How does a Volcano form?
Volcanoes form where molten rock (magma) from inside the Earth rises to the surface.
In which type of plate boundaries do volcanoes mostly form?
Convergent (subduction) or Divergent
What is a Hot Spot Volcano?
A hot spot volcano forms when magma rises from deep inside the Earth, away from tectonic plate boundaries. The magma pushes up through the crust and creates volcanoes, often in the middle of a tectonic plate.
In which type of boundary do Earthquakes mainly happen?
Transform boundary
What is a Tsunami?
A tsunami is a series of large ocean waves caused by the sudden displacement of water. Usually caused by earthquakes happening under water.
Name the main parts of a volcano structure
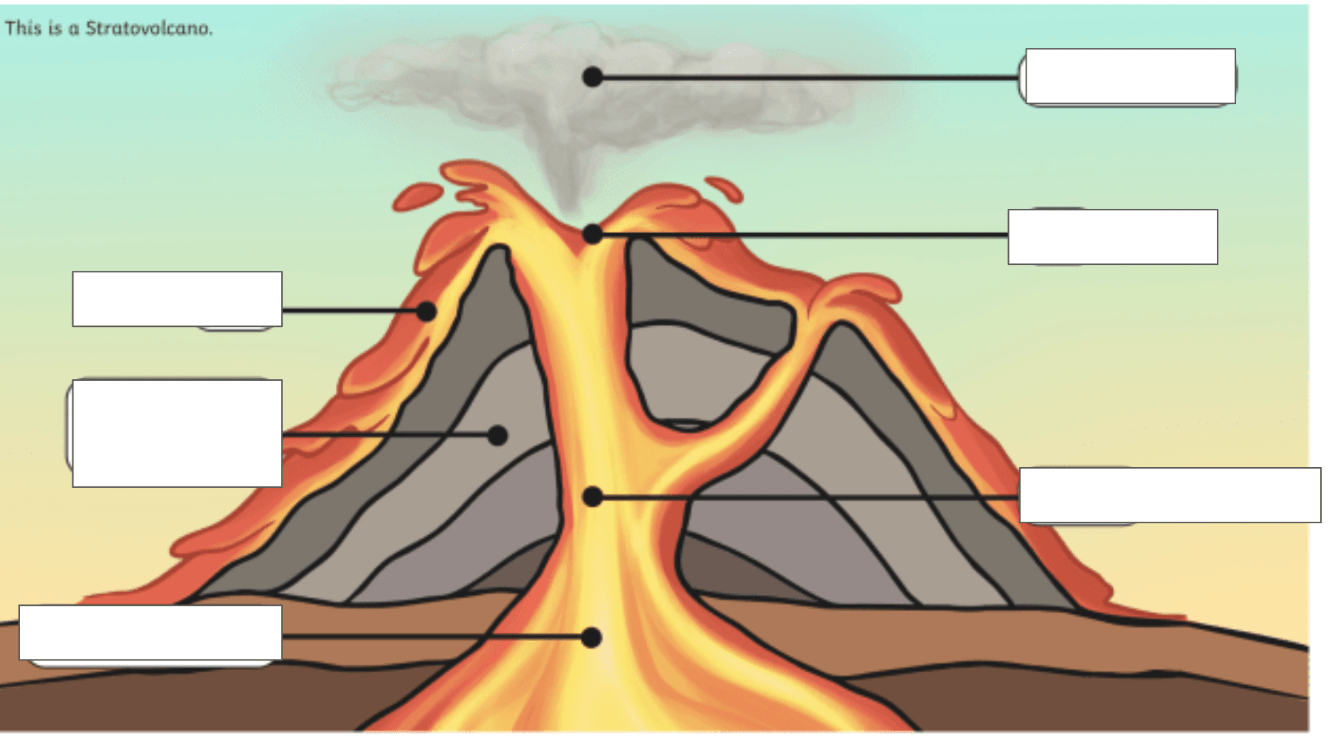
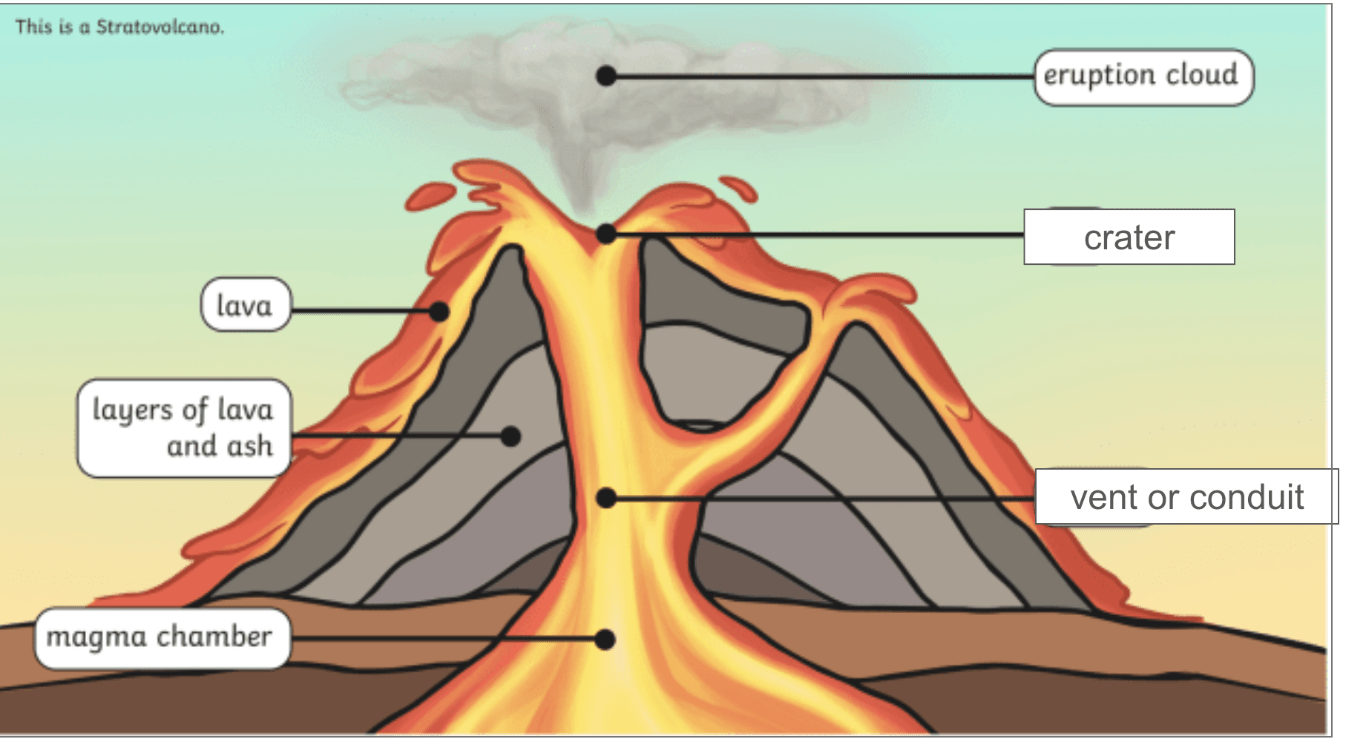
What is the difference between magma and lava?
Magma is molten rock beneath the Earth’s surface. It contains hot liquid rock, gases, and crystals. Magma is stored in magma chambers underground and is under high pressure.
Lava is magma that has reached the Earth’s surface through a volcano. Once it erupts, the pressure drops, some gases escape, and it cools to form solid rock.
What other things than lava are released in a volcanic eruption?
Ash, gas, and rock fragments
What do e call the force that opposes movement and that is the cause of earthquakes?
