Dysuria, Cystitis, Nocturia, abdominal pain/pressure, mild fever
s/s lower UTI
S/S Pyelonephritis
S/S cystitis
S/S Ureteritis
What are the symptoms of a lower UTI?
Bacteria enters the urethra and ascends towards the bladder
urethritis
cystitis
pyelonephritis
hydropnephritis
What is cystitis
analyzing urine for red blood cells, white blood cells or bacteria
What is urine sample?
The major calyces of the kidney converge to form this enlarged channel:
a. renal fascia
b. renal pelvis
c. renal pyramids
d. renal papillae
e. renal sinus
What is renal pelvis?
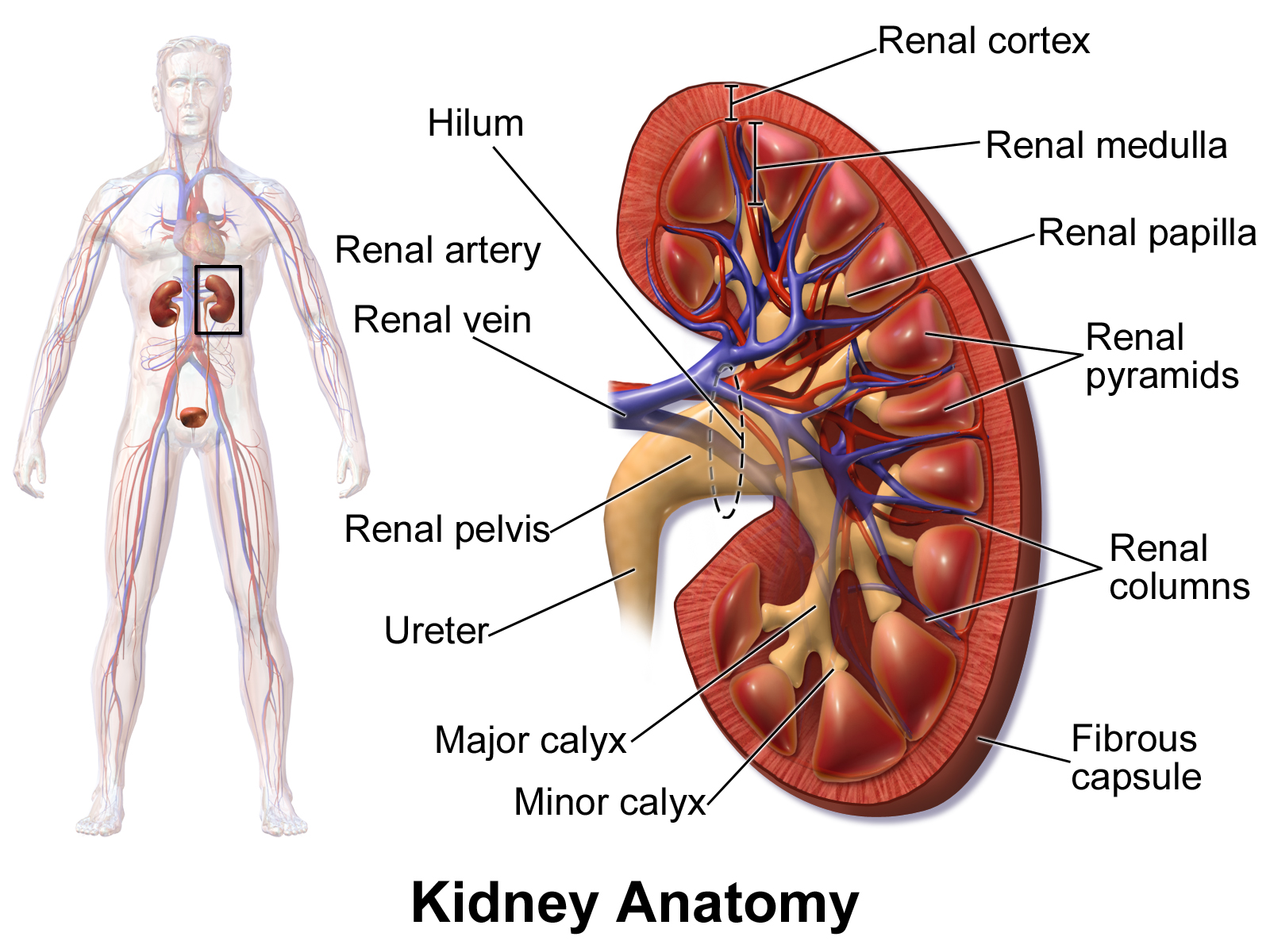
What organs are affected by an upper UTI?
