After World War I, totalitarian dictatorships were established in 3 countries under 3 men: (Name 2 of the 3)
1) The Soviet Union under Joseph Stalin.
2) Italy under Benito Mussolini.
3) Germany under Adolf Hitler.
This event started WWII. This country was quickly defeated by Germany because they lacked natural boundaries (i.e.- it has very flat plains that were easy to conquer).
:quality(70)/arc-anglerfish-arc2-prod-mco.s3.amazonaws.com/public/SQQPYPO7MJADZC5MCFIK5BFWF4.jpg)
Invasion of Poland
was a 50 year struggle between the United States (a democratic nation) and the Soviet Union (a communist nation) after World War II
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/58856815/184282094.0.jpg)
The Cold War
U. S, Britain, and France flew in supplies to the people of West Berlin after Stalin set up a blockade.
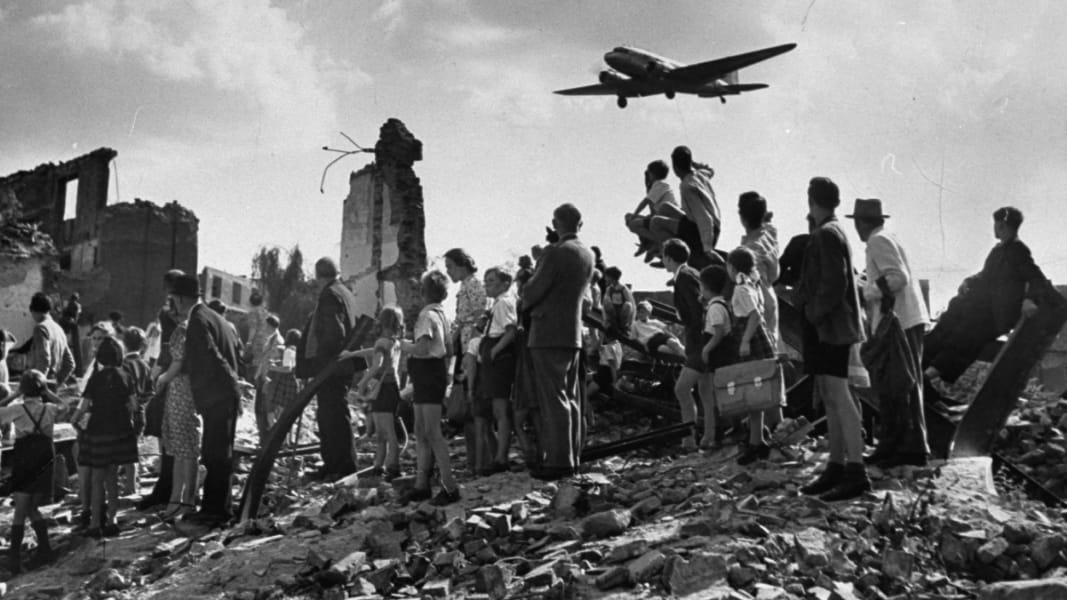

Berlin Airlift
was an event where the people of Russia overthrew their Czar (king) and created a new government.

The Russian Revolution
He was the first Communist dictator of China.

Mao Zedong
This was the event during World War II in which Hitler and the Nazis tried to kill all Jews in Europe. 6 million Jews and 6 million non-Jews were killed during this event.
The Holocaust
governments where one ruler has complete control over ALL aspects of life within a country. They control the political, social, and economic features of a nation.

Totalitarian governments
Japan launched a surprise attack against the United States. This event brought us (The United States) into World War II.

Pearl Harbor
This was a term used by Winston Churchill to describe the imaginary line dividing the democratic countries of Western Europe from the communist countries of Eastern Europe.

Iron Curtain
This was a military alliance between the United States, Canada, and the democratic nations of Western Europe. The nations of this alliance agreed than an attack on one nation in the alliance was considered to be an attack on all of the nations of the alliance
NATO
Lenin and the Bolsheviks gained the support of the Russian people by promising to provide them with “____, _____, and ______.” This slogan meant that they would take Russia out of WWI, give land to peasants, and feed everyone.
Peace, Land, and Bread
He was the ruler in China after Mao Zedong. Changed the economy of China from a command/communist economy (in which the government owns businesses) to a market/capitalist/free enterprise economy (in which individuals own businesses).
Deng Xiaoping
This U.S president (1981-1989) adopted a more aggressive stance against communism. Preferred Confrontation over Containment.

