Mr. C was admitted with CHF and labs revealed NA 120
1. why is Mr. C having hyponatremia
2. what are some expected medical / nursing interventions
1. due to fluid overload (dilutional hyponatremia)
2. fluid restriction, furosemide, neuro assessment, seizure precautions, stop IV fluids, cont with NA restriction, daily weight to monitor fluid status
what is the normal range for
PH, PCO2, HCO3
which levels are Acidosis, alkalosis
Ph: 7.35-7.45 <acidosis, >alkalosis
Pco2: 35-45 <alkalosis, >acidosis
HCO3: 22-26 <acidosis, >alkalosis
Mr. T was diagnosed with AFIB.
1. what are some priority assessment / why.
2. what are some expected medical / nursing interventions.
1. monitor neuro (risk for CVA), cardiac (tachycardia, reason for afib ex: MI/CAD)
2. medical: bb, ccb, AC vs NOAC (Heparin, warfarin, eliquis, xarelto), poss synchronized cardioversion.
nursing: cardiac monitoring, cardiac / neuro assmt, vitals
Mr F. was admitted with right sided fluid heart failure.
1. what are some s/s you expect to see
peripheral edema, weight gain, fatigue
ascities, enlarged liver,spleen
pronounced JVD
The nurse is instructing a hospitalized client with a diagnosis of emphysema about measures that will enhance the effectiveness of breathing during dyspneic periods. Which position would the nurse instruct the client to assume?
Sitting up in bed
Side-lying in bed
Sitting in a recliner chair
sitting up & leaning on an overbed table.
sitting up & leaning on an overbed table.
Ms C was admitted for hypotension due to dehydration. she was started on 0.9ns at 150cc/hr. the next day, she is complaining of SOB
1. what is possible the cause of her SOB
2. what are some anticipated interventions
3. what are some other symptoms this patient can experience
1. fluid overload from IV fluids
2. stop fluids, elevate HOB, resp assmt (listen to lungs, pulse ox, RR), apply o2 if needed. last resort: diuretics
3. edema, HTN, JVD, Crackles, frothy/reddish secretions, tachycardia
7.45, 47, 30
7.55, 40, 35
fully compensated metabolic alkalosis by respiratory acidosis
metabolic alkalosis (uncompensated)
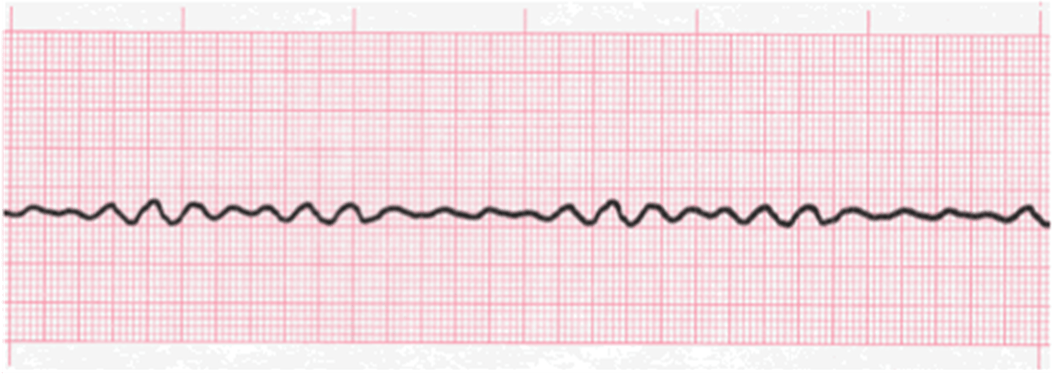
1. what is this rhythm
2. what is the treatment
Vfib
CPR / Defibrillation
Ms T was admitted with left sided heart failure. what s/s do you anticpate
1. pulmonary edema, SOB, coughing, confusion, wheezing / crackles, PND, orthopnea, tachycardia
Mr M. is admitted with exacerbation of his asthma and is having wheezing.
1. what is your priority assmt
2. what are some nursing interventions.
