WHAT PHASE OF RECOVERY OCCURS WHEN THE PATIENT ARIVES TO THE SURGICAL UNIT
PHASE 2
WHAT 5 THINGS MUST BE ASSESSED BEFORE FEEDING THE POST OP PATIENT
LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS
CAN THEY SWALLOW
DO THEY HAVE A GAG REFLEX
IS THE GI TRACT FUNCTIONING
ARE THEY NAUSEOUS OR VOMITING
NPO means
Nothing by mouth
nothing to drink or eat
No Ice chips, nothing by mouth
I ALLOW FLUIDS, EXUDATE, & BLOOD TO EXIT TISSUE
DRAINS
Penrose, Jackson Pratt, Hemovac
Prevent excess pressure from building up under excision
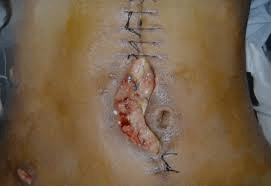
Dehiscence, Evisceration, & Infection
WHAT ARE POSSIBLE POST OPERATIVE WOUND COMPLICATIONS?
Cover with dry sterile dressing
Maintain bedrest with HOB at 20 degrees & knees flexed
Apply ABDOMINAL binder
Notify provider of occurrence
Continue to monitor/assess patient
I AM THE PAIN SCALE USED WHEN A PATIENT CAN UNDERSTAND & RESPOND TO QUESTIONS, BUT I ALSO NEED TO BE ABLE TO COUNT TO 10.
Numeric Rating Scale
^ systolic blood pressure
^ heart rate and force of contraction
^ respiratory rate
Dilated pupils
Rapid speech
WHAT ARE THE NONVERBAL PHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSES/INDICATORS TO PAIN
IMMEDIATELY ON ARRIVAL HOW OFTEN MUST THE RN PERFORM VITAL SIGNS
Every 15 minutes for the first hour
Every 30 minutes for the next 2 hours
Every hour for the next 4 hours
Then every 4 hours
How do you determine if a patient has the appropriate Level of consciousness to feed them?
Is the patient:
Alert, when you walk in the room or talk
Awake and can stay awake
Clear liquids consist of?
Coffee - BLACK
Tea - PLAIN
Carbonated drink
Bouillon/BROTH
Clear fruit juice
Popsicle
Gelatin
Hard candy
WHEN SHOULD THE RN EMPTY THE JACKSON PRATT OR HEMOVAC?
WHEN THEY ARE 1/2 FULL
WHEN THEY LOSE SUCTION/COMPRESSION
APPLYING A BINDER FOR DEHISCENCE DOES WHAT
PREVENTS EVISCERATION
Cover wound with sterile towels soaked with sterile saline
Bedrest with knees bent to prevent strain
HOB 20 degrees
Notify surgeon and prep for surgery
WHAT ARE THE INTERVENTIONS FOR EVISCERATION
this pain scale is best used on children and cognitively impaired adults or for patients with impairments in communication.
The Wong-Baker FACES Pain Rating Scale
Moaning - Groaning
Facial grimacing
Frowning
Crying
Agitation
Fidgeting
Withdrawal from painful stimuli
Guarding the painful area
Rubbing the area
WHAT ARE THE NONVERBAL BEHAVIORAL RESPONSES/INDICATORS TO PAIN
THINK OF THE POPULATION WE ARE LEARNING ABOUT.
What are 8 steps to implement with progressive ambulation
Patient is awake, alert, and can follow directions
Vital signs are stable
What was the patients ability pre-operatively
Sit & Dangle at bedside
OOB to chair
Walk in room
Walk in hallway
Consider Physical Therapy
As the nurse how do you assess the ability of the patient to swallow?
Determine if they can swallow their own saliva or a sip of water without coughing, gasping, or choking
Pureed food, soft meet, vegetables, cereal, & fruit
What foods are included on a soft diet
REEDA THE SITE
IS IT FULL
IS IT COMPRESSED
IS THE TUBING KINKED
IS THERE LESS OR MORE DRAINAGE & COCAF
IS THE PATIENT COMPLAINING OF CHANGE IN PAIN
HOW TO ASSESS SURGICAL DRAINS
Local edema & erythema, purulent exudate, hot to touch, pain
What are s/s of wound infection
GET OOB
EARLY AMBULATION
DEEP BREATH & COUGH Q 1 H
INCENTIVE SPIROMETER Q 1 H
HOB 90 DEGREE IF BED REST Q 2H FOR 1 HOUR
WHAT ARE INTERVENTIONS TO PREVENT ATELECTASIS & PNEUMONIA
THIS SCALE IS USED FOR WHICH PATIENTS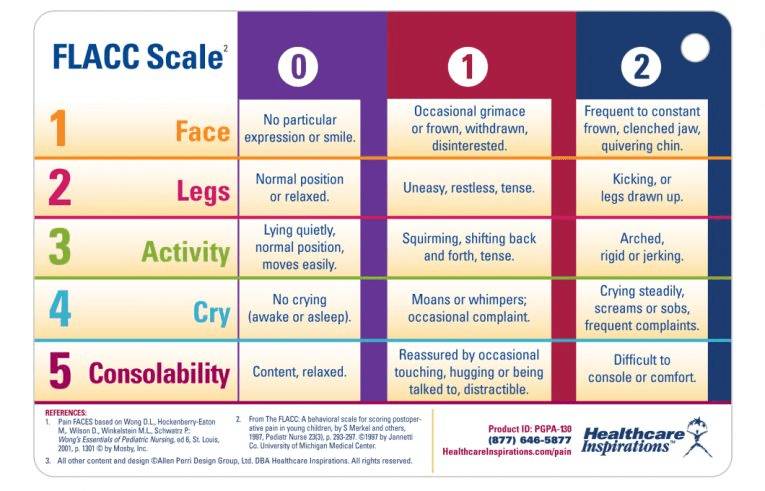
This scale is used for behavioral pain assessment for nonverbal or preverbal patients who are unable to self-report their level of pain.