Ronald Reagan
Stalin tried to modernize (update) the industry (factories) and agriculture (farms) of the Soviet Union by setting economic goals every five years what was this program called
5 year plans
This was the beginning of the final Allied push against Germany. It resulted in the eventual defeat of Germany
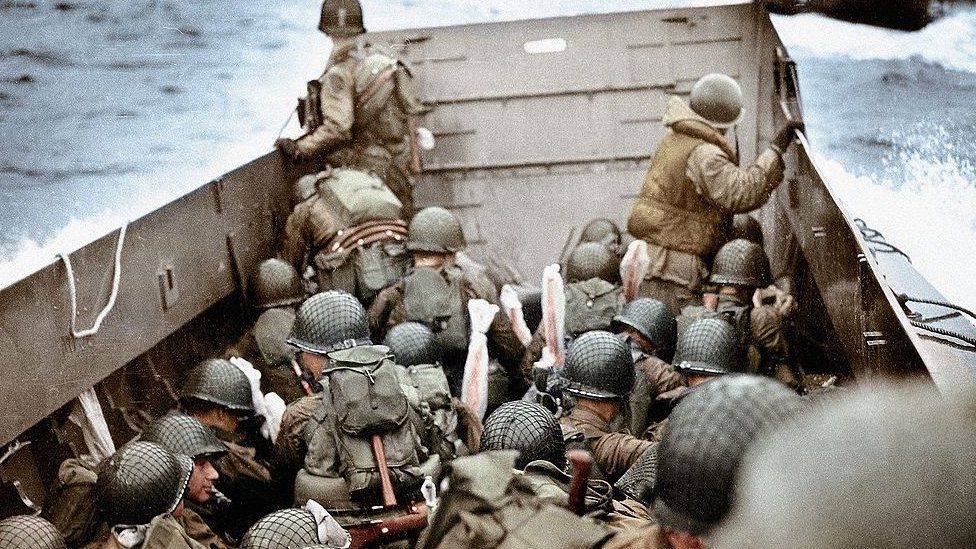

D-Day Invasion
This was the policy used by the United States in which it attempted to stop the spread of communism

Containment
A period of peace / reduced tensions between two groups that were previously at war, or hostile to each other (Between 1969 and 1979)
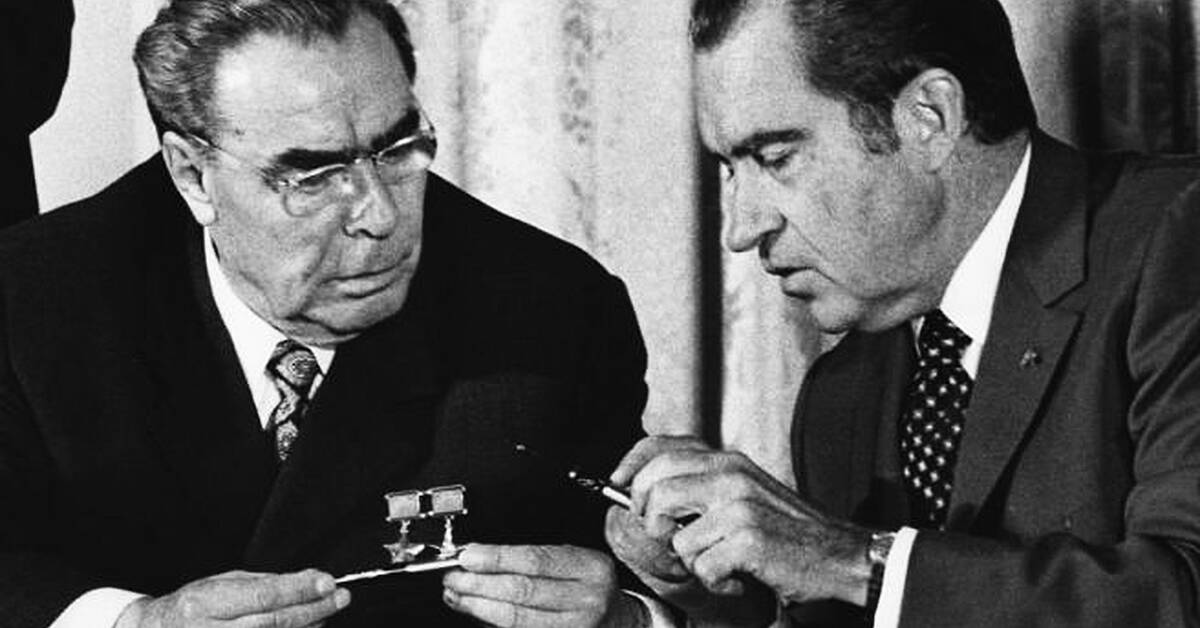