3. what inhaler do you expect with him experiencing wheezing
1. resp assessment (lungs, pulse ox, rr)
2. position in high fowlers, o2 if needed, remain calm
3. SABA (short acting beta adrenergic), Albuterol
Mr T. is admitted with muscle cramping and spasms (tetany). he also has been noted to have arrhythmias. labs show electrolyte abnormalities. what electrolyte imbalance do you think he has.
hypocalcemia
7.22, 35, 17
7.35, 32, 15
metabolic acidosis
compensated metabolic acidosis (resp system is removing more CO2 to compensate for the metabolic acidosis)
your patient was just started on digoxin for rate control for his Afib. what electrolyte do you want to make sure does not get to low and why
potassium (hypokalemia). will increase digoxin toxicity
1. what are some nursing interventions related to heart failure.
2. what blood levels are checked with heart failure & MI
3. what is the reason for heart failure
1. NA & Fluid restriction (decreases hospitalization), diuretics
2. BNP (B type natriuretic peptide) with HF. Troponin for myocardial infarction
3. Inability of the heart to pump enough blood to meet the metabolic needs of the body.
The nurse has a prescription to give a client salmeterol, 2 puffs and beclomethasone dipropionate, 2 puffs, by metered-dose inhaler. The nurse would administer the medication using which procedure?
Beclomethasone first and then the salmeterol
Salmeterol first and then the beclomethasone
Alternating a single puff of each, beginning with the salmeterol
Alternating a single puff of each, beginning with the beclomethasone
Salmeterol first and then the beclomethasone
(LABA / Steroid)
1. common side effect with isotonic fluids (0.9ns)
2. common side effects with hypotonic (0.45ns)
3. common side effect with hypertonic (3% Nacl)
1. fluid overload
2. cerebral edema (fluid going into cell)
3. pulmonary edema (fluid going out of cell to extracellular)
1. what acid base abnormality do you suspect he is at risk
2. what are some symptoms.
1. metabolic acidosis (due to inability to excrete metabolites, decrease HCO3 levels
2. lethargic, confusion, weakness, kussmaul respirations, nauseated, and tingling of the skin, hypotension,
patient is admitted with AMI in the hospital, what are some medications anticipated to be given
what diagnostic testing do anticipate will be obtained
MONA
Morphine: pain, decrease anxiety / agitation
Oxygen if needed
ASA: 325mg, chew, thin blood
Nitro: dilate arteries, decrease pain
BB: decrease further ischemia
ACE: remodeling, low ef
Statin: decrease formation of plaque
testing: 12 lead EKG, continuous pulse ox, Troponin, Cath
what is expected after administration of adenosine
aystole for few seconds
After the health care provider sees a patient hospitalized with a stroke who developed a fever and adventitious lung sounds, the following orders are written. Which order should the nurse implement first?
Anterior/posterior and lateral chest x-rays
Start IV levofloxacin 500 mg every 24 hours now
Complete blood count with differential
Sputum specimen for Gram stain and culture and sensitivity
Sputum specimen for Gram stain and culture and sensitivity
Mrs. L. missed her dialysis for 2 days straight and now is having arrhythmia issues.
1. what electrolyte imbalance do you think she might be experiencing?
2. while waiting for dialysis, what else can we administer. what assessment do we need to perform before administrating
3. what are some nursing interventions
1. hyperkalemia
2. sodium polystyrene sulfonate (kayexalate- (bowel), IV insulin/bicarb/d50/calcium
3. place on cardiac monitor, frequent electrolyte monitoring
1. what acid base balance is he at risk for
2. what are some s/s to expect
1. metabolic alkalosis
2. agitation, disorientation, seizures, coma, slowing of respirations, weakness
patient called your office complaining of chest pain during mowing. she took one nitro but it is not relieved.
1. what type of angina does she have
2. what should be her next action
1. unstable angina
2. call 911 since pain not relieved after first ntg and then take another 2 ntg 5 min apart.
when would you do
1. synchronized cardioversion
2. defibrillation
1. Afib, Aflutter, SVT, Pulse VT
2. Pulseless VT, VF
what type of breathing is recommended for patients having COPD / Emphysema
purse lip breathing.