Identify the number of A molecules that are left after 30 seconds.
5

Identify how much uranium-238 remains after 9000 million years.
26%
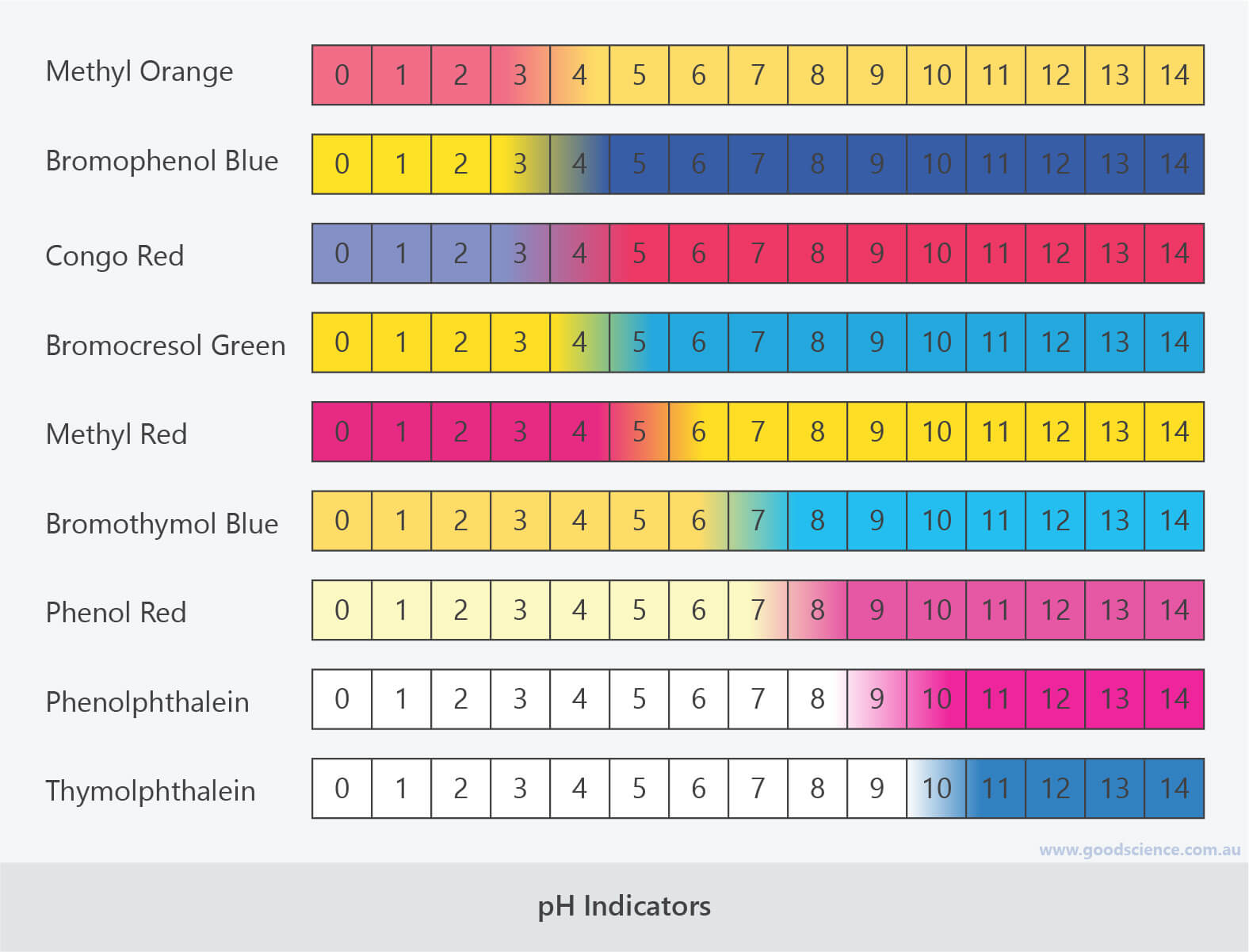
What colour will Congo Red indicator turn when placed into a substance with a pH 1?

Which two groups had the most similar Yield Loads?
Groups 1 and 2
A positively charged subatomic particle.
Proton
Identify when the amount of A was the same as the amount of B.
9

What is the half-life of uranium-238?
4500 million years

What is the possible pH range when Bromophenol Blue is blue and Phenol red is yellow?
5-6

Which matrix had the most variation in Ca+ sensitivity?
Uric acid - largest error bar
What pH range do alkalines/bases have?
8-14
How many seconds did it takes for A to reach 5 molecules?
30 seconds

How long does it take uranium-238 to reach 2 half-lives?
9000 million years

When Thymolphthalein turns blue, is it in an acid or a base?
Base
What do error bars tell us?
Error bars represent the variability of data and indicate the uncertainty or how precise the reported measurement is.
What is an ion?
An atom or molecule with a positive or negative electric charge due to the loss or gain of electrons.
Which line represents the reactants and which represents the products?
A = amount of reactants
B = amount of products

What is the half-life of radon according to this geiger counter reading graph?
~50 minutes

Which indicator would most accurately identify a solution as an acid or a base?
Bromthymol Blue - Yellow is acid only, blue is base only and green signifies a neutral solution.

Are any of the components (phosphate, oxalate and uric acid) statistically different from one another when judging by their error bars?
No, all the error bars overlap each other.
What is an isotope?
Forms of the same element that contain equal numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei.
Identify the relationship between A and B. Justify your response by referring to data points in the graph.
As B increases in number of molecules over time, A decreases.
At 0 seconds there is 50 molecules of B but 0 molecules of A. At 9 seconds there are 25 molecules of both A and B. By 60 seconds there are no more B molecules left and 50 A molecules.
What is alpha decay?
A type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus) and thereby transforms or 'decays' into a different atomic nucleus, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an atomic number that is reduced by two.
What is a neutralisation reaction?
Acid (H) + Base (OH) -> Salt + Water (H2O)
The acid and base neutralise each other to produce a neutral solution.

Which two groups are the most statistically different from each other?
2 and 4 - biggest gap between error bars
What causes radioactivity?
When an atom is unstable due to an excess of either neutrons or protons. A radioactive atom will attempt to reach stability by ejecting protons or neutrons, as well as other particles, or by releasing energy in other forms.