Detente
He was the ruler of Russia at the time. People thought that he abused his power by denying (taking away) the rights of the people.
Czar Nicholas II
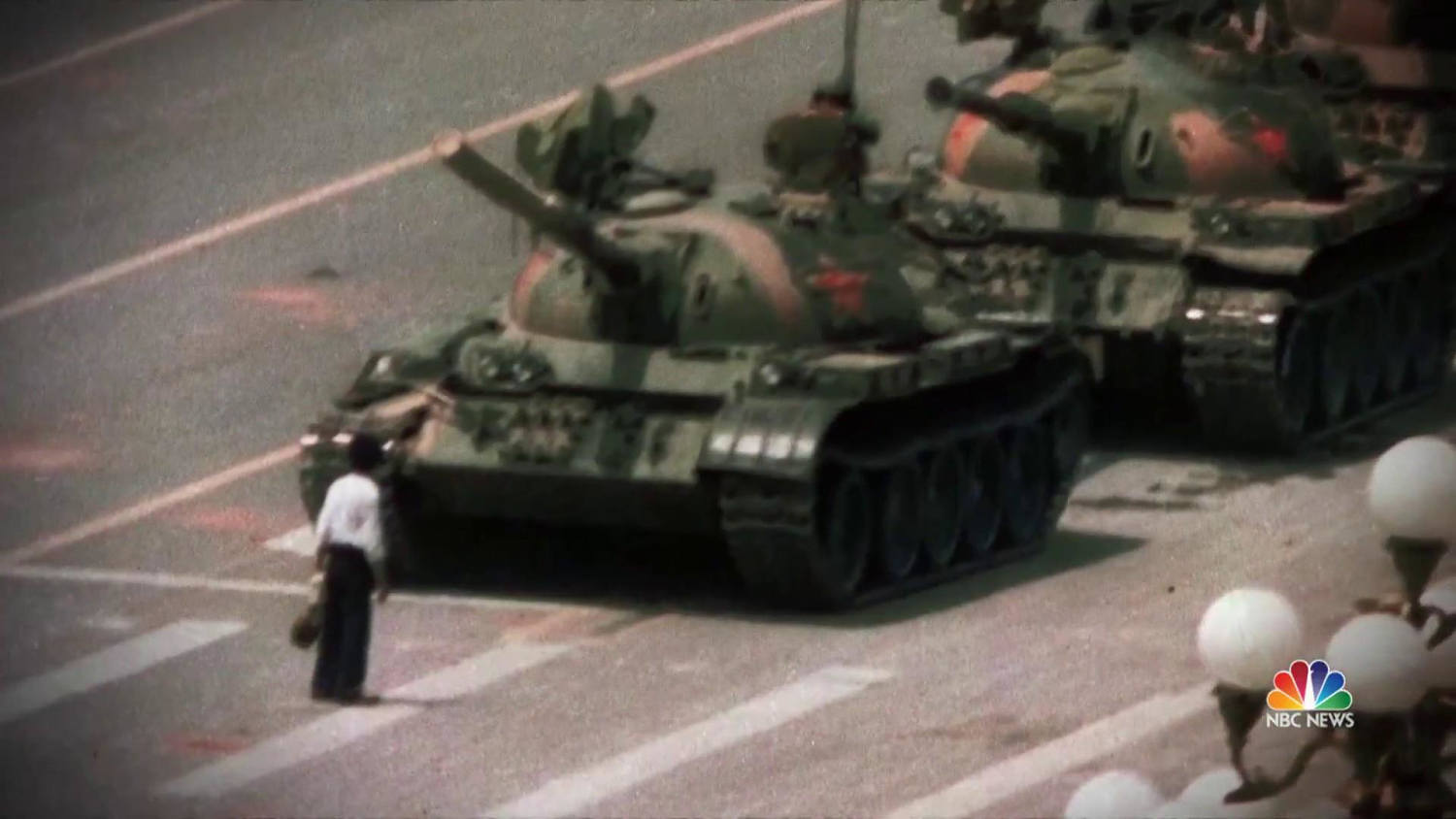
Protests where the Chinese peacefully demanded democratic reforms (changes)- They wanted more rights and a say in government.
b) Deng Xiaoping called in the army
c) This proved that China’s government was not willing to make democratic changes.
Tiananmen Square

a) This was a program in which Gorbachev allowed freedom of speech within the Soviet Union.
b) It was a major step towards democracy in the Soviet Union.

