Skipping over heavily fortified islands and focusing on strategic locations
Island-hopping or leapfrogging
This long battle was a turning point on the Eastern front
Battle of Stalinngrad
May 8, 1945
V-E Day
The countries in green on this map represent this group.
Allies
The strategy of appeasement was used to attempt to prevent war with this country.
Germany
U.S. President who made the decision to use the atomic bomb
Harry Truman
Germany used this tactic to take over Western Europe.
Blitzkrieg
This Allied victory was a turning point in North Africa.
Battle of El Alamein
August 15, 1945
V-J Day
This map represents this battle strategy.
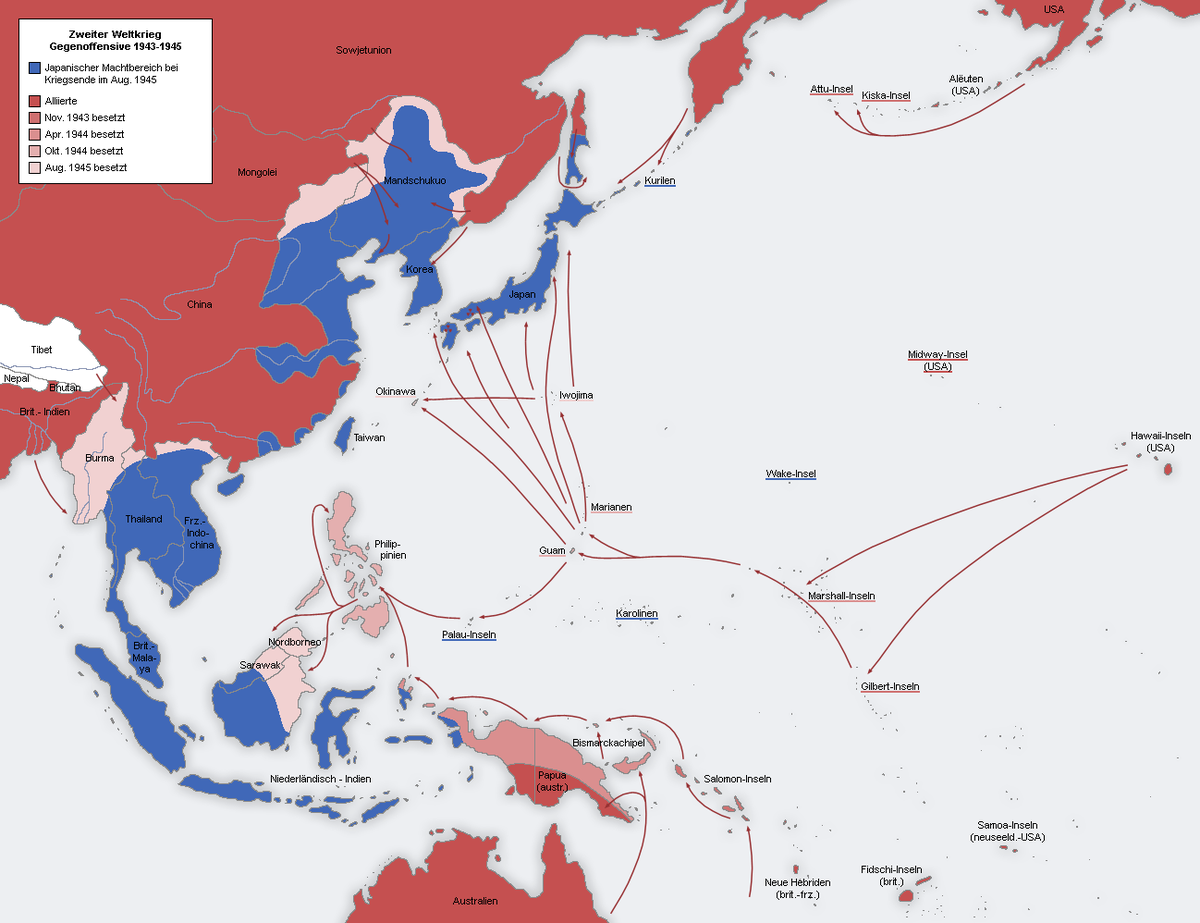
Island-hopping (or leapfrogging)
Hitler repeatedly broke this treaty in the years before WWII.
