What is photosynthesis? How is it part of the carbon cycle?
Process where green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize nutrients from carbon dioxide and water.
CO2 removed from the atmosphere by plants.
List 3 greenhouse gases
Any of the following:
carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapour (H2O), methane (CH4), nitrous oxides (NOx)
True or false: Saltier, cold water floats as it is less dense.
FALSE
Define the word: Biosphere
zone that encompasses all living organisms on the planet.
Apart from Carbon, list two other elements/compounds that are naturally cycled on Earth.
Any 2: Water, phosphorus, nitrogen
What is fossilisation? And how is it part of the carbon cycle?
Process in which an organism becomes a fossil (instead of decaying). If allowed to be compressed/built up can lead to carbon being stored as fossil fuels (coal, oil).
Provide a reason why the natural greenhouse effect is important.
Keeps Earth at a liveable temperature.
What is a "gyre"?
- Any large system of ocean surface currents moving in a circular fashion driven by wind movements.
- Effects the movement of surface currents
Define the word: lithosphere
upper layer mantle and the crust and includes all geological features on the surface of the planet.
List two ways that climate change has led to rising sea levels.
Melting of icecaps
Thermal expansion of seawater
What is combustion? How is it part of the carbon cycle?
Chem. reaction that involves oxygen and releases light and heat energy. Burning of fossil fuels which releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
List two sources of anthropogenic greenhouse gases.
Sources of anthropogenic greenhouse gases: coal, oil, gas, agriculture (e.g. farming of livestock),
What is the "thermohaline" circulation?
- Movement of ocean currents due to differences in temperature (thermo) and salinity (haline) in different regions of water.
- Colder/Saltier: More dense (sinks)
- Effects the movement of deep currents
Define the word: anthropogenic
Originating in human activities.
List the 4 Earth's spheres
biosphere, atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere
What is a carbon sink, and give 3 examples in nature?
- (AKA Carbon reservoir) Any feature of the environment that absorbs/stores carbon, and therefore keeping it out of the atmosphere. Examples e.g.: Limestone, forests, oceans, fossil fuels
Explain the natural greenhouse effect

Why is the movement of ocean currents important?
helps regulate Earth's temperature
Define the word: "Global warming"
Increase in the Earth's temperature due to the presence of certain human-made gases.
What is the difference between weather and climate?
- Climate: Weather conditions at a particular place over a long period of time based on the collection and analysis of large amounts of data.
- Weather: A snapshot of what the air and conditions are like in any one place on the Earth at any one time.
Draw the carbon cycle

Could be different
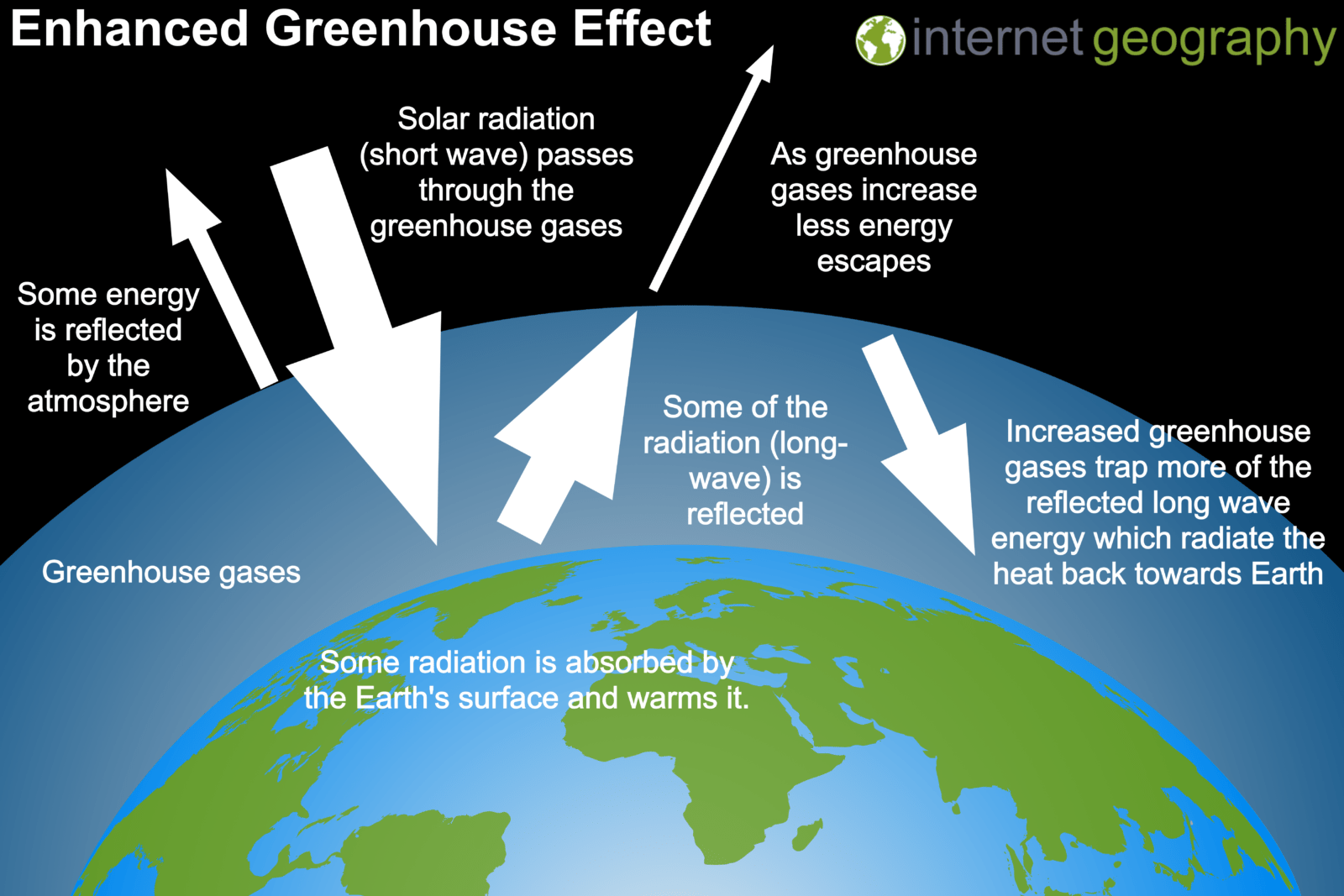
Explain the enhanced greenhouse effect.
Explain how ocean currents circulate heat around the world.
(Other answers could be accepted)
1. Warm, fast currents along the western edges of ocean basins move heat from the equator toward the North and South Poles.
2. Differences in density drive slow-moving ocean currents in the deep ocean.
3. When sea ice forms, it freezes the surface water leaving behind salt, which makes the remaining seawater saltier. Once this colder, saltier water becomes dense enough, it sinks to the deep ocean.
4. Warmer, less dense water from the Gulf Stream rushes in to replace the water that sinks. This motion helps power a global “conveyor belt” of ocean currents – known as thermohaline circulation – that moves heat around Earth.
Define the word: "albedo"
A measure of how much incoming radiation a surface reflects. Albedo ranges from 0 to 1.
List three extreme weather events (worsening due to climate change)
Any 3: Droughts, wildfires, tropical cyclones, floods, heavy precipitation, marine heat waves, heat extremes.