Experimenting over and over with the idea...
….WHAT IS: "that I can control this"
If this part of the brain, involved in emotional processing and response, is damaged by drug use, it can become hyperactive, leading to increased anxiety and stress responses- the typical fight, flight, freeze response
What is the Amygdala?
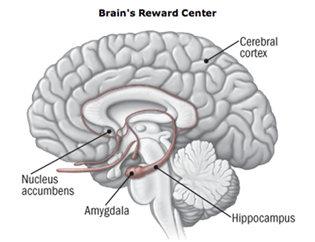
What happens in the brain that makes addiction so powerful?
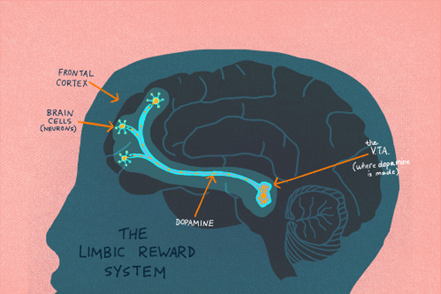
Drugs overstimulate the production of dopamine to unnatural levels, motivating an individual to use drugs again.
This kind of withdrawal typically involves more of the psychological and emotional aspects of withdrawal.
What is PAWS?
When a substance use addiction is often associated with mental health conditions such as depression anxiety mood disturbances trauma etc - this is known as what?
What is Co occurring disorder?
Trying to convince myself that I can …..….
WHAT IS: " I can stop anytime I want to”
If this part of the brain is damaged by addiction, memory and learning is reduced, leading to difficulties in forming new memories and recalling information.
What is The hippocampus?
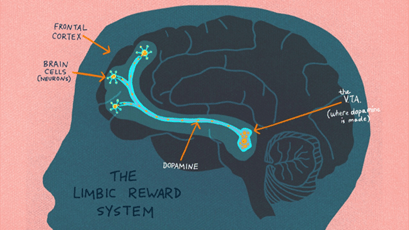
How does the brain's reward system contribute to the cycle of addiction?
Drugs target the brain’s reward system (often fueled by the natural brain chemical: dopamine) thus making people feel pleasure, relaxation, euphoria or other “good” feelings; making us want to repeat things that increase dopamine levels
Paws is especially true for what substance use disorder which is known for extremely unpleasant withdrawal symptoms as well as both physical and psychological cravings persisting for long periods after the drug use has stopped
What are Opiod Use Disorders?
Feelings of pleasure associated with substance use disorders are extremely powerful. What's the symptom is the person in recovery likely to experience?
What is Anhedonia?
“This couldn't happen to me because…. “
WHAT IS: " I'm too smart”
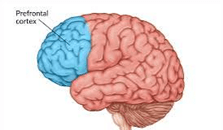
Located in the prefrontal cortex, if this part of the brain is damaged, decision-making, impulse control, and self-regulation are diminished
What is the Gray Matter part of the brain?
What are some physical changes that occur in the brain due to substance use?
Reduced Gray Matter: decision-making, impulse control, and self-regulation
Hippocampal Changes: This may lead to difficulties in forming new memories and recalling information
Amygdala Changes: leading to increased anxiety and stress responses, particularly during withdrawal or cravings
Cortical Thinning: cognitive deficits and an increased risk of mental health disorders.
what is neuroplasticity in the brain?
This is the brains incredible ability to reorganize itself. Even after prolonged substance use the brain can form new pathways and connections that help in recovery
our brains account for Approximately what percentage of our metabolism?
What is 25%
Convincing myself that “I just use drugs to have …..….
WHAT IS: " a good time and feel good and that's it”
Chronic exposure to addictive substances can lead to changes in this brain circuitry, making natural rewards (like food, social interactions, and pleasurable activities) less satisfying and reinforcing the cycle of addiction.
What are the Reward Pathways?
Substance use can affect the part of the brain that connects different brain regions, impacting communication between them.
What is Altered White Matter Integrity?
Why is the first year of recovery so challenging for people in Recovery?
What is : Some cognitive functions may begin to improve within weeks of sobriety - while others especially those involving impulse impulse control and decision making may take months or even years to cover.
This therapy is like a special tool that helps people think about their feelings and actions. It helps you build a better way to think when you feel sad or scared and teaches you to notice when you're having bad thoughts. Then it helps you change those thoughts so you can feel better and do better things
What is cognitive behavior therapy or CBT?
Thinking “ I only use because I want to”, when the evidence shows….….
WHAT IS: " it has just progressed to where you need to use
Changes in this part of the brain can impair executive functions, such as planning, decision-making, and impulse control, making it more challenging to resist urges and make healthy choices.
What is the prefrontal cortex?
What is Altered White Matter Integrity?
Injured pathways that connect different brain regions, impacting communication between them and potentially leading to cognitive deficits.
Have you ever heard of "Cortical Thinning"?
Cortical thinning refers to a decrease in the thickness of the cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the brain responsible for higher-order functions such as cognition, perception, and behavior. Some studies suggest that prolonged substance use can lead to cortical thinning, which may be linked to cognitive deficits and an increased risk of mental health disorders.
BONUS: What is your counselor's middle name?
Gregory Allan Pious X Barnier