This marker is found on all nucleated cells on the body.
What are MHC-1 markers?
The categories that these preventative mechanisms can be placed into.
What are physical, chemical or microbiota barriers?
The process by which solid materials are ingested by a white blood cell.
What is phagocytosis?
Another name for the 'third line of defence'.
The type of immunity resulting from the production of antibodies in response to exposure to a pathogenic infection.
What is natural adaptive immunity?
What are allergens?
A dry and thick outer layer composed predominately of dead cells that prevent external infection.
What is intact skin?
A mechanism to increase the migration of white blood cells to the site of an infection.
Two key qualities that differentiate the third line of defence from the second line of defence.
The type of immunity resulting from receiving antibodies from another organism.
What is natural passive immunity?
These proteins neutralise pathogens, can also be called immunoglobulins.
What are antibodies?
A thin region of living cells that may be ciliated to assist in the trapping and removal of pathogens.
What are mucous membranes?
Types of phagocytic leukocytes.
What are neutrophils and monocytes?
Pathogen fragments presented to lymphocytes.
What are antigens?
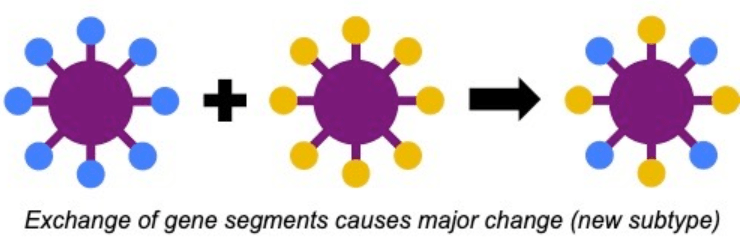
When cells get infected with multiple viral strains and the gene segments from the two strains get reassorted.
What is antigenic shift?
This pathogen has a simple non-cellular structure and a protein shell called a capsid that surrounds genetic material.
What are viruses?
A body secretion that contains the enzyme lysozyme which can destroy cell walls.
What is tears and saliva?
Signalling proteins that regulate communication within the immune system.
What are cytokines?
The light chain and heavy chain are often seen in a diagram of this molecule.
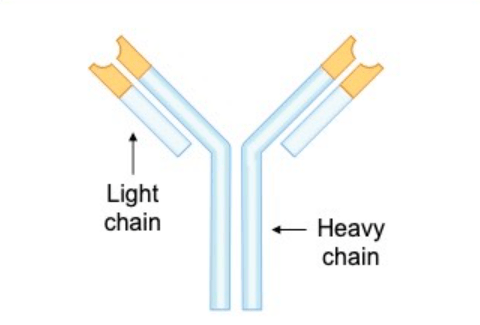 What is an antibody?
What is an antibody?
Diseases which are transferred from an animal host (usually a vertebrate) to a human host.
What are zoonotic diseases?
These cels are not nucleated, therefore not possessing MHC markers, and can potentially be transferred without rejection.
What are red blood cells?
The microbiota barrier that lines specific cavities in most animals.
What is normal flora?
Cells that non-specifically target and destroy virally-infected cells or cancers.
What are natural killer cells?
The cells produced during this stage that improve the secondary immune response in comparison to the primary immune response.
What are memory cells?
Individuals who are not immune to a pathogen are protected from exposure by the large amounts of immune individuals within the community.