Another name for Group A Streptococcus
What is Streptococcus pyogenes
The ability of a gram-negative bacterium to ferment what sugar is the first step in its identification
What is Lactose
The purpose of transport media is
What is to ensure the preservation of microorganism in the specimen
The Gram stain is a routine stain used in bacteriology to determine gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria based on the
What is the composition of the cell wall
Partial lysing of erythrocytes in a BAP around and under the colony is
What is Alpha hemolysis (green color)
This type of bacteria is able to live in the colon with little to no oxygen and is a predominant organism.
What is anaerobes
Organism associated with Tetanus
What is Clostridium tetani
Aerobes are bacteria that grow
What is ambient air
HACEK group includes
What is Haemophilus Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus), Cardiobacterium, Eikenella, and Kingella
The lowest concentration of antibiotic that inhibits growth of the test organism is the:
What is MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration)
Positive quality control organism for the bile esculin test
What is Enterococcus faecalis
Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections are transmitted
What is sexual contact
Beta-hemolytic streptococcus that is bacitracin resistant and CAMP test positive
What is group B streptococcus or Streptococcus agalactiae
Biochemically, Enterobacteriaceae species are gram negative rods that:
What is ferments glucose, reduce nitrate to nitrite, and are oxidase negative
Media supports the growth of one type or group of microbes, but not another
What is Selective
What stain is used for medically important fungi?
What is lactophenol cotton blue
Complete clearing of erythrocytes in a BAP around and under the colony
What is Beta hemolysis
The chemical or physical method that destroys all form of life is called
What is sterilization
What is Clostridium perfringes
Microaerophiles are bacteria that grow
What is in reduced oxygen concentration by increased carbon dioxide concentrations
Staphylococcus saprophyticus is presumptively identified by
What is novobiocin susceptibility
The agency that is responsible for setting guidelines and developing reporting standards for antimicrobial testing is CLSA which stands for:
What is Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute
Positive quality control organism for CAMP test
What is Streptococcus agalactiae (group B)
Neisseria meningitidis most commonly spreads by
What is respiratory droplets
An important case of pharyngitis
What is Streptococcus pyogenes
Two reagents used in the Voges-Proskauer test are
What is 40% KOH and alpha-naphthol
Media supports the grouping of microbes based on different characteristics demonstrated in the media
What is Differential
What is color forms (gram positive or negative) and shapes (cocci, rods, etc..)
What is non hemolytic or Gamma hemolysis
Why should health care workers was their hands after coming into contact with a patient?
What is to reduce the spread of pathogenic bacteria from one individual to another.
The characteristic colonial morphology of Actinomyces israelii on a solid agar resembles
What is a molar tooth
Capnophiles are bacteria that grow
What is an increase carbon dioxide concentrations
What is catalase
Organism considered universally susceptible to penicillin
What is Streptococcus pyogenes (group A)
Positive quality control organism for Bacitracin disk
What is Streptococcus pyogenes (group A)
Organism that caused pinkeye is
The optochin disk is used for the identification of
What is Streptococcus pneumoniae
Organism that is the most common cause of urinary tract infections (UTI's) in humans
What is Escherichia coli
Media that allows the growth of fastidious microbes through the addition of certain growth enhancers
What is Enriched
What is this gram stain result?
