Self regulation is being able to control your...
Emotions
All or nothing thinking
This is when we only look at situations in terms of extremes. Things are either all good or all bad.
Mental filtering
This happens when we only pay attention to the bad things that happen, but ignore all the good things. This prevents us from looking at all aspects of a situation and drawing a more balanced conclusion.
Thoughts on trial
CBT activity focused on the examination of irrational thoughts. You act as a defense attorney, prosecutor, and judge, as you compare evidence for and against a single thought. Like in a real court of law, only verifiable facts are admissible as evidence. Opinions, assumptions, and conjecture are not allowed.
To manage stress and anxiety, you should focus on all the things you can and cannot control.
True or False
False
Focusing on only the things you can control will help you better manage your stress.
Where can mindfulness be practiced?
Anywhere!
Mind reading
Assuming you know what others are thinking about you
Overgeneralization
Overgeneralization thinking occurs when a person focuses on a single event that occurred and they incorrectly conclude all similar events going forward will result in the same failure or negative experience.
Reframing
Technique that helps you challenge and modify irrational thoughts (i.e. cognitive distortions) to shift your mindset so you're able to look at a situation from a different perspective.
All stress is bad stress.
True or False
False
While chronic or excessive stress can be harmful, some stress ("eustress") can be beneficial. It can motivate you to achieve goals, improve performance, and even enhance your immune system in the short term.
When can mindfulness be practiced?
Anytime!
Catastrophizing
Assuming you know for sure that the outcome of an event is going to be bad
Blaming
Blaming others for your problems rather than taking responsibility.
Worry Tree
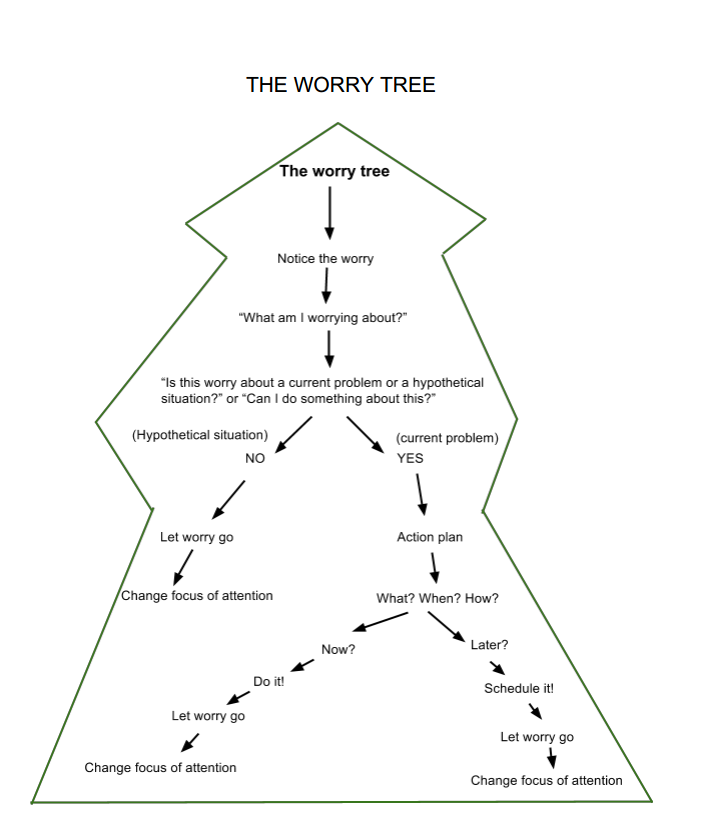 CBT technique that helps people manage their anxiety by visually organizing their worries and developing coping strategies. It involves categorizing worries into those that can be controlled and those that cannot, then creating action plans for the controllable ones and acceptance strategies for the uncontrollable ones.
CBT technique that helps people manage their anxiety by visually organizing their worries and developing coping strategies. It involves categorizing worries into those that can be controlled and those that cannot, then creating action plans for the controllable ones and acceptance strategies for the uncontrollable ones.
The Cognitive Triangle consists of thoughts, goals, and behaviors.
True or False
False
The Cognitive Triangle consists of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
What are some benefits of mindfulness?
Reduced stress
Improved focus
Improved coping
Better relationships
Increased creativity
And many more!
Emotional reasoning
You ignore the actual facts and perceive a situation based on how you feel even when there is no evidence to support this connection
Personilzation
Taking things personally and blaming yourself for things that are not your fault or out of your control.
Worst Case Scenario Planning
Deliberately imagining the most negative possible outcome in a situation to identify potential risks and develop contingency plans, but with a focus on managing anxiety by acknowledging the low probability of the worst scenario occurring.
With mindfulness a person can use all 5 of their senses to be in the moment and stay calm.
True or False
True
The practice of bringing intentional awareness to the present moment.
What is mindfulness?
Fortune telling
When we predict that things will turn out badly. But, in reality, we cannot predict the future because we don’t have a crystal ball!
Labeling
Applying a negative label to oneself or others based on a single event or behavior.
Example: You do poorly on a test and think "I'm a failure".
Decatastrophizing
CBT technique where you actively challenge and reframe extreme, catastrophic thoughts by evaluating the actual likelihood of worst-case scenarios, essentially "de-catastrophizing" your thinking by considering more realistic outcomes.
Mindfulness is easy and you should be able to do it right away.
True or False
False. Mindfulness takes practice.