Glasnost
Stalin took over the individual farms that people owned and forced people to live on large government farms (called collective farms) that were owned by the government
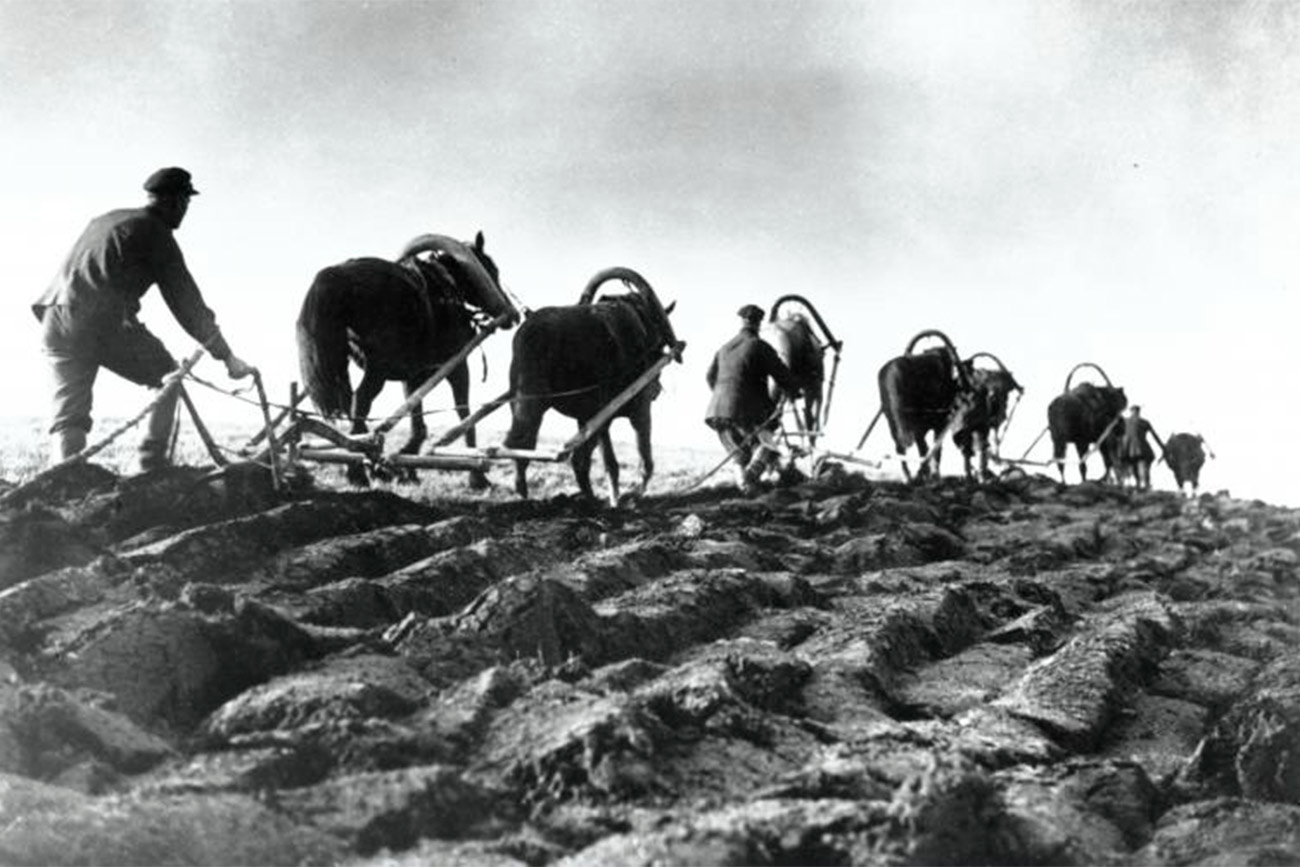

Collectivization
the organization that was created after World War II in order to solve international problems (like poverty and disease) and prevent future wars.

