This autoantibody is the most specific biomarker for primary membranous nephropathy and is used both for diagnosis and monitoring disease activity.
What is PLA2R (phospholipase A2 receptor) antibody?
The most likely electrolyte abnormality that causes this EKG finding:
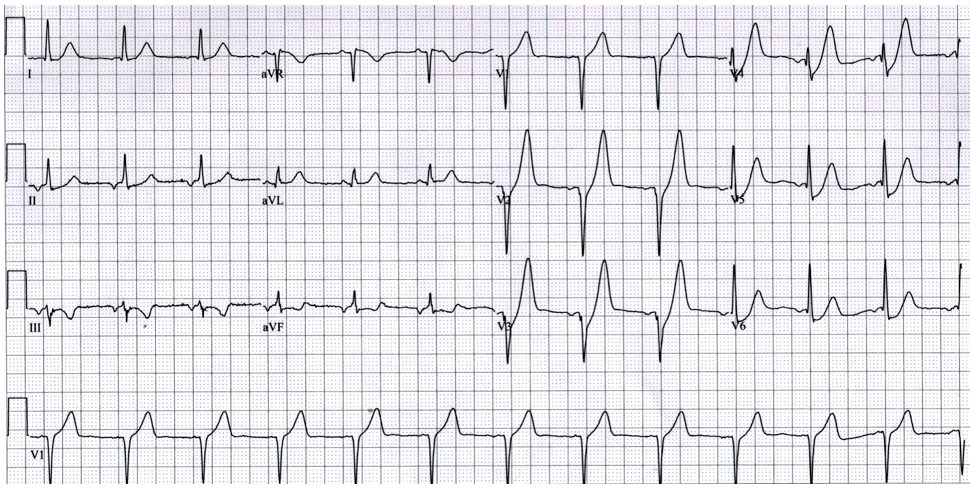
What is hyperkalemia?

This is the formula to calculate anion gap.
What is Na - (Cl + HCO3)?
OR (Na + K) - (Cl + HCO3)?
This the most common complications of peritoneal dialysis, presenting with abdominal pain and cloudy effluent.
What is peritonitis?
This type of renal stone is associated with urease-producing bacteria.
What are struvite stones?
This constellation of findings (syndrome) can be seen in a patient who presents with hematuria, HTN, and RBC casts. 24-hour urine with 2.2g proteinuria. Urine observed under microscope demonstrates the following:
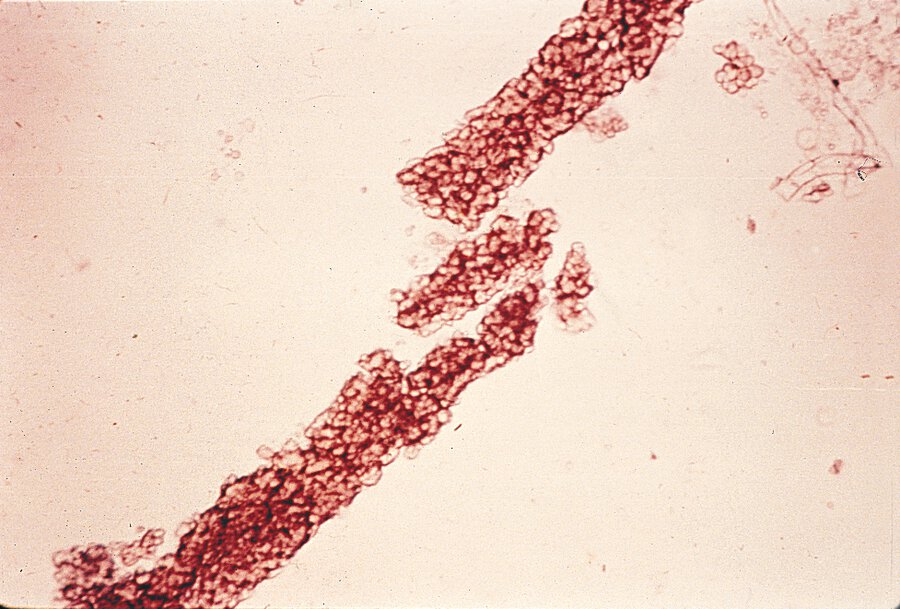
What is nephritic syndrome?
In the United States, this endocrine disorder is the most common cause of mild, often asymptomatic, hypercalcemia which is typically detected on routine labs.
What is primary hyperparathyroidism?

