Identify one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
- Size
- Membrane bound organelles
- Nucleus
Name the organelle that is a selectively permeable barrier that controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
Cell membrane
Name one structure of a capillary that makes it suitable for its function.
One cell thick, thin flat cells
Which enzyme breaks down lipids?
Lipase
Total number of ATP produced?
38
Identify one similarity between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Genetic material
What part of the phospholipid is hydrophobic?
Tails
Name one structural element of the small intestine that is suitable for its function.
- long and coiled
- villi
- large surface area: volume ratio
Where are Protease enzymes synthesised?
Pancreas
Where does glycolysis occur?
Cytoplasm of Mitochondria
Identify the organelle in the electron micrograph 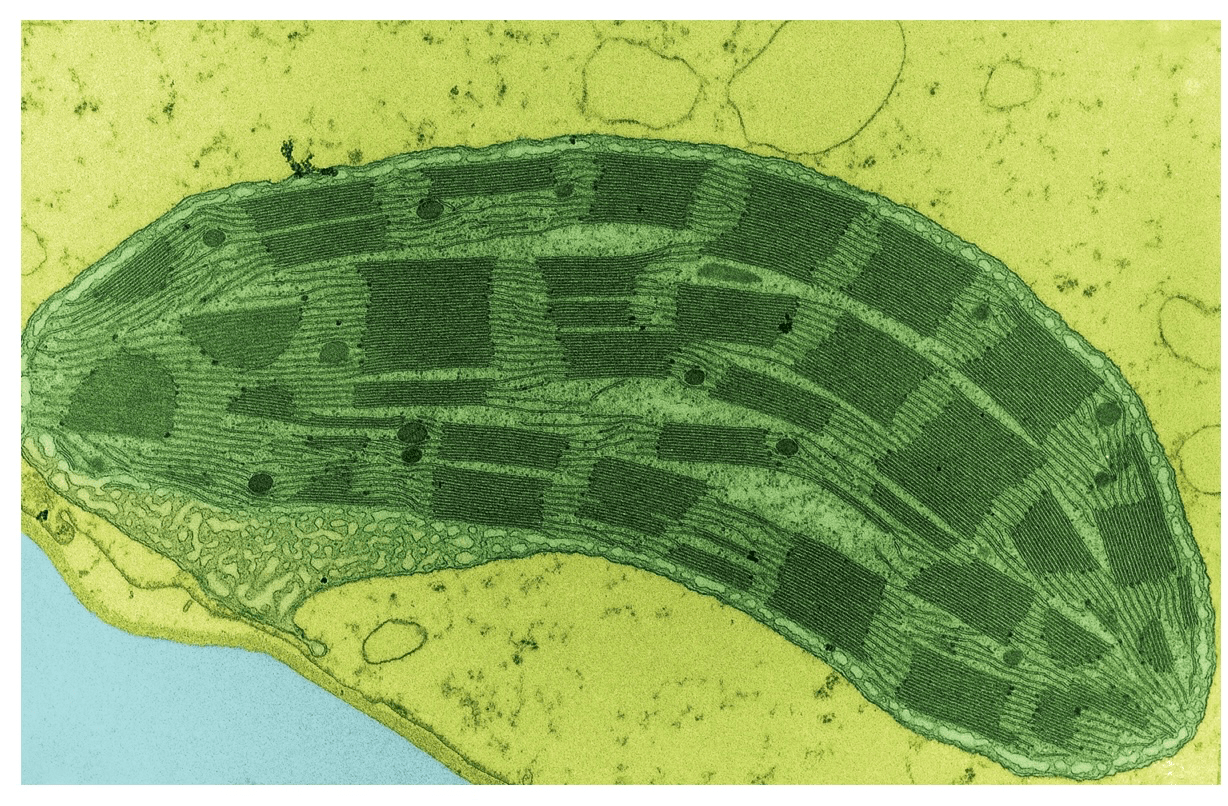
Chloroplast
The process by which molecules, or ions of liquids or gases, tend to spread out from different from regions of higher concentrations to regions of lower concentration
Diffusion
Blood vessels that carry blood away from the pumping heart.
Arteries
Where do enzymes bind to the substrate?
Active Site
carbon dioxide and water.
