This system is responsible for the classification, labelling, worker education and training for potentially hazardous materials in the workplace.
What is WHIMIS
Name the following microscope part:

What is the Mechanical Stage
This type of sample collection is most commonly used when looking for ectoparasites.
What is combing.
This liquid component of the blood is plasma but without clotting factors.
What is Serum
These WBCs are the most prevalent in our domesticated species and respond to stimuli such as infecting agents, foreign substances and cancers.
What are Neutrophils
Name the following test:
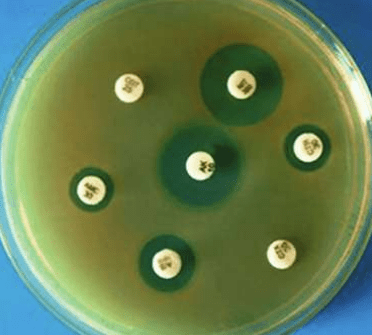
What is an Antibiotic Sensitivity Test.
This category of hazardous materials is represented by this symbol:

What is Corrosion?
This is calculated by multiplying the ocular magnification by the objective magnification.
The total magnification
These two types of sample collection can both be used to collect urine.
What is free-flow and cystocentesis.
This test gives the percentage of RBCs in the blood and is measured with a grid.
What is a PCV test.
These are the largest of the WBCs, with a variably shaped nucleus, diffuse chromatin and a blue-grey cytoplasm with vacuoles.
What is a Monocyte
These are the names of the three groups of bacteria according to shape.
What are Coccus, Bacillus and Spiral.
This biosafety level has the potential to cause serious and potentially lethal diseases and has a high risk of aerosol respiratory transmission.
What is Biosafety Level 3
This type of microscope generates an image by using a combination to increase magnification.
What is a compound microscope.
Name the anticoagulant inside the tube below:

What is Heparin
This type of artifact leaves RBCs looking hole punched and refractile.
What is water artifact
This WBC comes in a variety of sizes and is the most abundant in ruminant.
What is the Lymphocyte
Types of these can include transport, general purpose, enriched and selective and can be any material, liquid or solid.
What are culture medias.
This required piece of lab equipment is read by looking through an eye piece and displays a scale, and is commonly used for the measurement of total solids in plasma.
What is the Refractometer?
Name the function of the following microscope part:
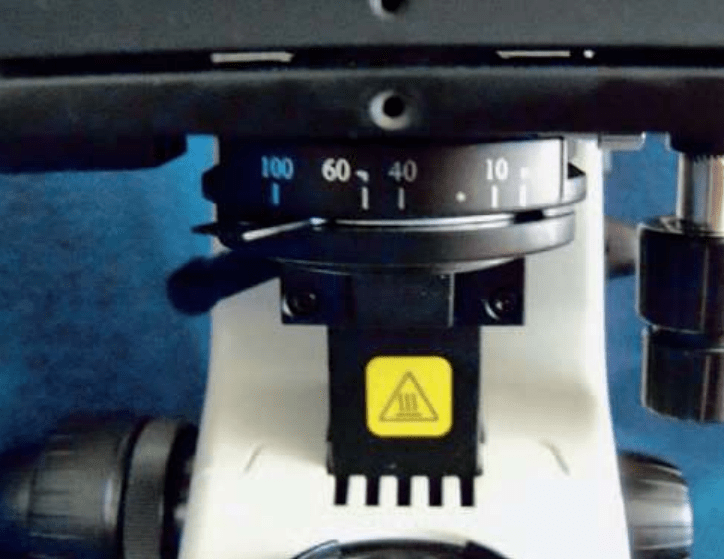

It opens and closes to control the amount of light that travels from the illuminator and through the condenser and the specimen. (Diaphragm)
What are the coccygeal vein and the jugular vein.
This RBC indices is the indicator of the average RBC size.
What is the MCV or the Mean Corpuscular Volume.
Name the following cell:

What is a Band Neutrophil
This type of agar plate strakinbg is seen below:
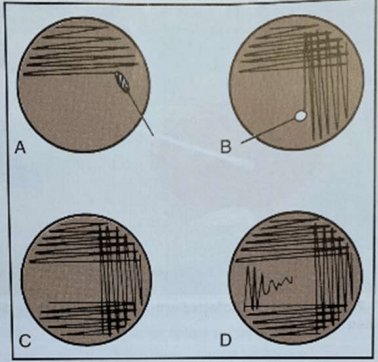
What is the Quad Streaking Method.
These are two types of centrifuges that might be found in a veterinary laboratory setting.
What are a swing arm centrifuge, an angled centrifuge and a microhematocrit centrifuge.
This part of the microscope is used to change the focus on one eye piece to compensate for differences in vision in the viewers two eyes.
What is the Diopter adjustment.
Name the method of sample collection seen below:
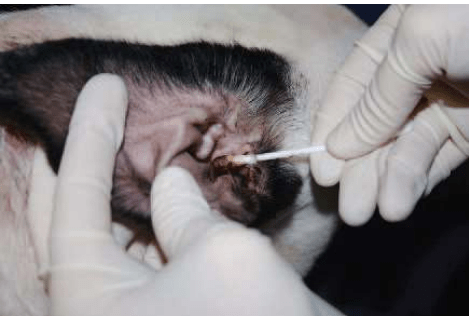
What is swabbing
These species have erythrocytes that are elongated and oval shpaed:
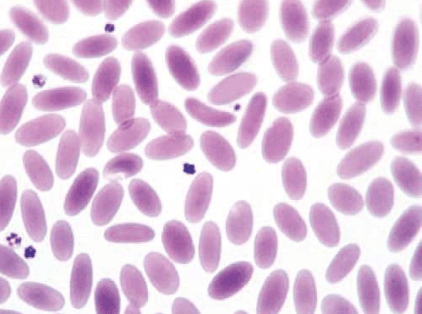
Who are llamas and camelids.
Name the following WBC type:
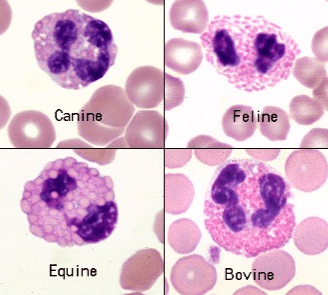
What is an Eosinophil.
These four requirements are needed for optimal bacterial survival.
What are temperature, pH, oxygen tension and nutrition.
Name the following piece of laboratory equipment:
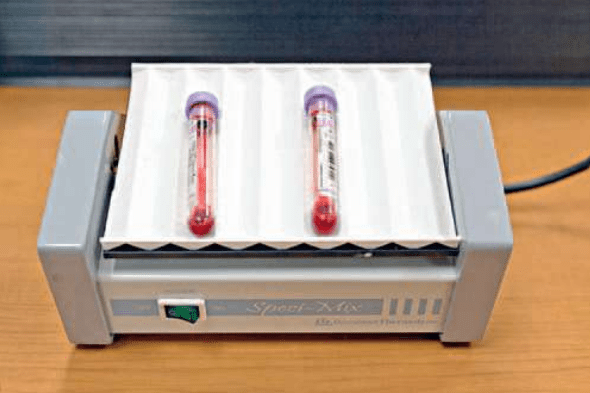
What is an Aliquot mixer.
The part of the microscope that consists of two lenses focusing light from the light source on to the object by raising or lowering.
What is the substage condenser.
This type of sample collection method is best used for flat, dry, superficial lesions.
What is skin scraping.
Name the following RBC abnormality:
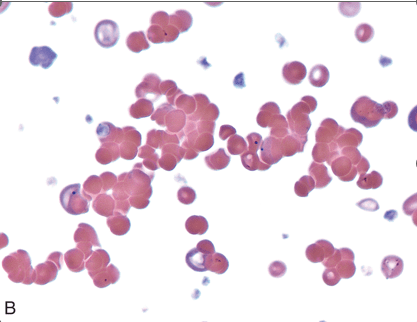
What is agglutination
Name this feline WBC:
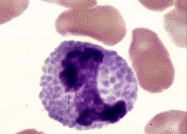
What is a Basophil
This phase of bacterial growth is the initial phase where the bacteria learn to adapt their metabolism to the recourses in their new environment.
What is the LAG phase.