Also effective for individuals that are unable to communicate their pain such as those on ventilators-unresponsive-confused.
Pain is assessed through observation of 5 categories including face, legs, activity, cry, and consolability.
WHAT ASSESSMENT & INTERVENTIONS MUST BE PERFORMED PRIOR TO ADMINISTERING AN OPIOID
IS THERE AN APPROPRIATE ORDER
WHEN DID THE PATIENT RECEIVE IT LAST, IS IT THE RIGHT TIME FRAM TO TAKE AGAIN
WHAT ARE THE VITALS SIGNS, SPECIFICALLY RESPIRATORY RATE
IS THE PATIENT AWAKE, ALERT AND NOT SEDATED
Progressive ambulation Intervention performed to prevent orthostatic hypotension and dizziness
Sit and Dangle the legs at the side of the bed.
Auscultating bowel sounds, hearing the patient belch and pass flatus
Signs & symptoms of a functioning gastrointestinal tract.
Coffee with cream, custard, sherbert, tomato juice, and pudding
Foods allowed on a full liquid diet
AFTER EMPTYING A JP OR HEMOVAC WHAT MUST THE RN DO?
COMPRESS THE DRAIN
CLOSE THE CAP
ENSURE SUCTION
VERIFY NO KINKS IN THE TUBING
CLIP IT TO THE GOWN
YOU ASSESS THE FOLLOWING NEW CHANGES AROUND YOUR PATIENTS SURGICAL INCISION
ECCHYMOSIS, HEMATOMA, INCREASED PAIN
WHAT IS POSSIBLE INTERNAL HEMORRHAGE
AMBULATION OR TURN & POSITION
ANKLE ROTATION & FOOT PUMPS & LEG EXERCISES
Anti-embolism stockings
Sequential compression devices
INTERVENTIONS TO PREVENT DVT BY PROMOTING VENOUS RETURN
AS A NURSE IF A PATIENT REPORTS PAIN WE USE A SCALE TO DETERMINE SEVERITY BUT WE ALSO NEED TO ASK ABOUT.....
PAIN QUALITY
PAIN PERIOSITY
PAIN INTENSITY
ANY SPECIFIC AGGRAVATING FACTORS
WHAT PAIN CONTROL METHOD REQUIRES
CONTINUOS PULSE OXIMETRY
CALLING FOR ASSISTANCE WHEN GETTING OOB
Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA)
WHAT DO YOU DO IF PATIENT EXPERIENCES ORTHOSTATIC HYPOTENSION?
LAY THEM BACK DOWN IN BED
PERFORM A SET OF VITAL SIGNS
PERFORM A PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT
A NORMAL REFLEX THAT CONTRACTS THE THROAT TO PREVENT CHOKING
GAG REFLEX
MUST BE PRESENT PRIOR TO OFFERING LIQUIDS OR FOOD TO THE PATIENT
Patient tray has bottled water, chopped apple, chicken breast, green beans, can of soda, & black coffee
What is a regular soft diet
WHAT PRE OPERATIVE ALLERGY ASSESSMENT MUST BE ASKED PRIOR TO PENROSE DRAIN PLACEMENT
DOES THE PATIENT HAVE AN ALLERGY TO LATEX
WHAT IS THIS?
WHAT IS EXTERNAL HEMORRHAGE
AFTER ASSESSMENT YOU SUSPECT A LEFT CALF DVT IN YOU POST OPERATIVE PATIENT. WHAT ARE YOUR INTERVENTIONS?
IMMOBILIZE THE LEFT LOWER LEG
CALL THE PRACTITIONER
ANTICIPATE AN ANTICOAGULANT SUCH AS HEPARIN
DO NOT EVER MESSAGE THE AFFECTED LIMB
SHARP OR DULL
ACHING - THROBBING - STABBING - BURNING
RIPPING - TEARING
WHAT ARE EXAMPLES OF PAIN QUALITY
Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA)
HAS TWO MODES, WHAT ARE THEY?
Mode 1 – patient pushes button for dosE
Mode 2 – pt pushes button for dose plus machine is administering a constant basal dose