What type of tissues do the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions innervate?
smooth muscles
cardiac muscles
glands
What are Olfactory receptors
-are chemoreceptors located on the dendrites of olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium
-olfactory sensory neurons can undergo cell division
True or False: Taste receptor cells are neurons.
False: they are a type of specialized epithelial cell and form form synapses with sensory neurons
What are hair cells and where are they found?
Hair cells are sensory cells found in the inner ear, specifically in the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals.
What is an engram and how does it reside in the brain?
an engram is a physical trace of memory in the brain, residing in neural circuits?
What are the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric divisions
Which cranial nerve transmits olfactory information to the brain, and what is the most important destination for olfactory information in the brain?
The olfactory nerve (Cranial Nerve I) transmits olfactory information to the brain, with the primary destination being the olfactory cortex.
Also, information is transmitted to the Orbitofrontal cortex (via the thalamus) and the Olfactory tubercle
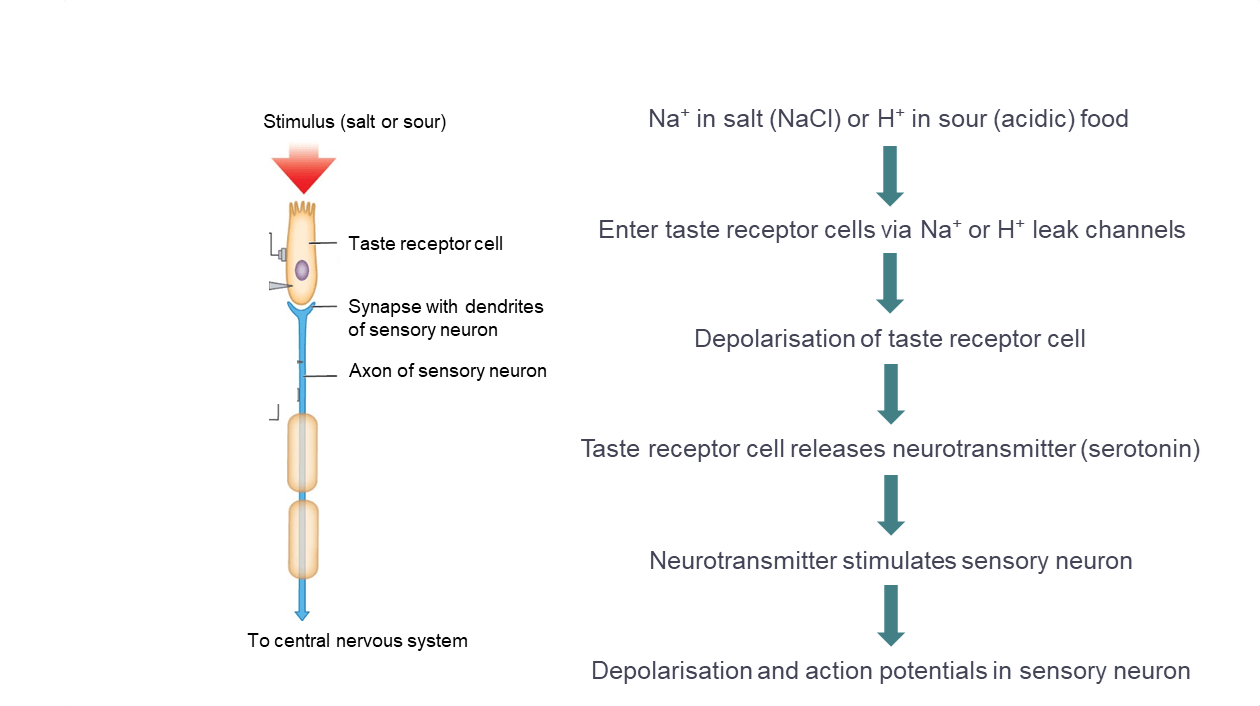
How does salty or sour foods cause depolarization of the taste receptor cells leading to the discharge of action potentials in sensory neurons?
Which cranial nerve transmits balance (vestibular) information to the brain stem and why does this information end up in so many brain regions?
The vestibulocochlear nerve (Cranial Nerve VIII)
This information is distributed to multiple brain regions to coordinate balance, posture, and spatial orientation and to keep our eyes focused on a specific point when the head is moving
Can you briefly describe declarative and nondeclarative memory and provide an example of each?
declarative memory involves facts and events (e.g., remembering a birthday), and nondeclarative memory involves skills and habits (e.g., riding a bike)
Which brain regions are important for memory?
the hippocampus, amygdala, cerebellum, and prefrontal cortex?
Can you briefly describe the anatomy and function of each division? Give an example of one function for each.
sympathetic division prepares the body for 'fight or flight' responses
the parasympathetic division promotes 'rest and digest' activities
the enteric division controls the gastrointestinal system
Which cranial nerves transmit gustatory information and where does this information end up in the cerebral cortex?
The facial nerve (Cranial Nerve VII), glossopharyngeal nerve (Cranial Nerve IX), and vagus nerve (Cranial Nerve X) transmit gustatory information to the brain. This information ends up in the Primary gustatory cortex.
What two factors are involved in LTP and LTD?
the frequency of action potential discharge in the presynaptic neuron and the degree of simultaneous depolarization of pre- and postsynaptic neurons?