Treaty of Versailles
The capital of Germany, where Hitler died by suicide on April 30, 1945
Berlin
Germany and Finland used this tactic against Leningrad
Blockade or seige
The Luftwaffe and RAF fought in this battle
Battle of Britain
June 6, 1944
D-Day
This map shows this empire at its largest in 1942.
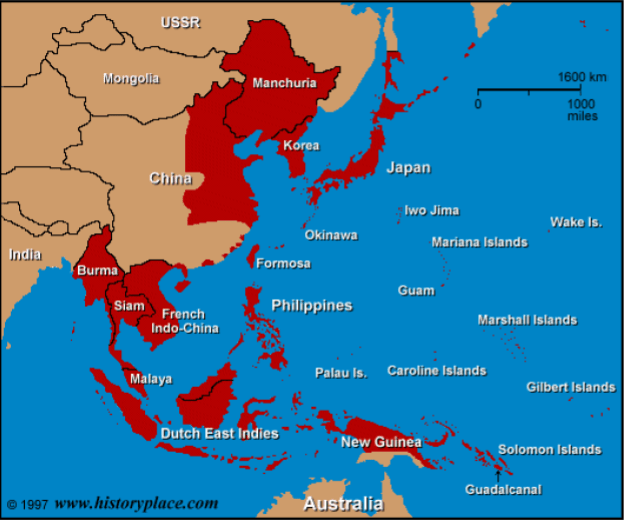
Japanese Empire
Agreement that gave the Sudetenland to Hitler
Munich Agreement
This was the code name for the project to develop the atomic bomb
Germany targeted civilians in this bombing campaign
The Blitz
This battle on the Western Front in June 1940 led to a quick surrender
Battle of France
December 7, 1941
This map represents the plan for this operation carried out by Germany.
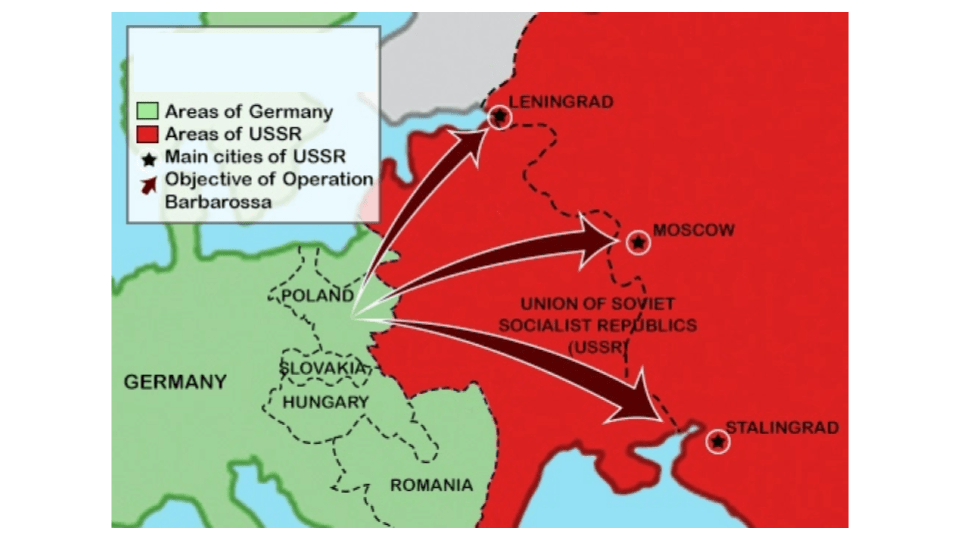
Operation Barbarossa
"Anschluss" was the term for this country reuniting with Germany.
Austria
American, British, and Canadian troops landed here on D-Day
Normandy
Hitler planned to weaken this nation's air defenses before invading
Britain
This June 1942 battle was a turning point in the Pacific
Battle of Midway
July 16, 1945
First successful test of the atomic bomb
The line on this map represents this.
Maginot Line
Hitler took this region of Czechoslovakia in September 1938
Sudetenland
These two battles proved to America how deadly it would be to invade Japan.
Iwo Jima and Okinawa