What is the function of cartilage?
To prevent friction in movement.
_______ has a flattened, broad surface.
Flat bone
Freely moveable joints are known as
Synovial Joints
The inner lining of a joint capsule
synovial membrane
Carpals are
short bones in the wrist
Examples of _______ bones are the vertebrae.
Irregular bones
Mention one main function of the skeleton.
Structure for your body - gives us shape!
Protection of organs
Allows movement
Makes blood cells
Stores minerals
What type of joint are the shoulder and hip
Ball and socket
Ligaments
join bone to bone and prevent unwanted movement
What type of bone is the sternum and ribs
flat
What covers bone?
Periosteum
______ spine supports the head and protects the spinal cord.
Cervical spine
An example of a pivot joint is found
C1 and C2 or between radius and ulna
Synovial fluid nourishes the cartilage T/F
T
What classification of bone are the meta-tarsals
long
Where do you find yellow bone marrow?
In the medulla (shaft) of long bones.
What is the name of this bone?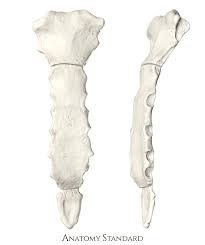
Flat bone (sternum)
What type of joint is the knee
hinge
All synovial joints have synovial fluid in them?
True
Long bones act as _______ to enable movement
levers
A bone cell is called an?
Osteocyte (or osteoblast).
What do you find in the gaps in spongy bone?
Red marrow
The knuckle (metacarpo-phalangeal) joint is a
condyloid
What 3 movements does a ball and socket enable?
Flexion/Ext
Adduction/abduction
Rotation
The process by which bones are continually broken down and remade
Remodelling