This capillary structure of the nephron functions as a nonselective filter
What is the glomerulus?
What FOUR parameters are assessed during the physical assessment/examination of urine?
What are color, clarity, specific gravity, and odor?
A pH greater than this value is consistent with an improperly preserved urine specimen
What is 8.5?
Name the cellular element shown below.
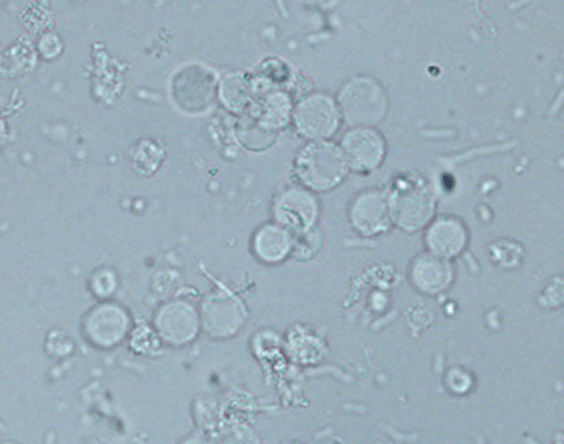
What are white blood cells?
A urine specimen yielding positive results for these two analytes on the urine dipstick indicates that a urine culture is necessary
What are leukocyte esterase and nitrite?
This structure of the nephron relies on active transport to reabsorb glucose into the bloodstream
What is the proximal convoluted tubule?
This term would be most appropriate to assess the clarity of the specimen shown below:

What is cloudy or turbid?
Urine run over from this acidic reagent pad onto the pH reagent pad can cause falsely low urine pH values
What is protein?
Name the cellular element seen in this image

What are Bacteria?
The presence of the crystal shown below would correlate with a positive chemical test for...

What is bilirubin?
Concentration of the urine begins in this tubular structure of the nephron, allowing the reabsorption of water in the descending loop and the reabsorption of sodium and chloride in the ascending loop
What is the Loop of Henle?
Name THREE non-pathological causes of turbidity in urine
What is acidic?
Identify the cellular element in this photo.
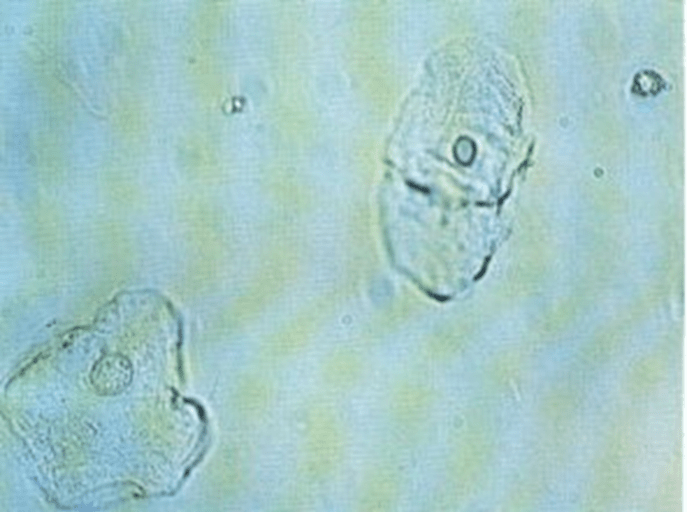
What are squamous epithelial cells?
Laboratory urinalysis findings of marked proteinuria, urinary fat droplets, oval fat bodies, renal tubular epithelial cells (RTE’s), epithelial, fatty, and waxy casts, microscopic hematuria are most consistent with this disease state
What is nephrotic syndrome?
The final concentration of the urine ultrafiltrate happens in this tubular structure in response to ADH secretion by the posterior pituitary gland
What is the collecting duct?
A urine specimen that is cloudy, has positive chemical tests for blood, and microscopically visible RBC’s will most likely be this color
What is pink/red?
Ionic strength altering the pKa of a polyelectrolyte describes the testing principle for this urine dipstick reagent pad
What is specific gravity?
Name the cellular element shown below.
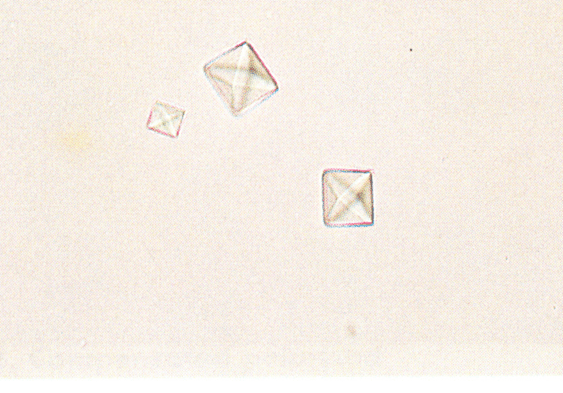
What are calcium oxalate crystals?
This diagnosis is consistent with a 28-year-old patient with the following urinalysis results:
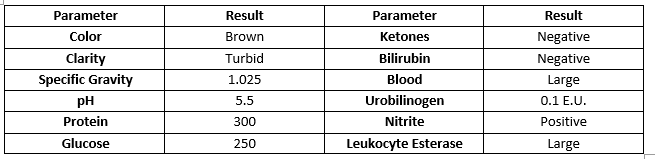
What is UTI/Cystitis?
Differences in size of these two blood vessels helps maintain hydrostatic pressure within the glomerulus to push glomerular filtration
What are the AFFERENT and EFFERENT arterioles?
Accumulation of homogentisic acid, causing a brown/black colored urine occurs in this disease state
What is Alkaptonuria?
A positive urine dipstick reaction for this should be correlated with the presence of white blood cells upon examination of the urine sediment
What is leukocyte esterase?
Name the cellular element indicated by the black arrows in the photo below.
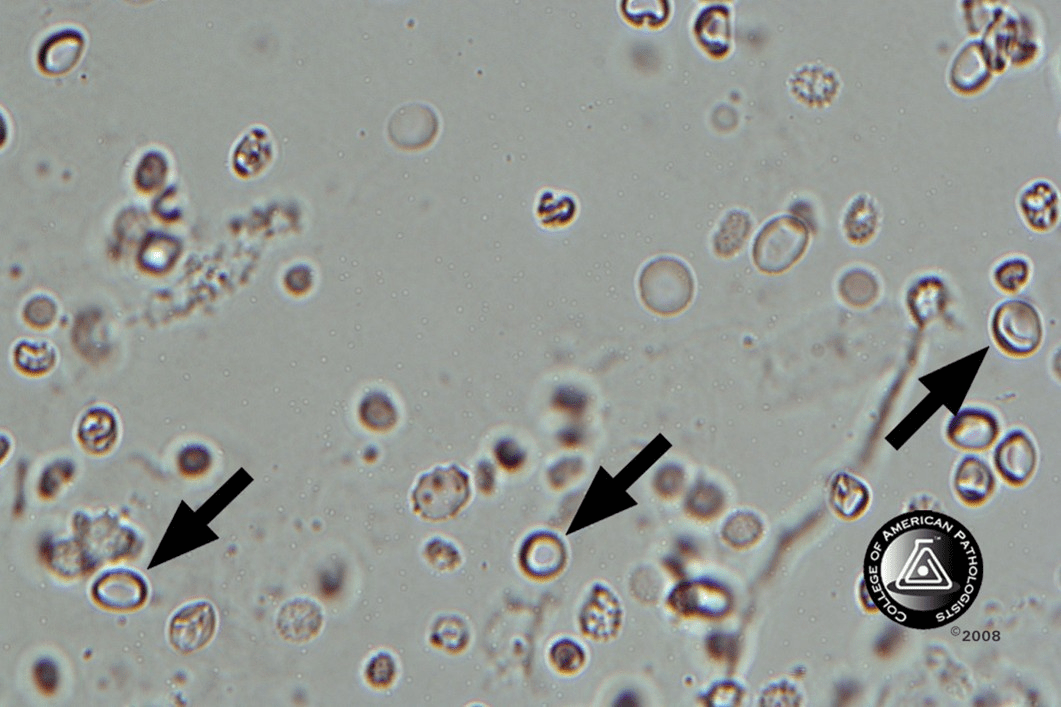
What are red blood cells?
In addition to a positive chemical test for blood, these TWO other results on the urine dipstick would be most helpful for assessing a patient with hemolytic disease
What are urine bilirubin and urobilinogen?