The hypocentre is also known as the....

the Focus!
True or false:
Tsunamis are a primary impact/hazard of earthquakes

False!! though it may seem like it, Tsunamis are in fact secondary impacts
What is a Dormant volcano?

A volcano that has not erupted for many years, but has potential (e.g Mt. Pinatubo erupted in 1991 after 500 years of dormancy)
What is the name of the substance that comes from the mantle and is stored in a volcano?
Magma! not Lava you idiot
At which plate boundaries do Earthquakes MOSTLYY OCCUR AT?
Hint: Friction

Destructive, Conservative and Collision!

What is Liquefaction??

Liquefaction is when soil or sand loses its stiffness and strength, in which it temporarily almost takes form of a liquid and allows things to be "swallowed" by the ground due to rapid and strong shaking of the ground.
Which types of plate boundaries do not form volcanoes?
Collision Plate boundary and Conservative Plate boundaries
What is a Lahar?

A river of mud and ash caused by rainfall
What is a seismometer?
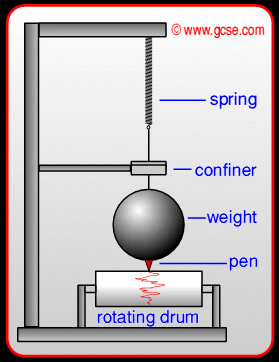
A seismometer detects vibrations caused by an earthquake. It plots these vibrations on a seismograph
Name two way we can predict an Earthquake

- use seismographs to measure increasing amount of tremors
- study previous earthquakes (similar patterns)
- strange animal behaviour (though it works, can be kinda sketchy in terms or reliability)
- Laser beams: highly accurate recording of minor movement of the earth's crust.
- Radon Gas: escapes from crust and can be measured, early sign of possible earthquake.
From which part of the volcano, does lava travel through to reach the crater?
/__opt__aboutcom__coeus__resources__content_migration__mnn__images__2017__01__hot-flowing-lava-e9cd29ef68df4f26beaf6358a8a20e5e.jpg)
The Main Vent !
In terms of time of day, how do Earthquake impacts differ?

Earthquakes at night create more hazards such as loss of vision. Earthquakes at night could also be safer as density of people outside are lower.
Name 2 ways a building can mitigate the impacts of an Earthquake on itself.

- Flexible steel frames that sway as the ground moves
- cross bracing in the framing of the building
- shutters to cover windows that may shadow
- rubberised foundation to absorb the shaking
- counter weights at the top of the building to prevent the building from toppling
- deep foundation to keep the building planted in the ground.
What type of lava does a composite volcano create?

Andesitic/Viscous Lava
Name a secondary impact of an Earthquake and elaborate why it affects the country/place in the long run.
- Debt due to high reparations
- unemployment
- contaminated water supply
- Tsunamis
What are ways to prepare and prevent for an Earthquake?

- Earthquake proof buildings
- Train population (National Earthquake Awareness Day)
- Train and organise emergency sevices
- Set up warning systems
- Have an emergency plan
Name 3 characteristics of the lava found in a shield volcano.
