TCAs function by inhibiting the reuptake of these neurotransmitters within the synaptic cleft, resulting in elevated concentrations.
Serotonin and norepinephrine.

TCA use has been demonstrated to heighten the risk of this, particularly in individuals aged 24 or younger.
suicidal ideation or behavior
TCAs should not be prescribed to individuals with a family history of this heart disorder or sudden cardiac death.
QTc interval prolongation

According to national mortality data from the NHS between 1975 and 1984, TCAs exhibited higher rates of death per 1 million prescriptions than other antidepressants, primarily attributed to elevated rates of suicide resulting from deliberate overdose. Due to their narrow this index, TCAs are prone to induce toxicity in the event of accidental or intentional overdose.
Therapeutic
TCAs act as competitive antagonists on postsynaptic Cholinergic (alpha-1 and alpha-2) and these two other receptors (name one).
muscarinic and histamine.
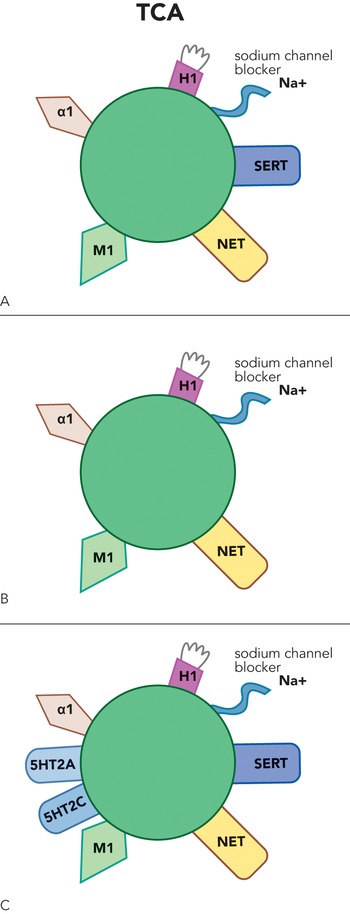
TCA-induced blockade of these receptors may lead to sedation, increased appetite, weight gain, and confusion in patients.
Histamine (H1).

TCAs should not be administered concurrently with this drug, due to the risk of developing serotonin syndrome.
monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
Patients with serotonin syndrome present with dilated pupils, hyperreflexia, myoclonus, diarrhea, tremors, and confusion. The treatment approaches for serotonin syndrome encompass cooling, discontinuation of serotonergic drugs, and the use of this drug.
Cyproheptadine.

The chemical structure of a TCA comprises a 3-ringed arrangement with an attached secondary or tertiary this chemical group. Hint: think of some of the names of TCAs.
Amines.
As per a meta-analysis from 1998,
the blockade of these receptors by TCAs can induce orthostatic hypotension and dizziness.
Alpha-1 adrenergic.

As per 1987 recommendations published in Psychosomatics,
The utilization of TCAs necessitates caution in individuals with this condition, as the drug's anticholinergic effects could potentially heighten the risk of an acute ocular crisis.
angle-closure glaucoma

As per a 10-year review published in 1980, signs and symptoms of TCA overdose include ECG abnormalities such as QTc prolongation and widened QRS complex, hypotension, seizures, tremors, coma, xerostomia, urinary retention, and respiratory depression. In a 1986 article on TCAs in Medical Toxicology, TCAs' most frequent causes of death are generally attributed to...(name 1 of 2).
hypotension or arrhythmias.