What kind of wave is pictured below?

Transverse wave
What kind of wave is pictured below?
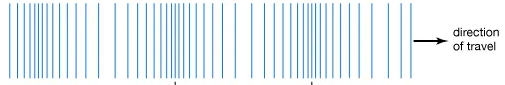
Longitudinal wave
What happens to volume as amplitude increases? Is this a direct or inverse relationship?
Volume increases; direct
Occurs when waves are not absorbed but instead bounce off and away from the surface.
(ex: echoes, mirrors)

Reflection
Sound Navigation and Ranging Technology; helps watercraft navigate through bodies of water and map the seafloor.
Sonar
Pick a vocabulary term to complete the sentence:
Sound waves travel faster through (gases / liquids / solids).
solids
Pick a vocabulary term to complete the sentence:
(light / sound) travels through transverse waves. Transverse waves (do / do not) require a medium.
light ; do not
Pick a vocabulary term to complete the sentence:
(light / sound) travels through longitudinal waves. Longitudinal waves (do / do not) require a medium.
sound ; do
What happens to pitch as frequency increases? Is this a direct or inverse relationship?
Pitch increases; direct
When waves are taken into an object.
(ex: sound proofing walls)

Absorption
Uses echoes of mechanical waves to create images of tissues, organs, bones, and fetuses (babies).
Ultrasonography
As temperature increases, the speed of sound _______________.
increases
What belongs in box A in the picture below?
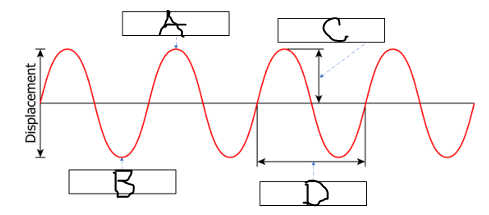
Crest
What belongs in box A in the picture below?
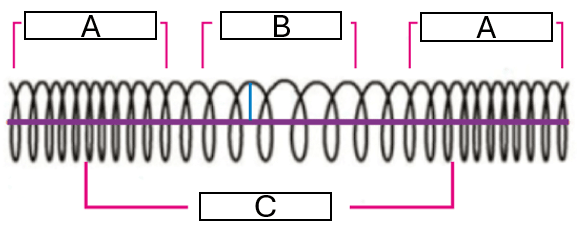
Compression
What happens to wavelength as frequency increases? Is this a direct or inverse relationship?
Wavelength decreases; inverse
When waves bend and change direction because of their speed changing due to entering a new medium.
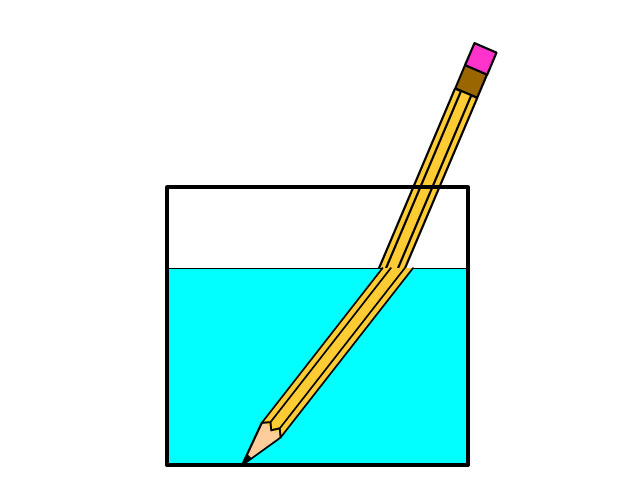
Refraction
Emits ultrasonic waves to determine the distance of nearby objects to prevent cars from crashing into objects.
Vehicle parking sensors
When the crests of one wave meets the crests of another, resulting in an increase in amplitude. (hint: ______________ interference)
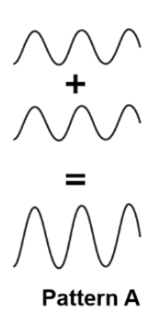
Constructive interference
What belongs in box B in the picture below?
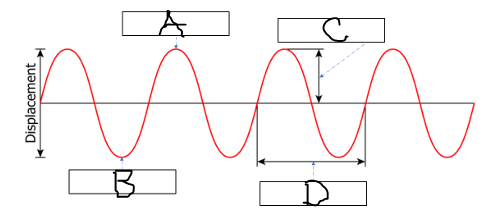
Trough
What belongs in box B in the picture below?

Rarefaction
What happens to pitch as wavelength increases? Is this a direct or inverse relationship?
Pitch decreases; inverse
When a wave passes completely through a medium.
(ex: light passing through a window)

Transmission
Use the energy of transverse ocean waves to generate electricity.
Wave power generators
When the crest of one wave meets the trough of another, resulting in the waves cancelling each other out. (hint: ______________ interference)
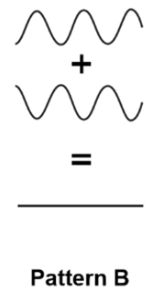
Destructive interference
What belongs in box C AND D in the picture below?
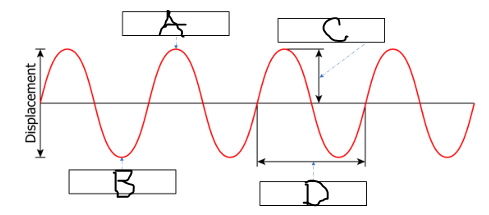
C = amplitude
D = wavelength
What belongs in box C in the picture below?

Wavelength
Draw a wave with low amplitude but high frequency.

The bending of waves as they pass around the edge of an obstacle or through an opening.
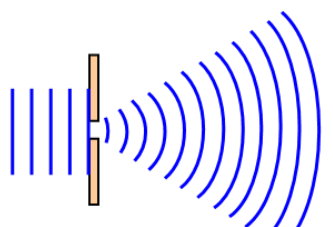
Diffraction
Similar to sonar, but used by animals such as bats and dolphins to help with hunting and navigation.
Echolocation
When two or more sound waves with like frequencies are combined, resulting in an increase in amplitude. (Hint: musical instruments use this to increase intensity and volume of sound.)
Resonance