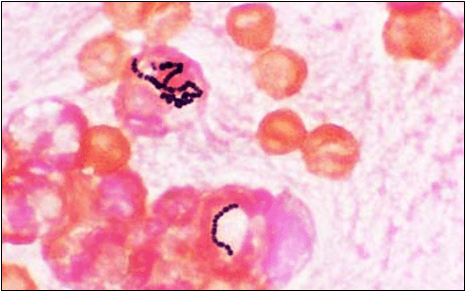
What is Streptococci: gram-positive cocci in long chains
Hemolysis, color, and elevation are all
What is colony characteristics
Blood and body fluids from all patients be considered infectious and capable of transmitting disease is:
What is Universal/Standard Precautions
Anaerobic bacteria most likely the cause of tooth abscesses
What is Porphyromonas gingivalis
Anaerobes are bacteria that grow
What is where little or no oxygen is present
Organism forms a small, fuzzy-edged colony with an umbonate center on blood or chocolate agar. This organisms could be
What is Eikenella corrodens
Antibiotics work by targeting
What is DNA replication, RNA transcription, and bacteria cell wall
Positive quality control organism for Indole
What is Escherichia coli
Which Haemophilus requires both X and Y factors
What is Haemophilus influenzae
Oxicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is
What is methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA)
Disease produced by a Salmonella species is a severe form of enteric fever
What is Typhoid fever
MacConkey (MAC) agar is used to
What is differentiate between lactose fermenters and lactose nonfermenter
What is this gram stain result
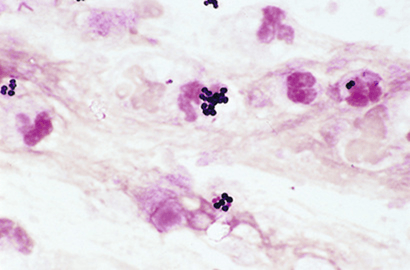
What is gram positive cocci in clusters resembling Staphylococcus
A hazy blanket of growth on the surface of the agar that extends way beyond the streak lines is
What is swarming
Quality control is designed to
What is to ensure the medical reliability of the laboratory data/results
A gram-positive bacillus was isolated from a wound specimen and had the following characteristics: double zone of Beta hemolysis, lecithinase positive, lipase negative, spot indole negative. The most likely identification is
What is Clostridium perfringens
Organism causes the disease called whooping cough
What is Bordetella pertussis
Disease is an extensive exfoliative dermatitis caused by staphylococcal exfoliative toxin
What is Ritter's disease (SSS)
Penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, and carbapenems all have this ring in their structure that is responsible for inhibiting the transpeptidation reaction, resulting in bacterial lysis and cell death
What is B-Lactam
Positive quality control organism for Oxidase
What is Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Organism is likely to cause an infection after a cat bite
What is Pasteurella species
The organism most commonly associated with neonatal purulent meningitis
What is Group B Strep (Strep agalactiae)
Bacteria that is the causative agent of the plague
What is Yersinia pestis
Thayer-Martin and Martin-Lewis media have antimicrobial agents added to
What is to prevent overgrowth of normal biota (flora)
This constituent of a gram-positive cell wall absorbs crystal violet but is not dissolved by alcohol, thus giving the gram-positive cell its characteristic purple color.
What is Peptidoglycan
Colonies of Bacillus anthracis are described as
What is Medusa's heads
What is PPE
Sodium polyanethol sulfonate (SPS) disk can presumptively identify
What is Peptostreptococcus anaerobius
The bacteria that plays an important role in the health of the female vaginal tract, protecting it against pathogens
What is lactobacillus
What are acute glomerulonephritis and rheumatic fever
What is inoculum preparation
Positive quality control organism for coagulase
What is Staphylococcus aureus
Organism that stains poorly with Gram's stain but it's characteristic seagull wing shaped rods stain well using carbolfuschin
What is Campylobacter
Organism in any number is significant in a UTI in a woman
What is Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Bacteria produces swarming colonies on nonselective media, such as sheep blood agar (BAP)
Medium is used to isolate Legionella
What is Buffered charcoal yeast extract (BCYE)
What is this gram stain
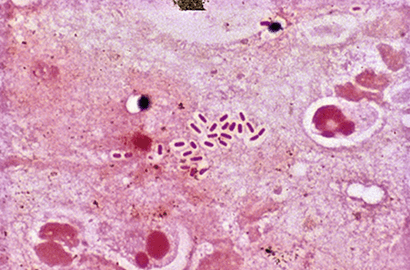
What is Gram-negative bacilli, encapsulated.
A microbiologist is reading the plates from a sputum culture. The culture is from a patient with cystic fibrosis. One organism dominates the blood agar, chocolate, and MacConkey plates. The MacConkey plate shows an organism with a green pigment and a metallic sheen. The probable identification for this organism is
What is Pseudomonas aeruginosa
A zone of inhibition is
What is the area around the antibiotic disk where the bacteria cannot grow
Intestinal abscess produces gray colonies with a brown color in the area around the colonies on a BBE plate incubated anaerobically. There is also a dark precipitate in the medium in the areas of heavy growth. A Gram stain of the colonies reveals gram-negative coccobacilli. The presumptive identification of the organism is
What is Bacteroides fragilis
Organism displays Babe's-Ernst granules on a gram stain
What is Corynebacterium diphtheriae
What is Nocardia species
On a breakpoint panel, when two concentrations are tested and no growth is present in either well, the isolate is
What is susceptible
Positive quality control organism for India ink
What is Cryptococcus neoformans
Organism that causes tularemia, which can be contracted from rabbits
What is Francisella tularensis