Adrenal gland
suprarenal gland
Kidneys
bladder
kidneys

chills/shivers, vomiting and nausea
s/s upper UTI
S/S Pyelonephritis
S/S lower UTI
S/S Ureteritis
What are the symptoms of an upper UTI?
Sexual intercourse, use of antibiotics, new sexual partners
What are the risk factors uti
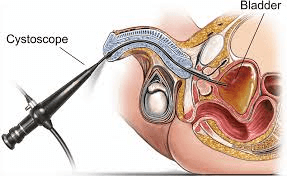
procedure with long thin tube to examine urethra and bladder
urinalysis
cystoscopy
pyelogram
uretereoscopy
What is cystoscopy?
This hormone secreted by the kidney triggers a cascade that regulates blood Na+ and blood pressure:
a. erythropoietin
b. vasopressin
c. renin
d. angiotensin
What is renin.

At what point in the man's life are they more at risk for urinary tract infection?
25 year old
60 year old
18 year old
45 year old
60 years of age.
UTIs in men are more common with older age. One reason is that older men are more likely to develop noncancerous enlargement of their prostate gland, called benign prostatic hyperplasia. The prostate wraps around the neck of the bladder, where the urethra connects to the bladder. Enlargement of the prostate gland can choke off the bladder neck, making it harder for urine to flow freely. If the bladder doesn’t empty completely, bacteria that are normally flushed out with the urine might gain a foothold.
pain and burning sensation during urination
What is dysuria?
urinary retention
What is the main cause of UTIs?
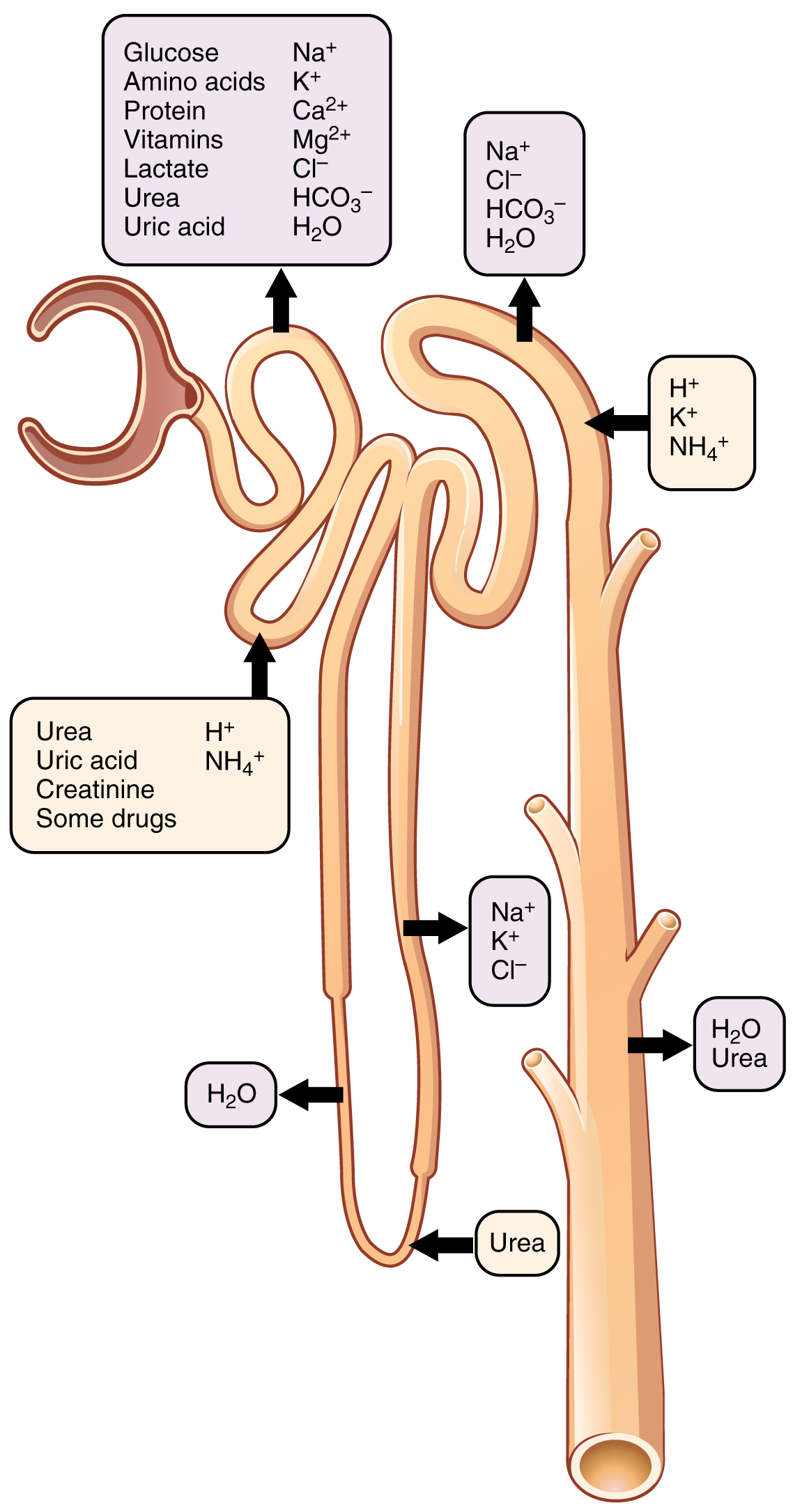
Water leaves the nephron by this mechanism:
a. active transport
b. filtration into the capillary network
c. osmosis
d. facilitated diffusion
What is osmosis

How many people have had a UTI sometime in their lives?
25% of women, 75% of men
40% of women, 12% of men
10% of women, 50% of men
80% of women, 75% of men
40% of women, 12% of men
frequent urination at night
What is nocturia?
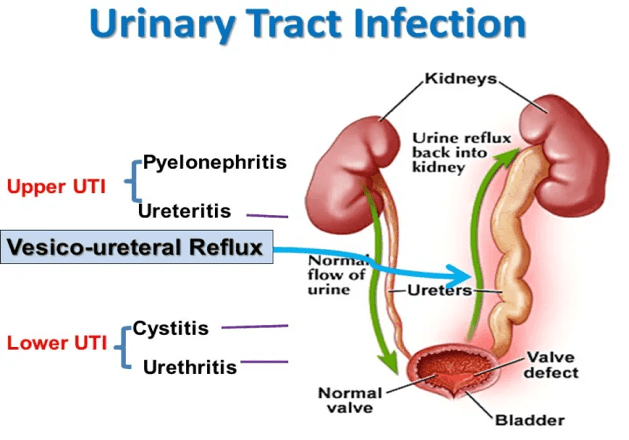
Describe the path of the ascending UTI?
bladder, ureter, renal pelvis, urethra
urethra to bladder to ureters to kidneys
urethra, ureter, bladder
nephrons, kidney pelvis, ureter, bladder, urethra
urethra to bladder to ureters to kidneys
By the time the filtrate reaches this, the glucose is usually completely reabsorbed:
a. the end of the proximal tubule
b. the tip of the loop of Henle
c. the end of the distal tubule
d. the end of the collecting duct
e. Bowman's capsule
What is the end of the proximal tubule
this urinary disease is categorized according to pre-renal, renal and post-renal causes.
Pyelonephritis
hydronephrosis
Acute Renal Failure
hydronephritis
What is acute renal failure.
Pre-renal (causes in the blood supply)
Renal (damage to the kidney itself)
Post-renal (obstructive causes in the urinary tract)
blood in the urine
What is hematuria?
gastrointestinal tract infections
origins of UTI
Chronic renal failure cause
increase in glomerular filtration rate
all are correct
What is the area that the bacteria causing UTIs originates from?
