The U.S. policy of staying out of European conflicts before WWII.
isolationism
A U.S. ban on oil exports to Japan.
Trade Embargo
The battle that marked a turning point in the Pacific in 1942.
The secret U.S. program to build the atomic bomb
Manhattan Project
African American pilots who served with distinction during WWII.
Tuskegee Airmen
Mandatory military service
The draft
The president who gave the Four Freedoms Speech.
Franklin D Roosevelt
The Japanese attack on Hawaii on December 7, 1941.
Pearl Harbor
The battle where U.S. Marines captured critical airfields near Japan. This iconic photo was taken at this battle:

Battle of Iwo Jima
The first nuclear weapon test in July 1945.
Trinity Test
The movement of African Americans from the South to Northern cities for war jobs
Great Migration
The first peacetime draft in U.S. history
Selective Service and Training Act
Laws passed in the 1930s to limit U.S. involvement in foreign conflicts
Neutrality Acts
The Axis nation that declared war on the U.S. four days after Pearl Harbor.
Germany
The largest Pacific battle that resulted in nearly 50,000 U.S. casualties and influenced the decision to use atomic weapons.
Battle of Okinawa
The president who ordered the use of atomic bombs.
Harry S Truman
A campaign calling for victory against fascism abroad and racism at home.
Double V Campaign
Food grown at home to support the war effort.
Victory Gardens
The 1919 treaty that punished Germany heavily and helped set the stage for WWII
Treaty of Versailles
Japanese suicide pilots.
Kamikaze pilots
The Allied invasion of France on June 6, 1944
D-Day (Normandy)
The secret laboratory in New Mexico where the bomb was developed.
Los Alamos
A program that allowed Mexican workers to temporarily work in the U.S.
Bracero Program
The symbol representing women working factory jobs during WWII.
Rosie the Riveter
A policy allowing countries at war to buy non-military goods if they paid cash and transported them themselves.
Cash and Carry Policy
Experts who decoded Japanese military messages.
Cryptographers
The military code name for D-Day.
Operation Overlord
The scientist who directed Los Alamos and helped build the atomic bomb.
J Robert Oppenheimer
Native American Marines who created an unbreakable military code.
Navajo Code Talkers
Certificates sold to Americans to help fund the war
War bonds
A law allowing the U.S. to sell or lend weapons to nations important to U.S. security
Lend-Lease Act
the U.S. destroyed 3 of these large naval ships at Midway.
Aircraft Carriers
Hitler’s final major offensive during WWII.
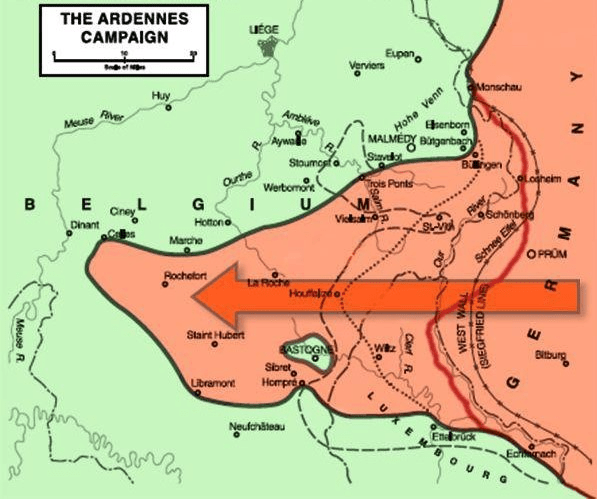
Battle of the Bulge
The plane that dropped the bomb on Hiroshima
Enola Gay
The forced removal and imprisonment of Japanese Americans during WWII.
Japanese American Internment
Limiting consumer access to goods during WWII
Rationing