Primary hyperparathyroidism: Autonomous overproduction of PTH from a parathyroid adenoma or hyperplasia → high calcium.
Secondary hyperparathyroidism: Compensatory PTH increase in response to chronic hypocalcemia (often from CKD or vitamin D deficiency) → calcium is usually low or normal.
Tertiary hyperparathyroidism: After prolonged secondary hyperparathyroidism, the parathyroid glands become autonomous, producing PTH regardless of calcium levels → now leads to hypercalcemia, even after the original cause (like CKD or hypocalcemia) is corrected.
The classic blood gas finding in salicylate toxicity.
What is mixed metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis?
This indication for urgent dialysis in a patient with advanced kidney injury/disease can be marked by fever, chest pain, and shortness of breath, possibly with a friction rub on cardiovascular physical exam.
What is uremic pericarditis?
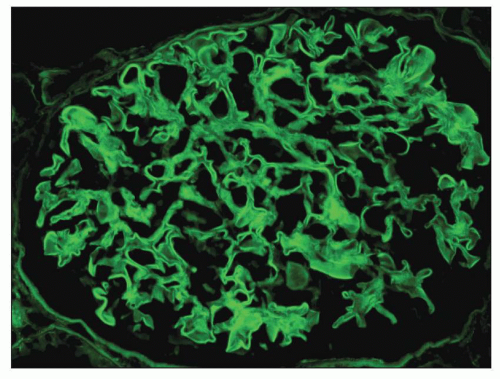
This condition may present with hemoptysis and hematuria, and the presence of linear IgG staining on immunofluorescence of renal biopsy is diagnostic.
What is anti-GBM (Goodpasture's syndrome)?
A 23yo M presents with microscopic hematuria, progressive renal failure, sensorineural hearing loss, and ocular abnormalities. His biopsy shows a "basket-weave" appearance of the glomerular basement membrane.
What is Alport syndrome?
X-linked hereditary nephritis caused by mutations in type IV collagen -- characterized by progressive renal failure, sensorineural hearing loss, and ocular abnormalities.
This electrolyte acts as a cofactor in the Na+/K+-ATPase pump, and when there is a deficiency in this electrolyte it can lead to reduced intracellular potassium uptake. Deficiency in this also increases activity of renal outer medullary potassium (ROMK) channels, leading to increased renal potassium excretion.
What is magnesium?
Summary:
1) Low Mg2+ --> Decreased Na+/K+-ATPase --> less K+ uptake into cells
2) Low Mg2+ --> Increased ROMK activity --> increased renal K+ excretion
3) Result: hypokalemia that is difficult to correct until magnesium is replaced
A patient with diabetes presents with mild hyperkalemia and a non-anion gap metabolic acidosis. Labs reveal urine pH <5.5. This type of RTA, caused by aldosterone deficiency or resistance, is most likely.
What is Type 4 RTA (hyperkalemic distal RTA)?
This calcineurin inhibitor is associated with nephrotoxicity, HTN, and neurotoxicity, and requires monitoring of drug levels.
What is cyclosporine?
This is the most likely etiology, as a form of extra-renal manifestation, for a subarachnoid hemorrhage found in someone with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
What is a ruptured berry aneurysm?
This ANCA subtype, directed against myeloperoxidase, is most commonly associated with microscopic polyangiitis and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis.
What is p-ANCA (MPO-ANCA)?
Tumor lysis syndrome causes these four primary electrolyte disturbances.
What is hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, and hyperuricemia?

This is the predicted PaCO2 level in someone with the following labs:
Na 140, K 4.0, Cl 107, HCO3 16, BUN/Cr 18/1.1, Glu 95
What is PaCO2 = 30 - 34 mmHg
Winter's Formula: PaCO2 = 1.5 x HCO3 + 8 (+/-) 2
During hemodialysis, rapid shifts in plasma osmolality can cause headache, nausea, seizures, and cerebral edema, a condition known as this.
What is dialysis disequilibrium syndrome?
These three drug classes are the most common culprits of this drug-induced type of AKI that prototypically presents with fever, rash, and eosinophilia. UA with pyuria. On renal biopsy this may demonstrate interstitial inflammatory infiltrates with eosinophils.
What are antibiotics (especially beta-lactams), NSAIDS, and PPI's?
What is acute interstitial nephritis?

