What does PVC stand for?
Premature ventricular contractions.
Define ventricular tachycardia.
A fast, abnormal heart rate. VT is defined as 3 or more heartbeats in a row, at a rate of more than 100 beats a minute.
What are the 2 abbreviations for ventricular fibrillation?
VF and V-fib.
Define asystole.
The state of total cessation of electrical activity from the heart, which means no tissue contraction from the heart muscle and therefore no blood flow to the rest of the body.
What is the location of all of these rhythms?
Ventricles.
Define PVC's.
A type of abnormal heartbeats, extra heartbeats that disrupt your regular heart rhythm.
What are a couple of symptoms of ventricular tachycardia?
Fast heartbeat or a fluttering feeling in the chest (palpitations), Dizziness, Lightheadedness, Chest pain, Neck tightness, Shortness of breath, Fainting, Cardiac arrest.
Define ventricular fibrillation.
A heart rhythm problem that occurs when the heart beats with rapid, erratic electrical impulses.
What are a few symptoms of asystole?
Loss of consciousness, not breathing, and no pulse. Before asystole occurs some symptoms include chest discomfort, shortness of breath, weakness, and tachycardia.

What rhythm does the image above show?
Asystole.
What are a few symptoms of PVC's?
Futtering, dizziness, pulsing sensations, feeling a skipped or extra heartbeat.
Is there treatment for ventricular tachycardia? If so, name them.
No treatment is needed if, you don’t have underlying heart disease, you are not having difficult symptoms, or your VT episodes don’t last a long time. If you do have symptoms, your healthcare provider might prescribe medicine (a beta-blocker or antiarrhythmic medicine) to control your heart rhythm.
What are the symptoms of ventricular fibrillation?
Chest pain, dizziness, palpitations, fatigue, etc.
What are some complications of asystole?
Fractured ribs, lung, and abdominal organ injuries, and abdominal/chest pain.
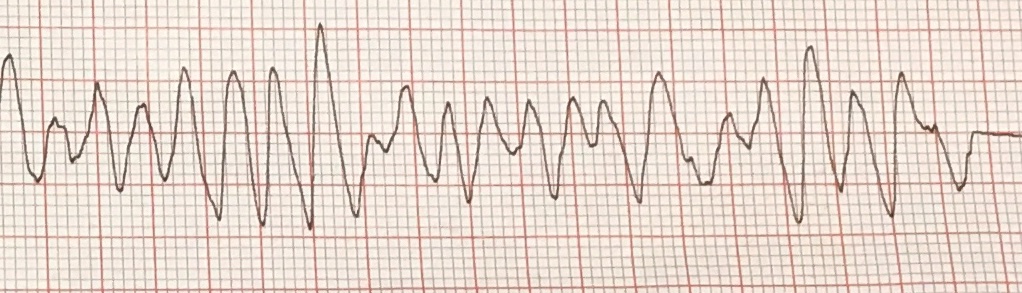
What rhythm does the image above show?
Ventricular fibrillation.
Do most people know if they are experiencing PVCs?
No.
Are there always symptoms present in all cases of ventricular tachycardia?
No, in some cases, there are no symptoms at all.
Is ventricular fibrillation deadly?
Yes.
Is asystole acute or chronic?
Acute, occurring after the sudden onset of cardiac arrest.

What rhythm does the image above show?
Ventricular tachycardia.
What are the ECG changes in cardiac monitoring for PVC's?
The ECG can detect the extra heartbeats and identify the pattern and source, these can be detected by seeing premature and long QRS complexes, they are not followed by a P wave and the T wave is large and in an opposite direction of the QRS.
What are some complications of ventricular tachycardia?
Some people may have mild symptoms from VT or no symptoms at all. But for others, VT can be very dangerous. It can lead to sudden cardiac arrest and death
What are the ECG changes in cardiac monitoring for ventricular fibrillation?
Begins with ventricular tachycardia and appears as a very irregular rhythm with indiscernible P waves or QRS complexes on ECG. Preceded by ventricular flutter which has rapid sinusoidal QRS complexes that can not be distinguished from T waves.
What are the ECG changes in cardiac monitoring for asystole?
No electrical current is present, so no changes are shown on the monitor. It is a flatline with no P waves or QRS complexes present.
What rhythm does this image above show?
PVC's.