis
trace it proximally until pierces the lateral intermuscular septum
What is the dissection plane for the dorsal Thompson approach
ECRB
EDC
What are the contents of the quadrangular space?
What nerve that comes from the space arises from which trunk?
axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery
middle
What is the medial-lateral width of the supraspinatus at its insertion?
12.7mm (7.7-17.7mm)
What is the 5th muscle to be reinnervated following a radial nerve injury
EDC
Proximal to distal:
1) brachioradialis,
2) extensor carpi radialis longus,
3) supinator,
4) extensor carpi radialis brevis,
5) extensor digitorum communis,
6) extensor carpi ulnaris,
7) extensor digiti quinti,
8) abductor pollicis longus,
9) extensor pollicis longus,
10) extensor pollicis brevis, and
11) extensor indicis proprius
The Leechavengvong procedure involves the transfer of the medial triceps motor branch of the radial nerve to a nerve that is located on what part of the brachial plexus?
Posterior cord
Leechavengvong procedure is a nerve transfer procedure to the deltoid muscle using the nerve to the long head of the triceps. It involves the transfer of medial triceps motor branch of the radial nerve to the axillary nerve.
What are the specific measurements of the radial nerve from the lateral and medial epicondyle (cm)
medial epicondyle - 20-21 cm
lateral epicondyle - 14-15 cm
What is the proximal internervous plane of the volar Henry approach (muscle and nerve)
Brachioradialis (radial nerve)
Pronator Teres (median nerve)
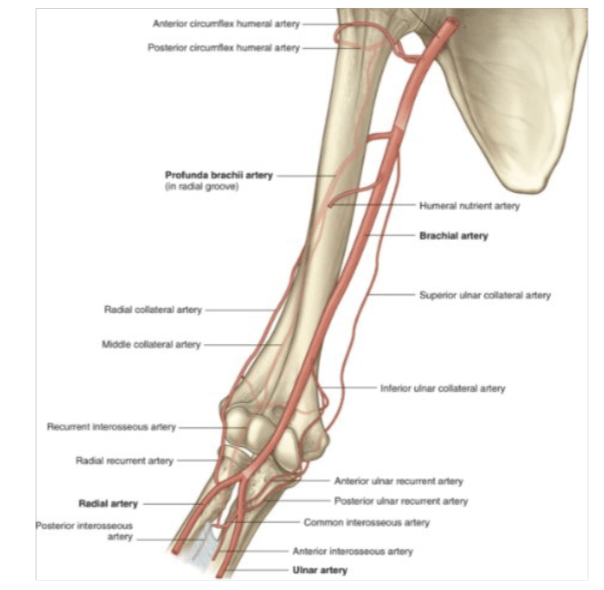
What are the contents of the triangular interval?
AND
what two arteries are branches of the artery from the interval?
radial nerve and profunda brachii artery
radial and middle collateral arteries