What enzyme is deficient in Essential fructosuria?
- Fructokinase
cardiomyopathy, muscle weakness, and hypotonia, respiratory insufficency are features of what glycogen storage disease
pompe disease
fair-skinned infant with blue eyes and a musty body odor what is most likely disease?
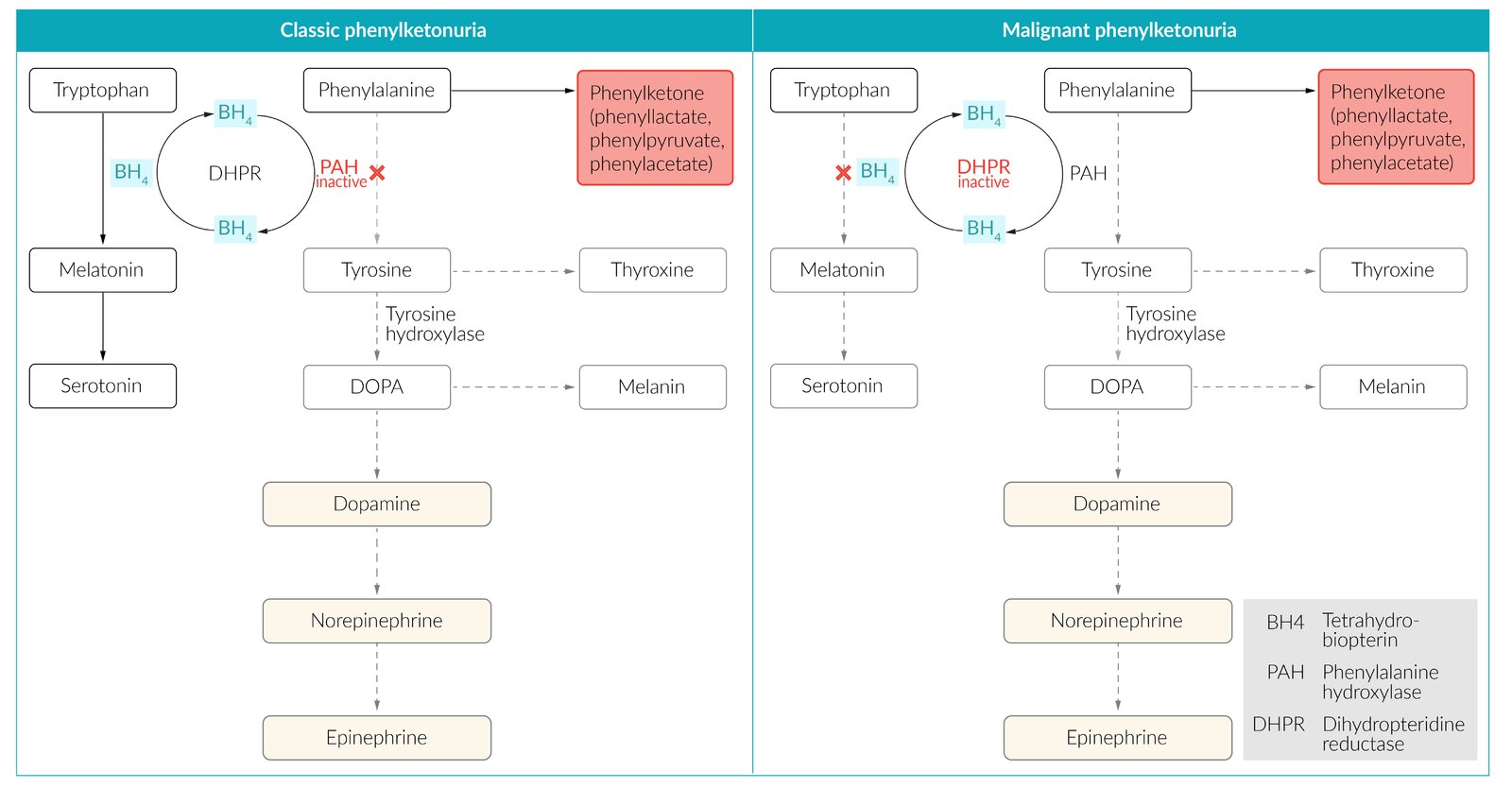
Phenylketonuria
Two most common causes of megoblastic anemia are what
Folate deficiency
Vitamine B12 deficiency
What is pernicious anemia?
what is there an increased risk for with this disese?
A type of vitamin B12 deficiency caused by autoantibodies against intrinsic factor and/or gastric parietal cells (type II hypersensitivity reaction)
- Increases the risk of gastric cancer
What enzyme is deficient in hereditary fructose intolerance?
- Aldolase B
What substance accumulates in the disease Galactokinase deficiency
- Accumulation of galactitol in tissues
what subtance is accumulated in Phenylketonuria and what substance is low (ie becomes an essential or needed to intake amino acid)
Accumulation of phenylalanine
mpaired conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine → tyrosine becomes nutritionally essential (classical PKU)
hyper segmented neutrophils is associated with what
BOTH folate and vitamin B12 def causing megoblastic anemia
what is the schilling test?
- Schilling test: a test to determine the cause of vitamin B12 deficiency [4]
- Consists of four stages that assess impaired vitamin B12 uptake
- Bloating, sweating, vomiting
- Failure to thrive
- Jaundice (can progress to cirrhosis)-- ie Liver failure
- Severe hypoglycemia: seizures, hypotonia, poor feeding, cyanosis, irritability
- Hepatomegaly
all sx start after weaning off breastmilk and starting consuming foods
what is the disease?
Hereditary fructose intolerance
what enzyme is deficient and what substance accumulates in classic galactosemia?
- Galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase

A low levels tyrosine leads to decrease production of what substance which can cause pale skin?
what lab value can differentiate folate def and vit B12 def?
what is the value in each?
- Methylmalonic acid (MMA) is normal in Folate def (unlike in vitamin B12 deficiency, where MMA is ↑)
accumulation of abnormal lysosomal substances in the serum
- Coarse facial features
- Corneal clouding
- Gingival hyperplasia
- Claw hand deformity
- Kyphoscoliosis
- Abnormal bone growth and restricted joint movements
- Failure to thrive (growth failure by 2 years of age) [16]
- Developmental delay
- Increased plasma levels of lysosomal enzymes
- Inclusion bodies in peripheral blood lymphocytes
what lysoome storage disease?
I cell disease
how can you dx heridatary fructose intolerance or essential fructosuira with a urine sample?
- Detection of reducing substances (fructose)
- Poor feeding
- Failure to thrive
- Vomiting, diarrhea
- Jaundice, hepatomegaly
- Cataracts
- Cognitive impairment
- ↑ Risk of E. coli sepsis (esp. in neonates)
- Hypoglycemia
sx of what disease?
classic galactosemia
A newborn infant comes in for vomiting jaundice and hepatomegaly. These sx can be seen in the in born errors of metabolism hereditary fructose deficiency and Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase deficiency (classic galactosemia)
what feature will point more towards hereditary fructose deficiency? think timing of sx
hereditary fructose def--sx start after breastfeeding ends and introducing whole foods
also associated with severe hypoglycemia 20 -30 min after food injestion
Pt with malabsoprtion disorder presents with a heart attack. PT has history of pallor, fatigue. Lab values show megoblastic anemia and hypersegmented neutrophils.
what most likley caused the heart attack? (what substance)
inc level of homocystine
seen in both B12 and folate deficiency
Alpha-galactosidase deficiency is what disease?
Fabry disease
Hereditary fructose intolerance leads to build up of what substance?
Accumulation of fructose-1-phosphate
both glactokinase deficiency and classic galactosemia are treated the same. what is the treatment
- Complete cessation of lactose-containing feeds and lifelong adherence to a galactose-free and lactose-free diet
a flattening of a curve showing no increase in diffusion speed as solute concentrations increase is called what
ie what principle is happening and what type of diffusion does this happen to
transporter saturation occurs with facilitated diffusion
name 4 causes of folate deficiency
- Malnutrition
- Insufficient intake, malnutrition (e.g., “tea and toast” diet)
- Chronic alcohol use
- Malabsorption
- Small bowel disease (e.g., tropical sprue, celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease)
- Surgical resection of the small intestine
- Increased requirement
- Pregnancy/lactation
- Severe hemolytic anemia
- Drug-related [2]
- Methotrexate
- Antiepileptic drugs (e.g., phenytoin)
- Sulfonamides
- Trimethoprim
is Fabry disease X linked?
yes, mainly affects boys