Identify the organelle in the electron micrograph 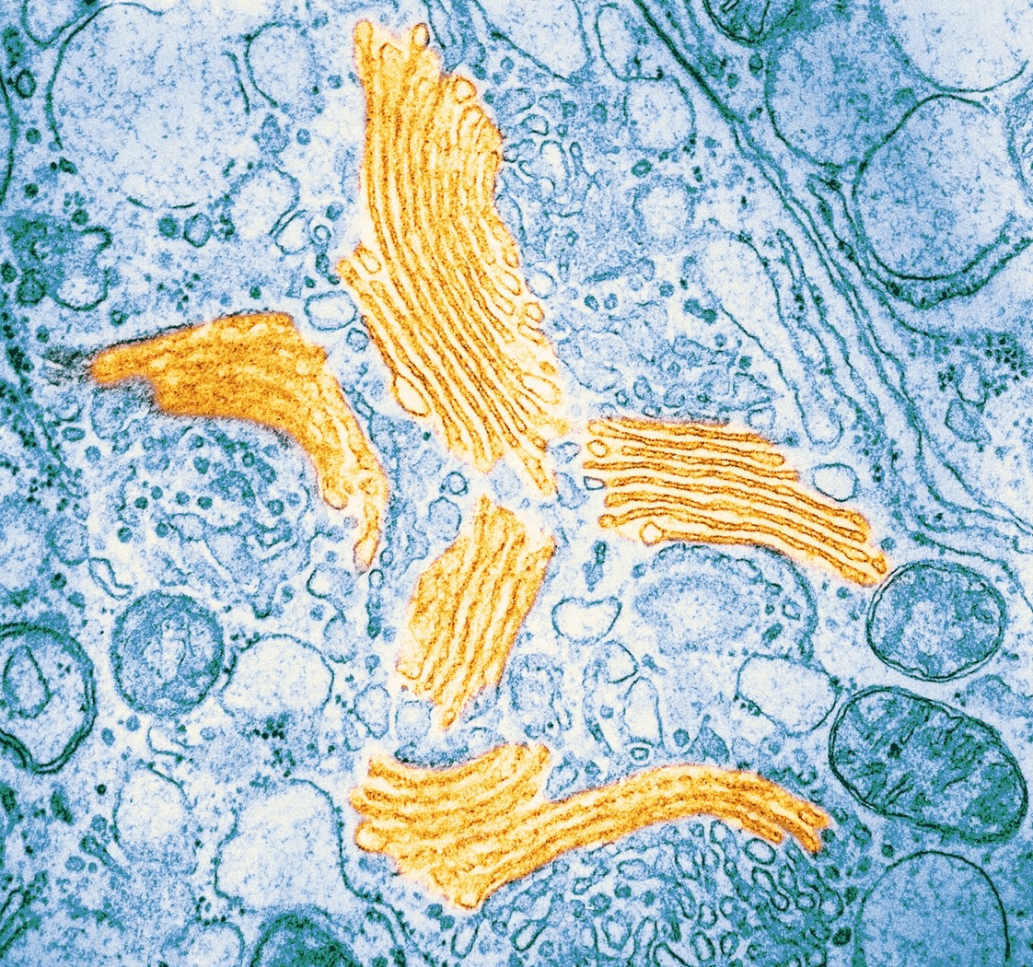
Golgi Apparatus
Give an example of a molecule that would use active transport.
Charged, large or lip insoluble.
What is the main waste product of the excretory system.
Urine
What is lowered to allow enzymes to speed up rate of reaction?
Activation energy
Name two hydrogen carriers involved in Cellular respiration.
NADH
FADH
Which cell is a plant cell?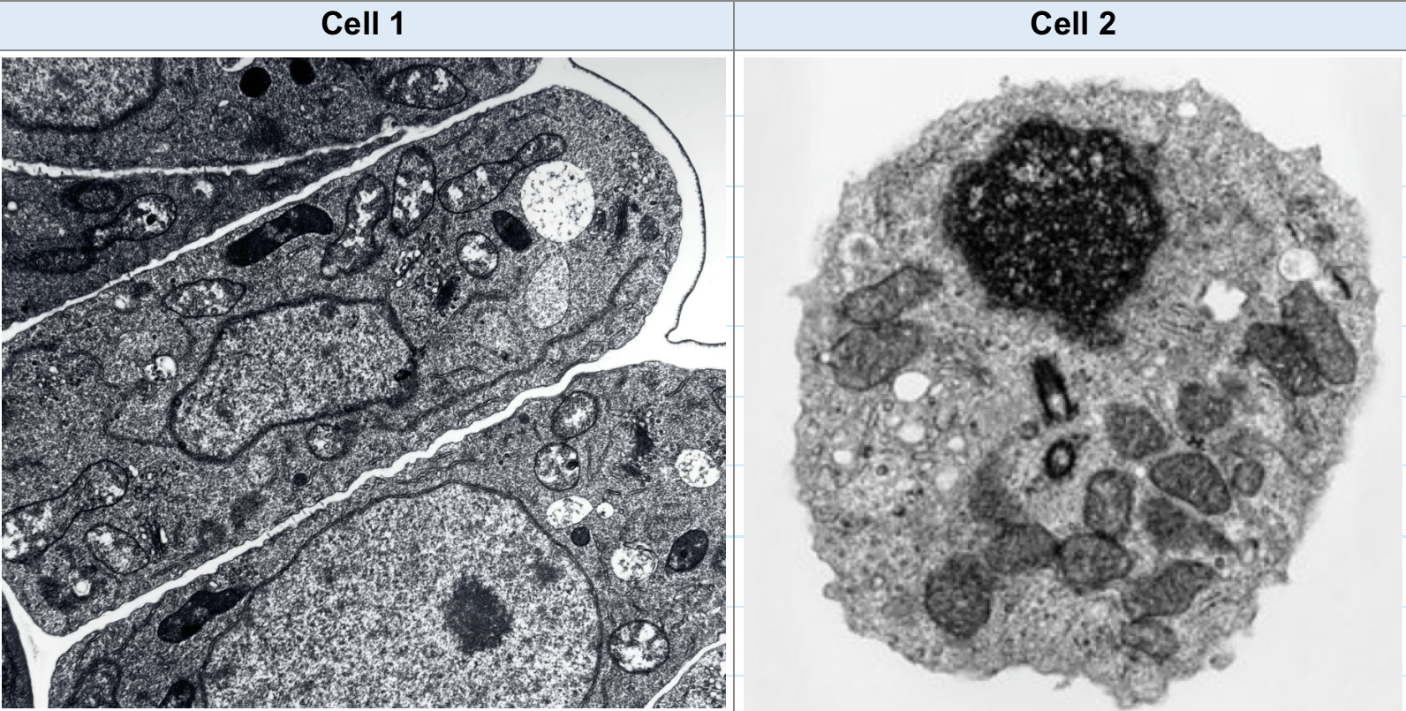
Cell 1
Exocytosis
Explain how oxygen is transferred from alveoli to capillary.
Concentration gradient
Name 4 factors that influence enzyme activity.
1. Temperature
2. PH
3. Substrate Concentration
4. Inhibitors
What is pyruvate converted to if there is no oxygen for aerobic respiration?
Lactate