Which term is defined as "The process of receiving and detecting raw sensory information via our sensory organs and sending it to the brain."
Sensation
Name a sense. 100 points available for each unique one listed!
Main 5: Sight, touch, taste, smell, sound.
Additional: Proprioception (awareness of movement/orientation), thermoception (heat), nociception (pain), equilibrioception (balance), time.
Other answers (with justification) may be accepted (some contention amongst psychologists).
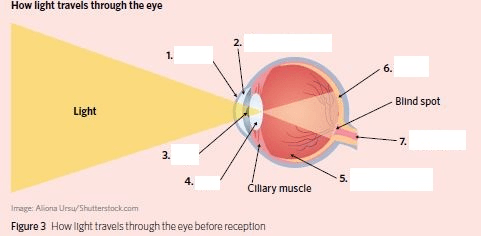 Several parts of this diagram of the eye are missing. 100 points per unique part that you can name!
Several parts of this diagram of the eye are missing. 100 points per unique part that you can name!
1. Cornea
2. Aqueous humour
3. Pupil
4. Lens
5. Vitreous humour
6. Retina
7. Optic Nerve
We can detect five basic flavours. Name them (100 points per unique response!)
Sweet, Salty, Sour, Bitter, Umami
Which Gestalt principle can be defined as "group together items that are physically close to one another"
The proximity principle
Consider this diagram. Which word is missing from the OUTPUT side?
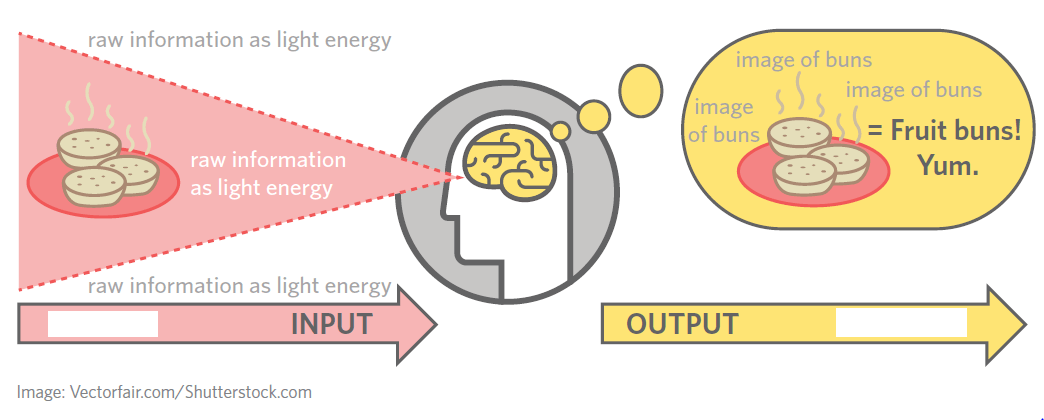
Perception
 Which Gestalt principle does the following diagram represent?
Which Gestalt principle does the following diagram represent?
The closure principle
Genetics
This part is responsible for seeing finer conditions like colour
Cones
Sensation occurs in three distinct stages. Name them.
Reception (Where we first receive the sensory information)
Transduction (Where the information is converted into a neural impulse)
Transmission (Where the information is transmitted to the brain for processing)
Visual constancies describe our ability to perceive objects as staying the same even though the sensation of the objects may change. Three constancies that affect our interpretation of visual stimuli are...
Shape, size and brightness
Describe how age can affect our perception of flavour.
As we age, our perception of flavours becomes less sensitive. This is similar to other senses such as sight, hearing, smell, etc.
Define selection (the first substage of perception)
The process of attending to certain features of sensory stimuli to the exclusion of others.
Perception consists of 3 stages. Name them.
Selection
Organisation
Interpretation
Our perceptual set can be affected by a number of things (A visual example is included below). 200 points for each factor you can name, and another 200 points if you can describe how it contributes to perceptual set.
200 points for each factor you can name, and another 200 points if you can describe how it contributes to perceptual set.

Consider the perceptual set for taste - past experiences, mood, motivation, appearance of food, etc. What factors may influence how we perceive something tastes?
Appearance (colour, shape), Packaging (logos, brands, images), Culture.
What word is described by the following definition: "A perceptual phenomenon characterised by the experience of unusual perceptions in one sensory system after another sensory system has been activated"
Provide an example of this for full points!
Synaesthesia. Examples will vary
The space in which a sensory stimulus can be detected by a sensory receptor is better known as what?
Receptive fields
Describe the monocular pictorial depth cue of relative size. Give an example.
The relative size of objects to one another in our visual field helps us to judge distance. For example, if we have two one litre water bottles and one appears smaller, we know that this smaller one is further away thanks to our knowledge of their size and our ability to compare them relative to one another.
Describe the process of sensation related to taste in terms of the 3 key stages of sensation
Reception - gustatory receptors receive information about food.
Transduction - Chemical molecules get converted into chemical energy.
Transmission - Sent from the mouth via cranial nerves to the primary gustatory cortex in the brain.