Mechanical vs. Electromagnetic
Wave Interactions
Wave Parts & Properties
Sound
EM Spectrum
100
Requires a medium in which to travel.
What is a mechanical wave?
100
Bending of waves from one medium to another
What is refraction?
100
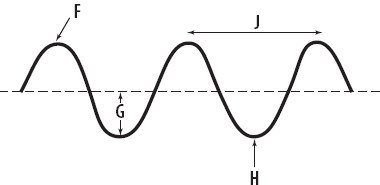 Represented by letter J.
Represented by letter J.What is one wavelength?
100
Travels the fastest in this medium.
What is solid?
100
Travels the slowest in this medium.
What is solid?
200
Particles vibrate parallel to the direction the wave travels.
What is a longitudinal wave?
200
 The straw in water.
The straw in water.What is refraction?
200
The part of the wave from rest to trough.
What is amplitude?
200
Due to reflection of sound waves.
What is an echo?
200
Property that all EM waves have in a vacuum.
What is speed?
300
Sound is an example.
What is a mechanical or longitudinal wave?
300
 Wave interference is greatest when opening is equal to the size of the wave.
Wave interference is greatest when opening is equal to the size of the wave.What is diffraction?
300
The relationship between wavelength and energy.
What is indirect or inverse or opposite?
300
Perception of sound affected by frequency.
What is pitch?
300
When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle.
What is total internal reflection?
400
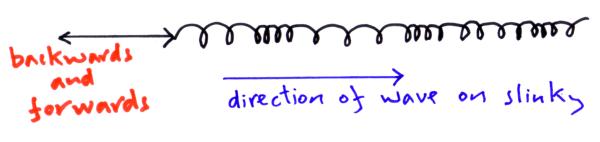 The loosely coiled area in a longitudinal wave.
The loosely coiled area in a longitudinal wave. What is rarefraction?
400

What is constructive interference?
400
The factors that affect wave speed.
What are medium and temperature?
400
Chris is 10 cars behind a fire truck siren, Carter is driving the fire truck with Giye riding shotgun and Daniel is 10 cars ahead of the fire truck. Who hears the highest change in frequency?
Who is Daniel?
400
EM wave used for sanitizing tools and vitamin D production.
What is ultraviolet (UV) waves?
500
Could be detected in a vacuum chamber.
What is electromagnetic waves?
500
The science behind noise cancelling headphones.
What is destructive interference?
500
The relationship between wave speed and frequency.
What is no relationship or none?
500

What is the Doppler Effect?
500
The order of EM waves from highest energy, highest frequency and shortest wavelengths
What is gamma, x-rays, ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, microwaves, radio waves.