United Nations
What was the Cuban Missile Crisis (1962)?
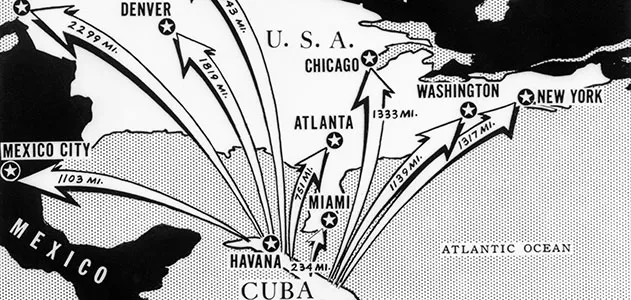
a) Began when the United States discovered that the Soviet Union was building missile bases in Cuba (a new Communist nation) and pointing nuclear missiles at the United States.
b) The crisis ended when the Soviet Union agreed to remove the missiles.
c) This event is the closest the world has ever come to nuclear war between countries.
The United States and Soviet Union competed to build up the largest supply of nuclear weapons.
Arms Race
This was the radical (extreme) group that was leading the Russian Revolution. The leader of the Bolsheviks was a man named Vladimir Lenin.
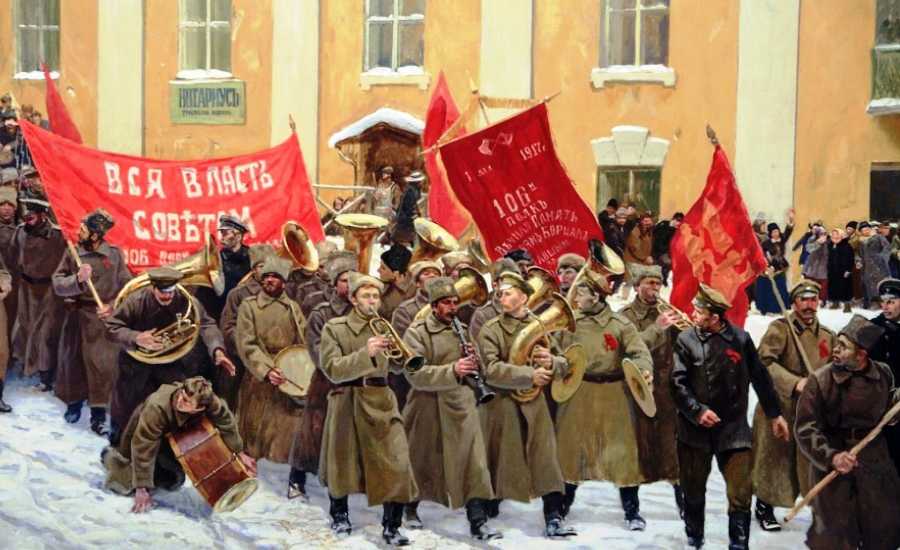

The Bolsheviks
This was the attempt by Mao to modernize (update) the industrial (factory) and agricultural (farm) production of China.
b) Peasants in China were forced to move onto large government farms.
c) NOTE: This program was very similar to the Five Year Plans and Collectivization that took place in the Soviet Union under Joseph Stalin.
The Great Leap Forward
This was a program in which Gorbachev changed the economy of the Soviet Union from a communist/command economy (where the government owns and operates businesses) to a market/capitalist/free enterprise economy (where individuals own and operate businesses.
Perestroika
This is a policy where an aggressive nation is given what they want by other nations in order to avoid war. At the Munich Conference in Germany, Great Britain appeased Hitler by giving him control over Czechoslovakia. This led Hitler to demand even more land
Appeasement
This was a document created by the United Nations that lists the rights that ALL people should have within their nations. This includes the right to freedom of speech, the right to life, and the right to participate in government.
Declaration of Human Rights
This 1972 treaty between The United States imposed limits on the nuclear capability of Russia & USA
SALT Treaty
Varies
Identify 3 main causes of the Russian Revolution

Weak leadership (Czar Nicholas II)
World War 1
Industrialization (workers strikes)
Famine
Lost to Japan in Russo-Japanese War 1905
This was a period in China where Mao used violent young Communist soldiers (known as Red Guards) to eliminate all of the opposition (enemies) that he had within China.

The Cultural Revolution
The eighth and last leader of the Soviet Union, General Secretary of Communist Party from 1985 until 1991. Introduced concepts of Glasnost and Perestroika

Mikhail Gorbachev