Friction
What is the difference between the focus and the epicentre of an earthquake? Label the diagram
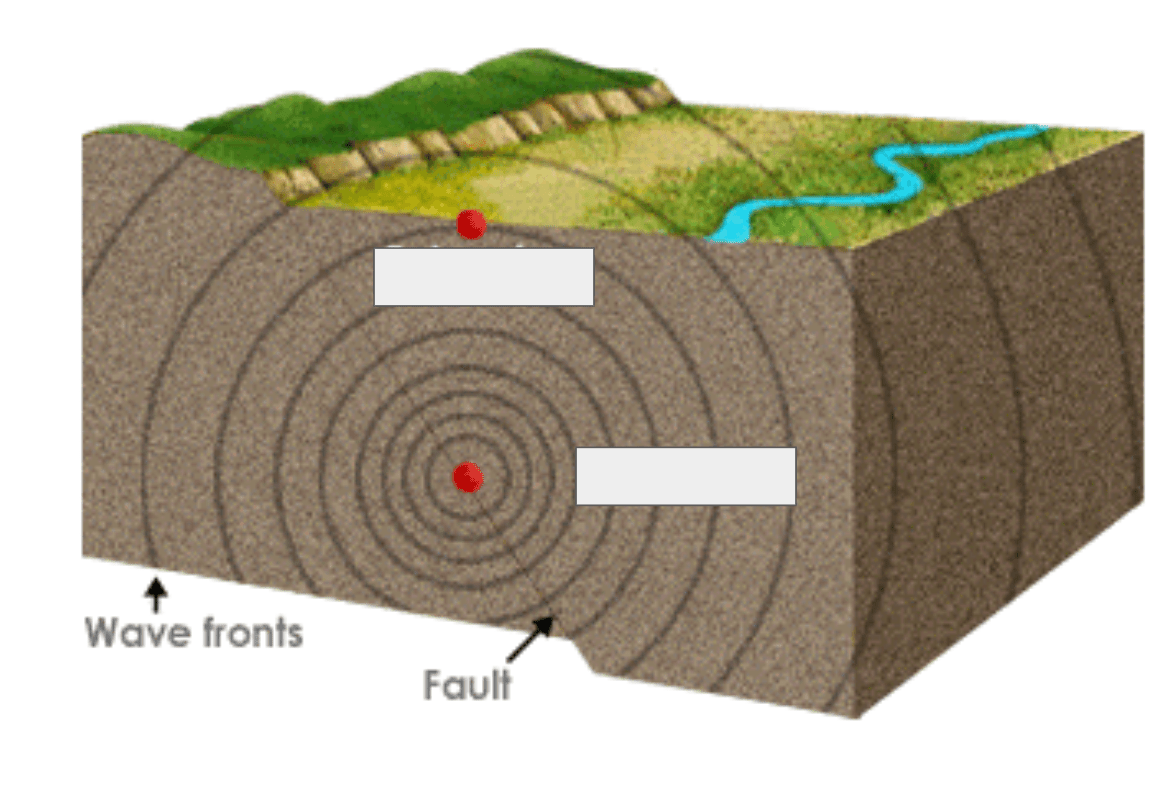
focus - underground
epicentre - above ground
What is the difference between an active, a dormant and an extinct volcano?
Active = erupting or likely to erupt
Dormant = “sleeping,” could erupt again
Extinct = “dead,” unlikely to erupt
What do we find in the chamber of a volcano?
Magma
How do geothermal water and mud pools occur?
Geothermal water and mud pools form when underground water is heated by hot rocks or magma, rising to the surface as hot springs or bubbling mud.
What de we use to measure the intensity of an earthquake?
Seismograph
What do we call the waves in an erthquake?
Seismic waves
What is a Caldera volcano?
Calderas are large, basin-like depressions formed when a volcano collapses into itself after a massive eruption empties the magma chamber.
What is a Stratovolcano?
These are tall, cone-shaped volcanoes made of alternating layers of lava, ash, and rock.
They erupt thicker, stickier lava and often have explosive eruptions.
What is the difference between a Stratovolcano and a Shield Volcano?
A stratovolcano is steep and explosive with thick lava, while a shield volcano is wide and gentle with runny lava.
What do we call the 2 types o waves in an Earthquake?
P and S
Where are Tsunami y waves larger in the ocean or close to the shore?