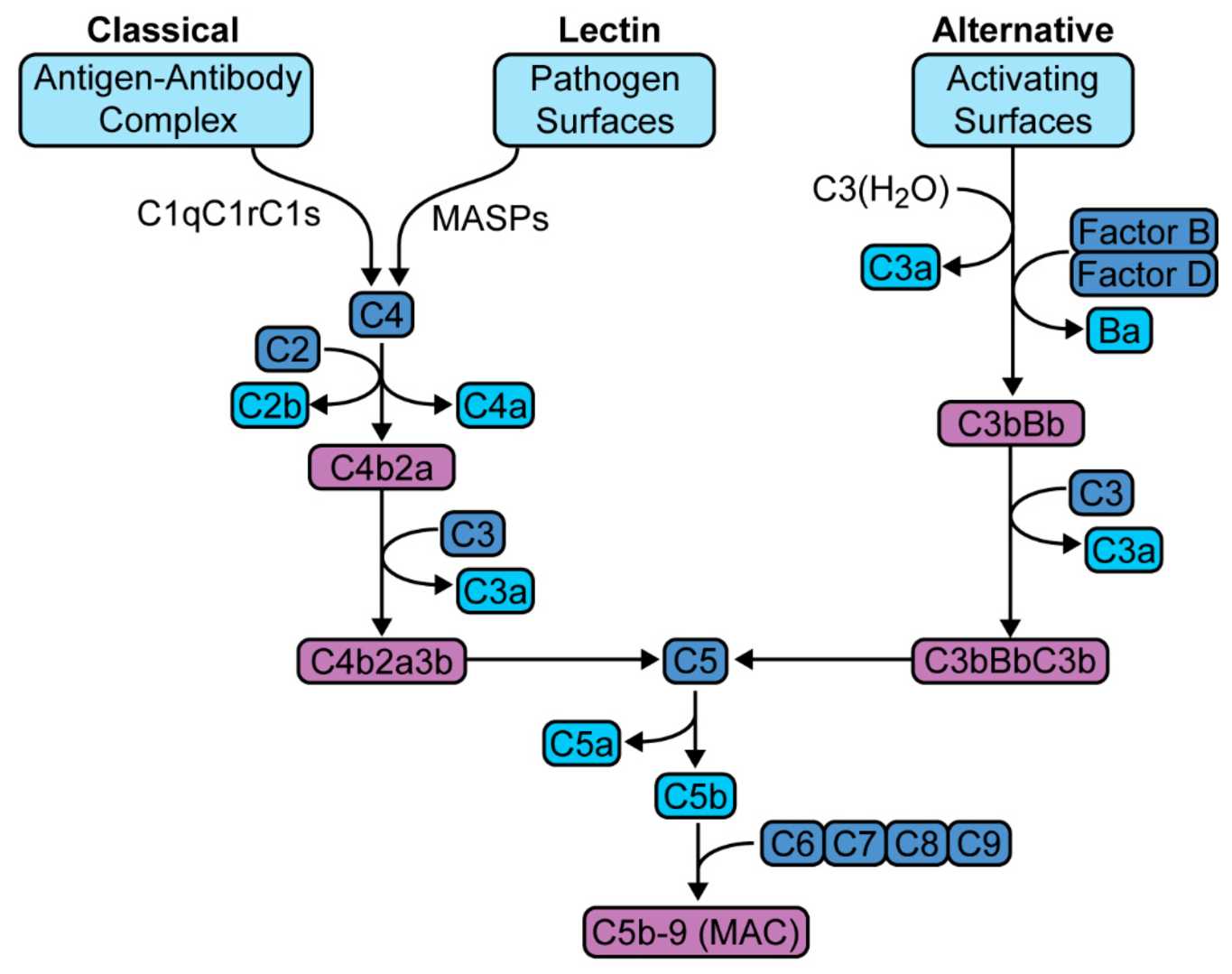
Low levels of this complement component are characteristically seen in post-infectious glomerulonephritis, while levels of the other major complement pathway component remain normal.
What is low C3 (with a normal C4)?
Alternative Pathway
A patient presents with Na 121. You think they are euvolemic, without hyperglycemia nor any other extra solutes of concern (HLD, protein). You order these labs, with their expected values/cutoffs, in order to diagnose SIADH. (provide >/</=, and provide the numerical cutoff)
What is:
Serum Osm: (Low) <280 mOsm/kg
Urine Osm: (High) >100 mOsm/kg
Urine Na: (High) >40 mEq/L
In this 2018 multicenter French trial (2018 Lancet), sodium bicarbonate infusion to maintain a pH of 7.30 in critically ill ICU patients did not significantly improve outcomes overall, however it did demonstrate reduced need for RRT in those with AKI.
What is the BICAR-ICU trial?
Participants: Adult ICU patients admitted within 48 hours w/ severe acidemia (pH <7.2, PaCO2 <45, bicarb <20)
Intervention: 4.2% NaHCO3 infusion to achieve and maintain pH 7.3
Primary Outcome: Composite of all-caue mortality at day 28 or presence of at least one organ failure at day 7
Secondary Outcomes: Organ failure scores, RRT requirement, and vasopressor use
Results
Primary Outcome: no significant difference between NaHCO3 and control
Subgroup Analysis: In those with AKI, bicarb infusion associated with reduced 28-day mortality and decreased vasopressor requirements
RRT: Bicarb administration decreased need for RRT compared to controls
Beyond 1 year, the most common cause of renal allograft loss, characterized by gradual decline in renal function and biopsy showing interstitial fibrosis and transplant glomerulopathy?
What is chronic allograft nephropathy (chronic rejection)?

These derangements are typical for the autosomal recessive renal disorder, Gitelman Syndrome, a disorder often marked by S/S's of muscle weakness/cramps, fatigue, salt craving, thirst and polydipsia. (Comment High/Low/Normal on the following -- serum K, serum bicarb, serum Mg, serum renin, serum aldosterone)
What is hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis (high bicarb), hypomagnesemia, and hyper-renin/aldo?

