Prevention
care
Large, shallow wounds with irregular margins that typically develop on the lower leg or ankle
What is Venous Stasis Ulcer
Erythema, non-blanchable to touch. Reversible if pressure is relieved by frequent turning, positioning and pressure relieving devices.
What is a stage I pressure injury?
This factor causes skin elasticity to decrease, which correlates with longer healing times. This factor cannot be changed or improved.
What is age?

What is tunnelling
Name two types of debridement
What is surgical debridement, biological debridement, enzymatic debridement, and autolytic debridement.
The most important treatment to heal a pressure injury?
What is relieve the pressure?
Leaving the wound to heal naturally
What is secondary intention
A dry wound typically located on the plantar foot or toes that is surrounded by hyperkeratotic tissue (callus)
What is a neuropathic (diabetic) foot ulcer
Appears shallow crater/blister with red/ pink wound bed. No slough. Or an intact or open/ruptured serum-filled blister.
What is a stage II pressure injury?
Patients with poor mobility should be turned and repositioned this frequently (What do we do at MECC?)
What is at least every 3 hours?
Abnormal passage/opening from one organ to vessel/organ
What is a fistula
Debridement by using a wet to dry dressing
What is mechanical debridement?
Adhesive, semi-permeable, non-absorbent dressing that allows exchange of oxygen.
What is a transparent film?
Healing by delayed primary closure, occurs when there is a need to delay the wound-closing process
What is tertiary intention
Wound with deep round/punched out, dry appearance and sharply demarcated borders and usually painless
What is an arterial ulcer
Full thickness tissue loss in which the base of the ulcer is covered by slough or eschar in the wound bed.
What is an unstageable pressure injury?
Use this to offset pressure over bony prominences
What are pillows or wedges?
Black or brown nonviable tissue that is not a scab
What is an eschar?
Debriding by using a hydrocolloid
What is autolytic debridement?
Home care does not see patients daily or twice a day. Their job is to
What is teach patients/caregivers wound care.
Healing that occurs when a clean laceration or a surgical incision is closed primarily with sutures, Steri-Strips, or skin adhesive
What is primary intention
These type of wounds have 6 stages according to the latest guidelines
What are pressure injuries
Full thickness tissue loss. No bone, tendon, or muscle exposed.
What is a stage III pressure injury?
This can be used for stage I pressure injuries
White soft tissue in periwound area
What is maceration
Santyl is an example of this type of debridement
Gold standard treatment for skin tears
What is Tegaderm?
Happens when a wound has a great deal of lost tissue, or is extensive and the edges can't be brought together
What is secondary intention
A partial or full thickness wound in which a flap may or may not be present
What is a skin tear
Full thickness tissue loss with exposed bone, tendon or muscle. Months or years may be needed for healing.
What is a stage IV pressure injury?
Using this tool will help identify high risk for pressure injury patient.
What is the Braden Scale?
Tissue recedes beneath the skin, creating shelf of skin or free edge with space underneath
What is undermining
Honey uses this type of debridement
What is autolytic debridement
Wounds are cleansed with this solution
What is normal saline or wound cleanser?
The wound may need to drain or antibiotics may need to kick in before the wound is closed
What is tertiary intention
A combination of friction and pressure causes this
What is shearing force?
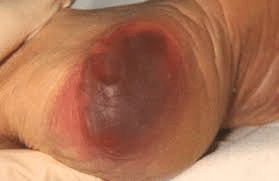
What is Deep Tissue Injury
List at least 3 factors of wound healing:
What are age, nutrition, medications, malnourished, tissue perfusion, obesity, chronic diseases, smoking
Beefy, bumpy red in color tissue in a wound
What is granulation tissue
This type of debridement you can do in the office for neuropathic ulcers
What is sharp debridement
Nonadherent dressings that conform to the wound shape and absorb exudate. Provides moist wound bed, Packs wounds, supports debridement
What are alginates
What diet and vitamins promote wound healing?
High Calorie/ High Protein Diet
Vitamin C and Zinc