What is viscosity?
The thickness of a fluid, the measure of how well it will flow.
What is its volume?
The amount of space that a object/material uses.
What is buoyancy?
The upward force exerted by a fluid.
What states of matter are considered fluids?
Liquids and gases
What is the density of water?
1g/mL
What is low viscosity?
It is when a fluid will flow freely and quickly, a thin fluid like water.
Less dense fluids will do this when placed on top of denser fluids.
They will float.
What is the relationship ship between buoyant force and gravity?
They are opposing forces, gravity pulling down and buoyant force pushing up.
What are the properties of fluids?
They flow and take the shape of their container.
What is the density of a rock that has a mass of 550g and a volume of 25cm3?
22g/cm3
According to the Particle Model of Matter, what happens to a fluid when the temperature rises?
The particles gain energy and move faster. This weakens the bonds between then and allows them to move more freely, lowering the viscosity.
What is the formula for calculating density.
Density = mass(g) / volume(mL or cm3)
This type of buoyancy occurs when an object stays suspended in the fluid without rising or sinking.
Neutral buoyancy
This property describes how easily a fluid flows, and is one of the major ways fluids are compared.
Viscosity
If a ship weighs 83 743kg and it displaces 79 326kg of water, is it positvely, neutrally, or negatively buoyant?
Negatively buoyant
What is flow rate?
The measurement of the distance travelled by a fluid in a certain amount of time—is used as an indicator of viscosity.
Using the particle model of matter, explain why a substance is more dense.
There are more particles packed into the same amount of space.
When the weight of an object is less than the weight of the fluid it displaces, this occurs.
Positive buoyancy
Fluids expand and become less dense when this environmental factor increases.
Temperature
A drop of motor oil takes 7.43s to fall 26.4cm. What is its flow rate?
3.55cm/s
Rank these from low to high viscosity: lava, cream, milk, mayonnaise, dish soap.
Milk, cream, dish soap, mayonnaise, lava
What happens to a fluid when you add solutes like salt?
It becomes more dense.
The buoyant force depends on both the density of the fluid and these properties of the object.
The mass and shape of the object.
This force, caused by a fluid, acts upwards and is important in determining whether an object sinks or floats.
Buoyancy
What did you find if the object has a mass of 107g and when put into a graduated cylinder the level goes from 10mL to 15mL?
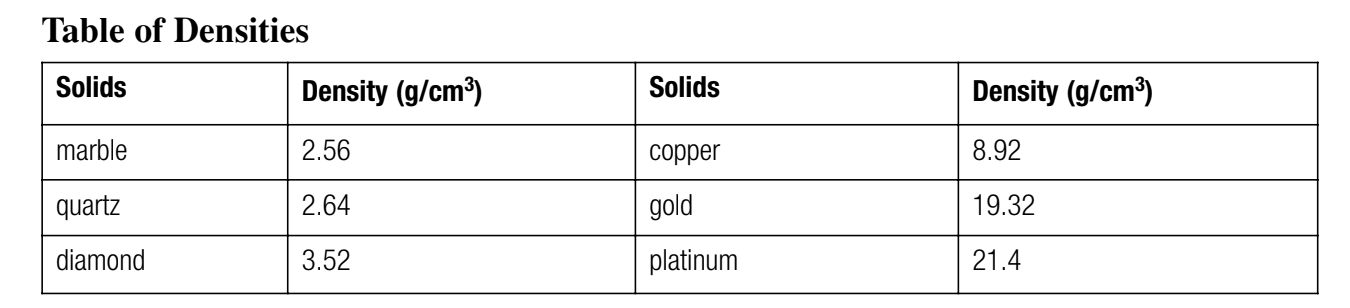
Platinum
Which fluid once took over a decade to form a single drop, demonstrating extremely high viscosity.
Pitch
Why is water unique when discussing its density?
It is the only substance where it is less dense as a solid than a liquid.
The weight of the object is greater than that of the water is is displacing.
What is the formula for concentration?
Concentration = mass of solute (g) / volume of solvent (mL)
A cup of some unknown fluid loses volume due to evaporation. It goes from 80g to 60g. What volume was lost if the density of the fluid is 3.7g/mL?
5.4mL