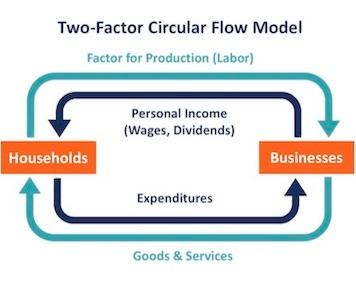
Draw the circular flow model
A producer’s ability to provide enough of a good or service to meet customer demand.
What is supply?
The oldest producers in any economy. They produce food and other agricultural products. They may also mine raw materials.
Describe primary producers.
the ‘alternative choice’ given up whenever a decision is made
Define opportunity cost
Paid employment at a job, trade or profession
Define 'Work'.
Food & Water.
Expensive new clothing & a mobile phone.
Identify 2 needs and 2 wants.
Downward slope
In what direction does a demand line slope?
Healthier options, environmentally friendly & socially responsible.
What are 3 ways producers may change their products to respond to consumer demand?
Land, labour, capital & entrepreneurship
What are the factors of production?
Anything related to financial gain, for example income, superannuation and staff discounts.
What are material reasons for working?
Households & Firms
What are the 2 main sectors in the economy?
The point at which the supply and demand curves intersect.
What is the equilibrium?
Loyal, discount, impulsive and needs-based.
List the different types of consumers
When a business will add a mark-up to the price of an item to cover the cost of the item, other costs and make a profit
What is cost plus mark-up?
Anything related to non-financial gain, such as ideas, thoughts and feelings
Things that we all want but we cannot afford to pay for as individuals. Examples include hospitals, schools and public transport.
What are 'collective wants'?
Supply will increase
What will happen to supply when the price increases?
If it makes the producers more profit or there is large demand for consumers who must be willing to pay for the charge.
Should producers respond to consumers?
When a business may enter the market with a low price to encourage consumers to try the new product. Once the product builds up enough regular customers, the business may raise the price to a level that is more profitable
What is penetration pricing?
Income depends on the type of work you do. It can be paid in wage, a salary or business profits. The amount of income a person receives will vary depending of the amount you work, the difficulty and specialised nature of the work, qualifications and experience and the number of people willing to do the work.
Describe one material reason for working
It is the problem of scarcity. This is when we have limited resources to meet unlimited needs and wants.
Define the 'economic problem'.
states that as the price of a good or service rises, the quantity demanded decreases, and as the price falls, the quantity demanded increases.
Describe the Law of Demand
Someone who will continue to buy a particular good or service from the same business (producer) for a long time.
The Land, Labour and Capital needed to make a car is expensive which is why you are not able to buy a new car for $100.
A lollipop is cheap to make as the Land, Labour, Capital are not that difficult to get and therefore you will not need to pay more than 50 cents for a Chupa Chup.
What is the relationship between price and the factors of production?
The ability to learn new skills. The opportunity to learn keeps many employees interested and helps them avoid becoming bored with their jobs.
Identify and describe one non-material reason for working.