What does GIS mean and how is it different than "mapping"?
Geographic Information Systems
Definition: GIS is a system that allows us to store, analyze, and present data that are specifically linked to a geographic location.
GIS includes spatial analyses! So an example of using GIS is say we have a question are there bus stops in the walking range of each school in San Diego? This could be important, as not all schools have access to their own bus system, and not all kids have the privilege to be dropped off at school each day. We can use GIS to analyze the area around each school to see if there is a bus stop available and then have the information of what schools do need access to this basic need!
What are the 6 map elements that need to be included in any final map?
Map itself, legend, north arrow, scale bar, data source, and title of the map!

What is vector and raster data? Name an example of each.
Vector: discrete data such as points, lines, and polygons (trees, roads, buildings)
Raster: continuous data (such as precipitation and elevation)
What is the buffer tool? Name a short example of how you would use it.
Creates buffer polygons around input features to a specified distance. 
An example would be I want to find all bus stops that are a quarter of a mile around a school. I would create a buffer polygon specified at a distance of 0.25 miles around the school and then find all schools that overlap with that buffer polygon.
What is metadata? What is included in it and why is it important?
It is data about the data that includes information such as who created the layer, when it was created, spatial and attribute descriptions, projections & coordinate systems, scale. It is important because we need to make sure our data is accurate and is coming from a trustworthy source.
What is a basemap?
It is the background layer that should be included in all maps. It provides geographic context for any spatial data that we are including on our map!
What is the attribute table?
It is the tabular data that is included with a piece of spatial data. Here is an example in ArcGIS Pro: 
Attribute tables are very important as they are what we change our symbology based on (symbology include the colors and shape of symbols on our map)!
What is the clip tool? Name a short example of how you would use it.
Extracts the input features that overlays a clip feature.
An example would be I want to look at the locations of schools around in San Diego. However, I only want it to display schools within my own town of University City. Therefore, I would clip a layer of all SD schools to a layer that just outlines my town so I only have schools located in UTC.
What are projection systems and why are they important?
Projections are calculations that allow us to map 3D data on a 2D surface such as a computer screen or a piece of paper. See example of orange on bottom of screen!
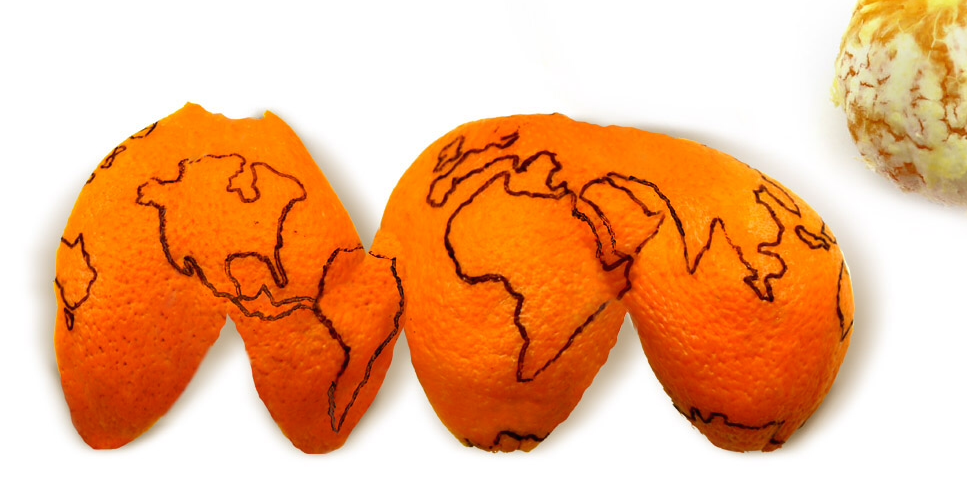

There will always be distortion going from a 3D surface to a 2D surface. Projections allow us to minimize that distortion specifically in the geographic location that we are focusing on for our map!
What is symbology? What are the different types if you can remember?
Symbology refers to how we change the colors and shapes of data in our map! We change the symbology based on information in the attribute table. There are three different types of symbology:
1. Single Symbol: everything is the same color. This is good for data that we don't care about differences in!
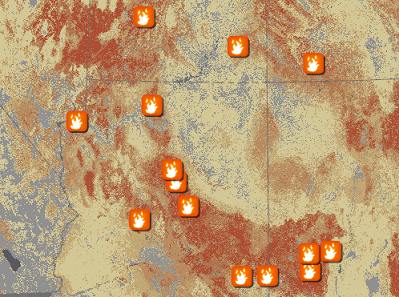
2. Unique Values: means features are color-coded based on categorical attributes.

3. Graduated colors: Assigns a single color per range of numbers. Perfect for range-based numerical data.
Name a few pieces of information that you may find in the attribute table for a grocery store layer.
Names of grocery stores, x and y coordinates of where they are located, size of building in square foot.
What is the selection tool?
There is the selection by attribute and selection by location. They both allow us to select certain pieces of data in a layer based on certain parameters.
Selection by attribute allows us to select data based on information in the attribute table.
Selection by location allows us to select data based on how it overlaps other spatial data in our map:
