What is the most common type of cerebrovascular disease?
What is Stroke
What are the four quadrants of the abdominal anatomy called?
What is the right upper (RUQ), left upper (LUQ), right lower (RLQ), and left lower (LLQ)
TRUE or FALSE
ABDOMINAL ANEURYSMS ARE CLASSIFIED ACCORDING TO THEIR LOCATION RELATIVE TO THE RENAL ARTERIES
What is True
Vessels returning blood to the heart include?
What is the right and left pulmonary veins and the superior and inferior vena cava
What does ESRD stand for?
What is End Stage Renal Disease
What is PAD?
Signs / Symptoms?
Risk Factors?
Treatments?
What is Peripheral Arterial Disease
Signs/Symptoms - LE Pain/Claudication, Numbness, Weakness, and Coldness
Risk Factors - Smoking, DM, HBP, HLD, and Advanced Age
Treatments - Lifestyle Changes, Medications, Surgery - Angioplasty
True or False
The bilaterally paired internal carotid and vertebral arteries deliver an abundant supply of oxygen-rich blood to the brain
What is True
What is the first major branch off the aorta that runs anterior (front) and just below the diaphragm?
What is the celiac trunk
VESSEL DIAMETER GREATER THAN 1 TIME BUT LESS THAN 1.5 TIMES THE NORMAL DIAMETER IS KNOWN AS?
What is ARTERIAL ECTASIA
Which vessels convey blood away from the heart?
What is the aorta and the right and left pulmonary arteries
The Brescia-Cimino graft is made by surgically connecting what vessels?
What is the radial artery and cephalic vein
What are the (2) types of Stoke and what is the primary reason each may occur?
What is Hemorrhagic & Ischemic
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when an artery ruptures, causing bleeding around the brain, and is usually caused by hypertension, aneurysm rupture, arteriovenous malformations, or trauma
Ischemic stroke occurs when a region of the brain is blocked or significantly reduced, and can be defined by being a thrombotic or embolic event
What are the two vessels that come off the aorta, and are they on the left/right?
What are the left and the vessels are the carotid and subclavian
A condition where the median arcuate ligament, a fibrous band of tissue that crosses over the celiac artery (the main blood vessel supplying the stomach, liver, and spleen), compresses the artery
What is Median Arcuate Ligament Syndrome
A thrombus that is made of multiple layers?
What is a Laminated Thrombus
TRUE or FALSE
Coronary arteries supply deoxygenated blood to the heart muscle, and cardiac veins drain away the blood after it has been oxygenated
What is False
What are (3) reasons why a Graft has more problems than a AVF?
What is -
- Mortality risk
- More complications
- Short access survival (more procedures)
- Higher costs
What is the most common LE Aneurysm?
What are the symptoms?
What are the Treatment options?
What is a Popliteal Aneurysm
Often Asymptomatic, a Pulsatile mass at the knee, LE Pain & Swelling, and Cold or blue feet
Endovascular Stent and/or BPG
What side is the brachiocephalic, and what is another name for this vessel?
What is the right and the innominate
These veins drain blood from the liver and are one of the first major branches off the IVC
What is the Hepatic Veins
A thrombus that is stuck to the wall of a vessel is known as a?
The electrical pathway of the heart is primarily governed by the cardiac conduction system, which includes the following (4) key components:
What is -----
Sinoatrial (SA) Node: Acts as the heart's natural pacemaker, generating electrical impulses that initiate each heartbeat
Atrioventricular (AV) Node: Receives impulses from the SA node and delays them slightly to allow the atria to contract before the ventricles
Bundle of His: Transmits impulses from the AV node to the ventricles through the right and left bundle branches
Purkinje Fibers: Distribute the electrical impulse throughout the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump blood
What is a TRAS-Renal Artery Stenosis
TRUE or FALSE
- Patients will develop Post-Thrombotic Syndrome, or PTS, due to an acute DVT and or valve damage
- A provoked blood clot will require about 3-6 months of anticoagulation therapy, while an unprovoked clot may take 6+ months, even indefinitely
- (3) Goals of DVT Treatment are to prevent a clot from growing and/or traveling, breaking up the clot, and preventing new clots from forming, with anticoagulants almost always being a part of the first goal.
What is False
What is True
What is True
What is the main venous structure in the neck?
What is the IJV, Internal Jugular Vein
What are the three branches of the Celiac Trunk?
What is the Lt. Gastric, Splenic, and Common Hepatic artery
A CONGENITAL SYNDROME THAT IS THE RESULT OF A CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISORDER THAT TYPICALLY ASSOCIATED WITH AORTIC ROOT, THORACIC AND ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSMSIS IS KNOWN AS?
What is MARFAN AND EHLERS-DANLOS SYNDROME
Lack of blood flow causes the tissue in the heart muscle to die is known as a?
What is an MI, Myocardial Infarction
What is the main vascular complication that can occur from a liver transplant?
What is an HAT - Hepatic Artery Thrombosis
What are the main causes of CVI?
Signs/Symptoms?
And how is it classified by Duplex US?
What is vein walls become damaged due to prior DVT, congenital absence/weakness, prolonged hypertension, and trauma
What is LE heaviness, fatigue, swelling, aching, itching/burning, skin changes, varicose veins, and ulcers
What is Reflux duration: >0.35 seconds for Perforators, >0.5 seconds for superficial veins and >1.0 second for deep veins
The internal carotid and basilar arteries converge, divide, and anastomose to form what?
What is the name of the syndrome when the compression of the left renal vein causes kidney-related issues like flank pain and hematuria?
What is Nutcracker Syndrome
A Life-threatening medical situation that causes blood to flow b/w layers of the aortic wall, creating a new channel, is known as a?
What arterial layer is affected by this condition?
What is an aortic dissection
What is the media
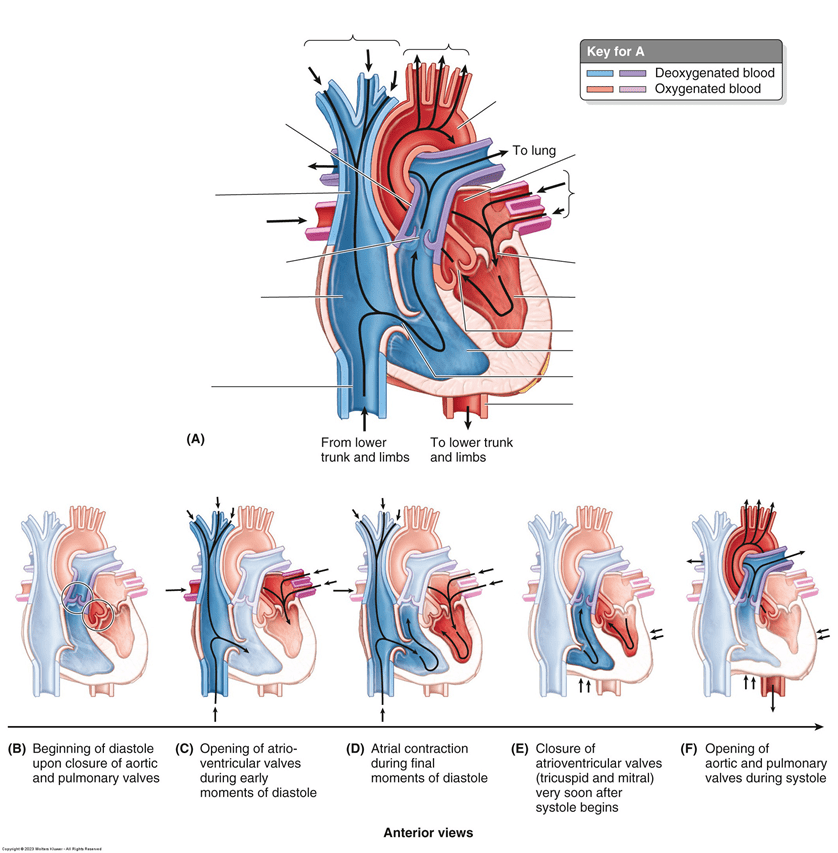
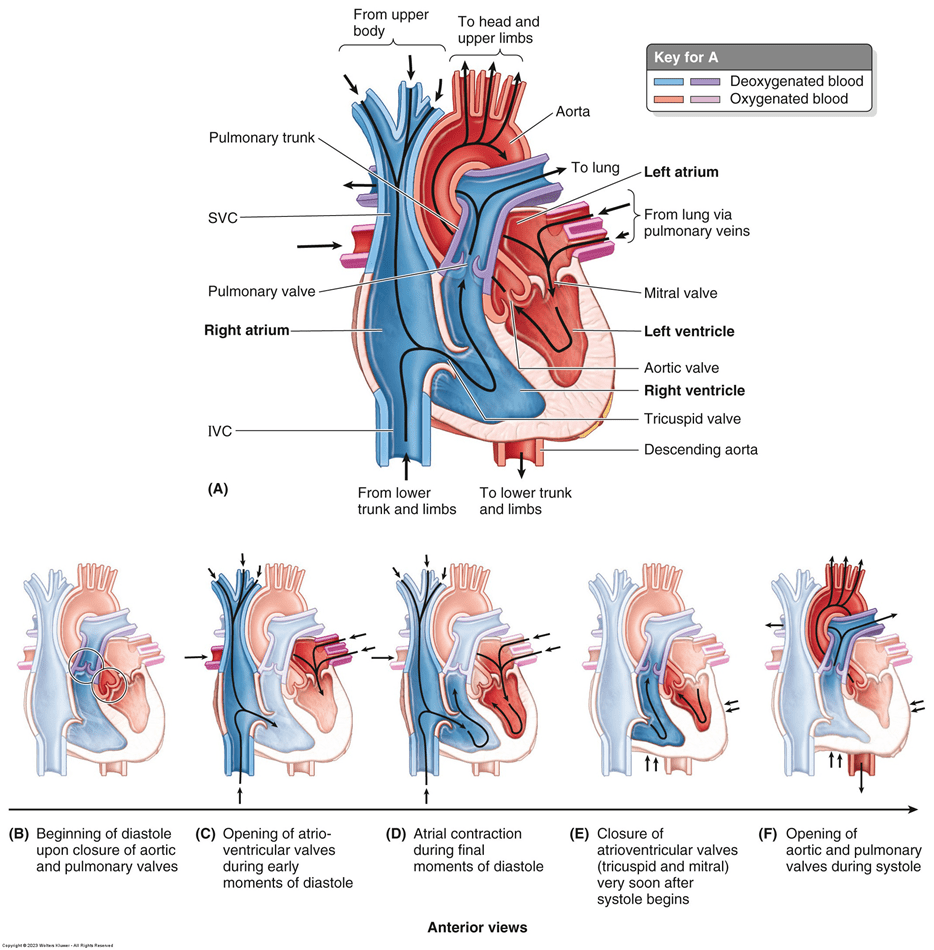
How many valves are in the heart, what are they called, and where are they located?
What is (4),
Tricuspid valve: Located between the right atrium and right ventricle
Pulmonary valve: Located between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery
Mitral valve: Located between the left atrium and left ventricle
Aortic valve: Located between the left ventricle and aorta
What is the Arterial Inflow and Venous Outflow for a Kidney Transplant?
What is ---
Arterial Inflow - Iliac & Renal Arteries
Venous Outflow - Iliac & Renal Veins
TRUE or FALSE
- Type 1 Diabetes is more common than Type 2 Diabetes?
- Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes share many symptoms, including increased thirst, frequent urination, extreme hunger, and fatigue.
- Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes treatments are not the same, though they share some similarities, like lifestyle changes.
What is False
What is True
What is False. The fundamental difference is that type 1 diabetes requires insulin because the body doesn't produce it, while type 2 diabetes often starts with oral medications and lifestyle changes, and insulin may be needed later if other treatments fail
What condition causes inflammation of blood vessels that can affect the brain and nervous system, potentially causing strokes, clots, and other conditions?
What is Vasculitis
This vein directly transports blood to the liver; however, in this image, an abnormal finding is causing dilation of the vein and a lack of color. What is this vein, and what is the likely diagnosis?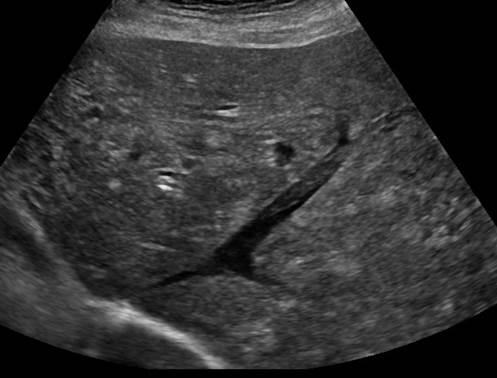
What is the Portal Vein Thrombosis

What are some classifications of Type A, and what part of the Aorta is affected?
What is the Ascending Aorta, Classifications are :
- Very life-threatening
- May dissect the aortic valve or rupture into the pericardium
- Surgical Repair is indicated
How many chambers are there in the heart? What
are they called, and what are the functions?
What is (4)-
Right Atrium: collects blood from the body and passes it to the right ventricle
Right Ventricle: pumps blood through the pulmonary artery to the lungs, where it is oxygenated
Left Atrium: collects oxygenated blood from the lungs and passes it to the left ventricle
Left Ventricle: pumps blood through the aorta to the rest of the body
What is the Arterial Inflow and Venous Outflow for a Liver Transplant?
What is ---
Arterial Inflow - Hepatic Artery & Portal Vein
Venous Outflow - Vena Cava & Hepatic Vein
- What disease is known as the arterial pulselessness disease, mainly affecting the carotid and radial arteries
- What condition is known as an non-atherosclerotic, non-inflammatory arterial disease that most commonly involves the renal and carotid arteries.
- What condition occurs when proteins affect the body's connective tissue, which supports and gives structure to organs, bones, and other connective tissues
What is Takayasu Arteritis
What is Fibromuscular Dysplasia Disease (FMD)
What is Marfan’s Disorder
Identify the vessels?
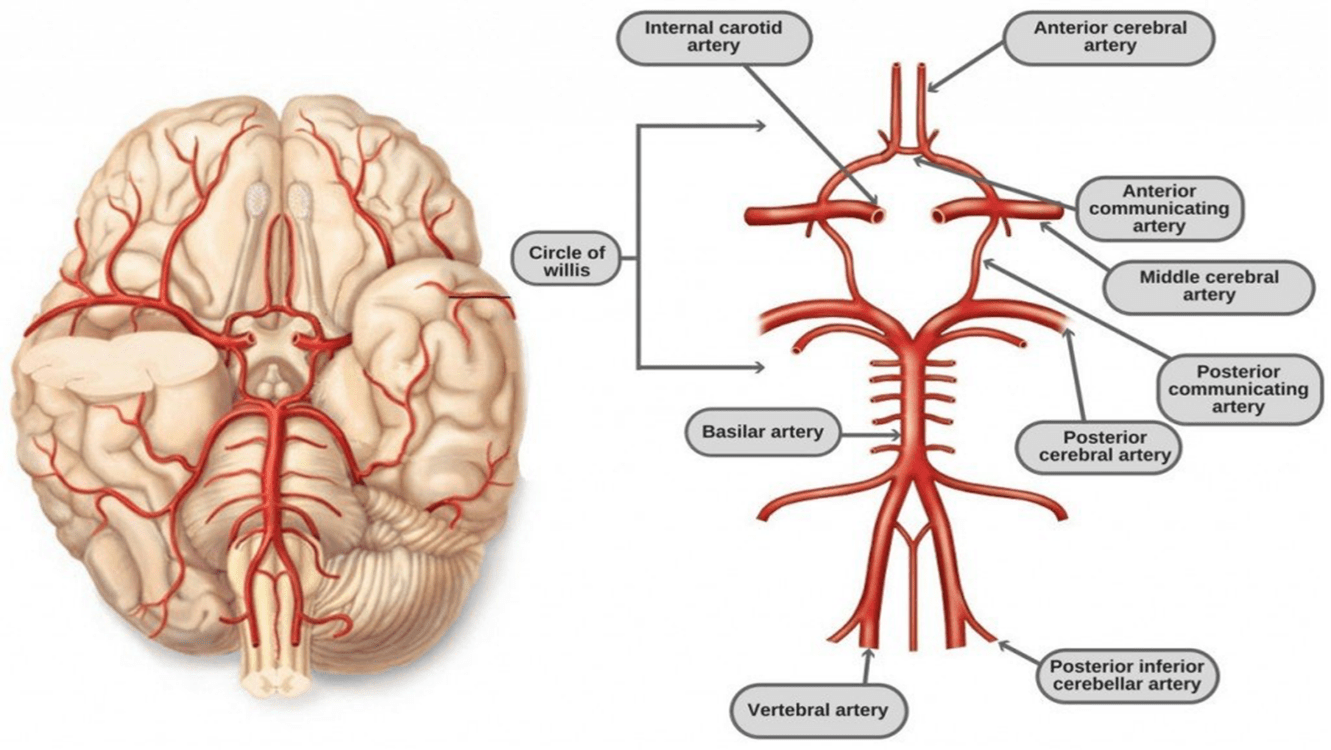
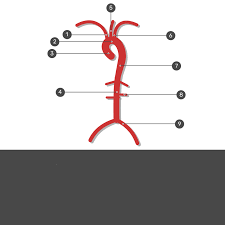 Identify the vessels?
Identify the vessels?
What is:
(1) Brachiocephalic Trunk
(2) Arch Aorta
(3) Ascending Aorta
(4) Descending Aorta
(5) Lt. Common Carotid Aorta
(6) Lt. Subclavian Artery
(7) Descending Aorta / Celiac Trunk
(8) Renal Artery (Left)
(9) Common Iliac Artery (Left)

What are the classifications of Type B, and what part of the Aorta is affected?
What is the Descending Aorta, The classifications are:
- Less life threatening- heart not involved
- Occludes branches, paraplegia, renal failure, bowel death, leg ischemia
- Managed medically if possible
- Control patient hypertension
Identify the following cardiac vessels?
What are (3) other complications that can occur other than a stenosis or thrombosis in a renal and/or liver transplant?
What is ---
- Pseudoaneurysm
- Dissection
- AVF
- Hematoma
- What condition occurs from compression on the neurogenic (most common), venous, or arterial systems?
- Which vessels are mainly affected, and how is it tested with US?
What is Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What is the Subclavian Vessels
What is assessing the subclavian artery waveforms during different positional maneuvers, with the onset/symptomatic being the most important