What is the name of the most common test used in the treatment for a UTI?
urinalysis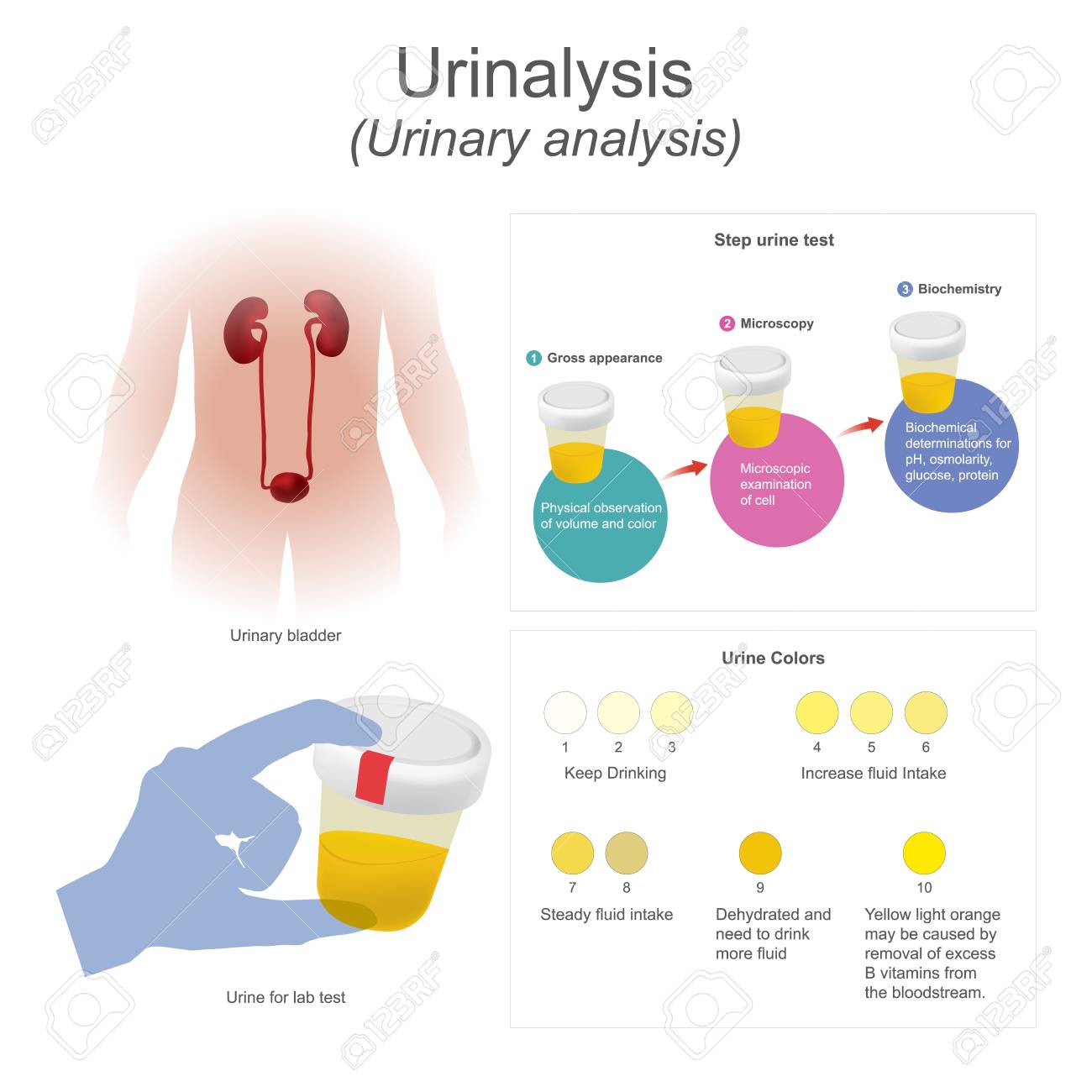
This is the basic histological and functional unit of the kidney:
a. glomerulus
b. filtration membrane
c. nephron
d. podocyte
e. renal corpuscle
What is a nephron

What are 3 symptoms of upper UTI that are not symptoms of lower UTI?
Fever chills
headache urgency
abdominal pain flank pain
costo-vertebral angle tenderness
dysuria malaise
Fever, chills, headache, malaise, abdominal pain, flank pain, costo-vertebral angle tenderness, increased WBC.