Close to the shore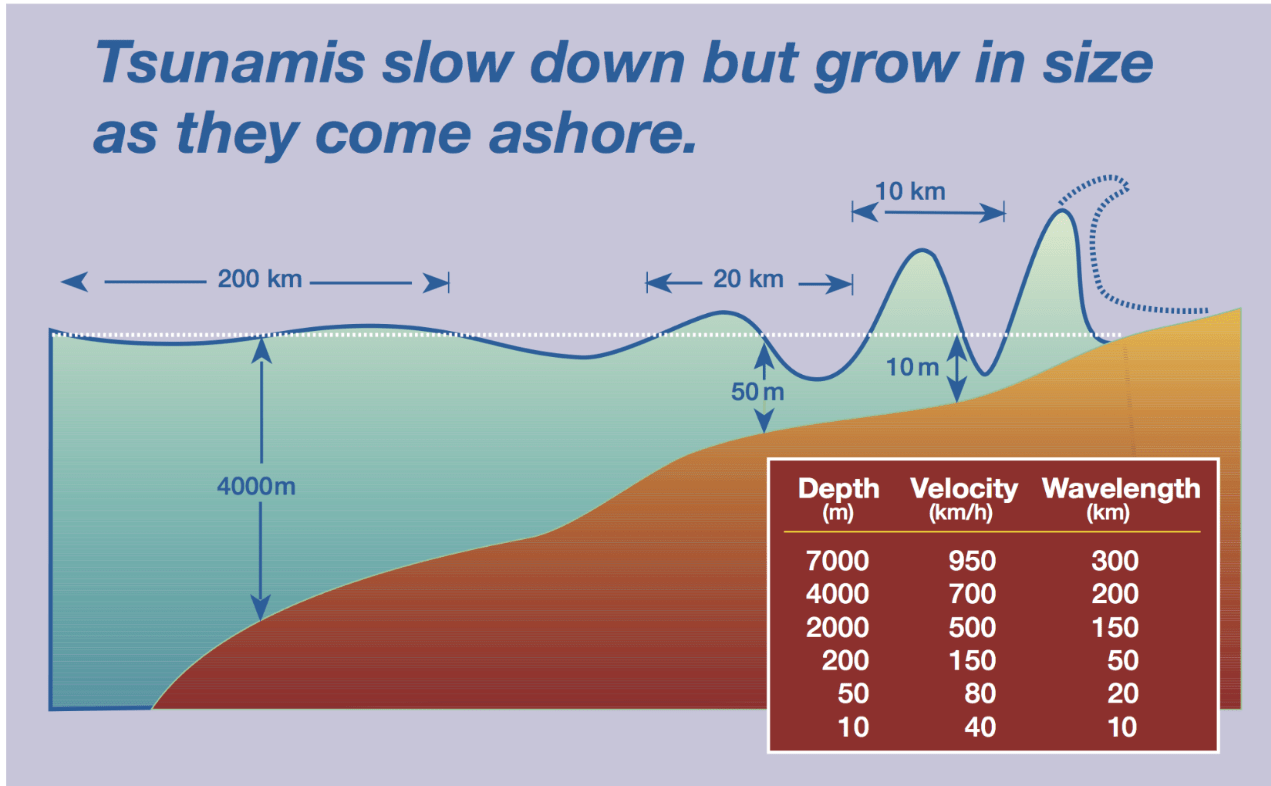
What is a subduction sone and what happens in it?
A subduction zone is a type of convergent boundary where one tectonic plate slides underneath another and sinks into the Earth’s mantle. This usually happens when a denser oceanic plate collides with a lighter continental plate. The dense oceanic plate melts in the mantle
Name three different types of lava and what makes it different?
Lava is molten rock that erupts from a volcano and is made of magma, which contains molten rock, minerals, and dissolved gases.
There are three main types:
Basaltic lava – low in silica, runny, flows easily; forms shield volcanoes.
Andesitic lava – medium silica, thicker, flows slower; often forms stratovolcanoes.
Rhyolitic lava – high silica, very thick and sticky, eruptions are explosive.
The silica content controls how runny or thick the lava is, which affects the shape of the volcano and eruption style.
What are typical gasses in a volcanic eruption? (name three)
Water vapor (H₂O) – the most abundant gas
Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
Sulfur dioxide (SO₂)
Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S)
Other gases in smaller amounts, like carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and methane
What is the difference between magnitude and intensity of an earthquake and what is the name of the scale used to measure each one?
Earthquakes are measured in two main ways:
- by the magnitude (energy released) Richter Scale
- and by the intensity (effects on people and buildings) Mercalli Scale
What is the difference between a P and and S wave in an Earthquake?
P-waves (Primary waves) Fastest seismic waves, arrive first at a location (longitudinal wave)
S-waves (Secondary waves) Slower than P-waves, arrive second. (transverse waves), only travel though solids