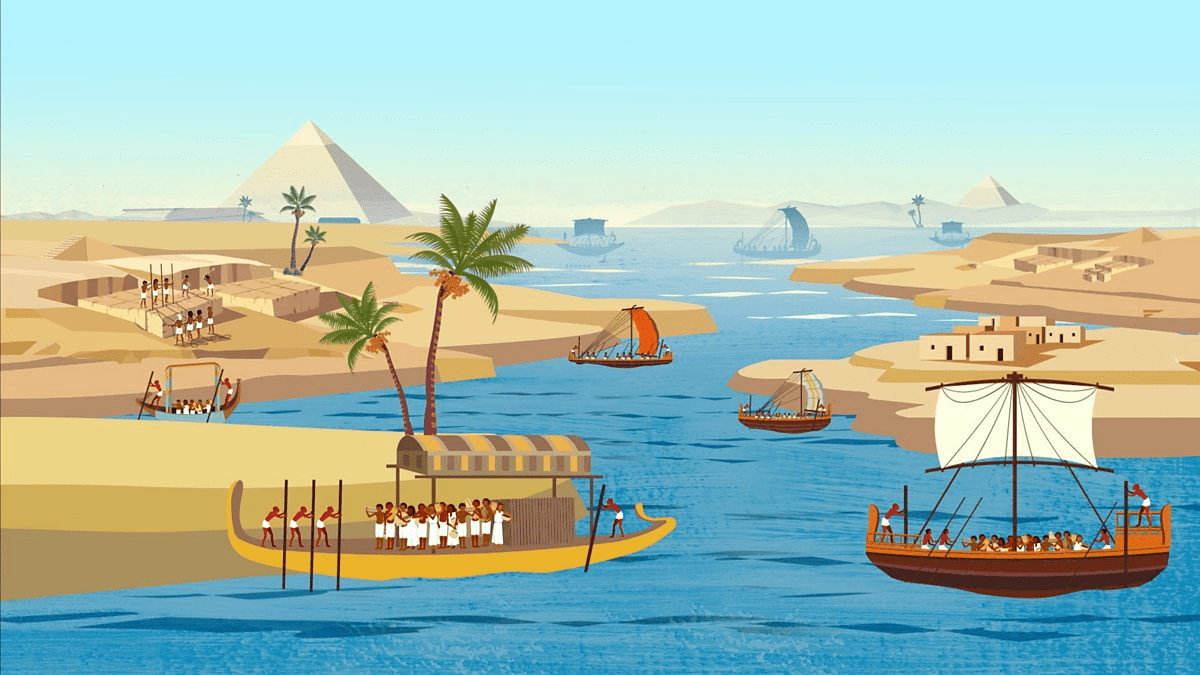
 What river was essential for life in Ancient Egypt?
What river was essential for life in Ancient Egypt?
The Nile
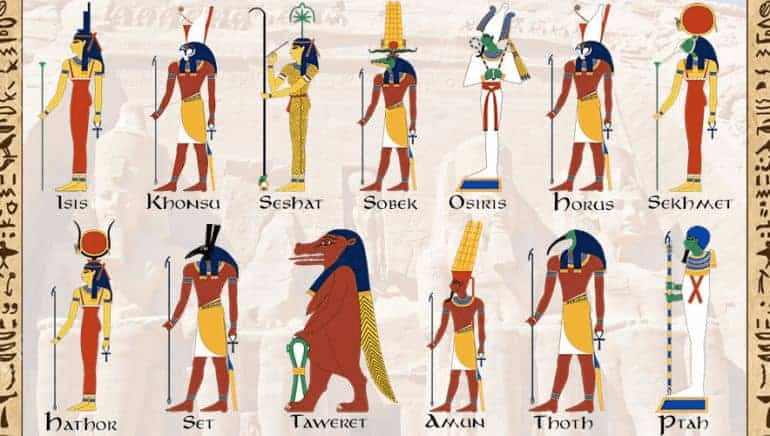 Was Ancient Egyptian religion monotheistic or polytheistic?
Was Ancient Egyptian religion monotheistic or polytheistic?
Polytheistic.
Who was at the top of the social hierarchy?
The Pharaoh.
What process preserved bodies for the afterlife?
Mummification.
Who was considered a living god on Earth?
The Pharaoh.
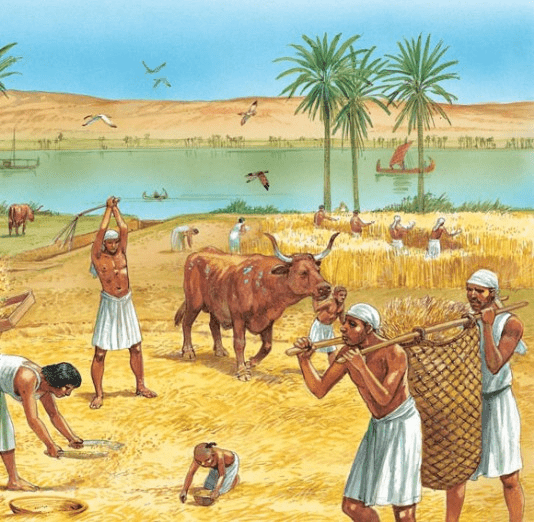 Why did most settlements form along the Nile?
Why did most settlements form along the Nile?
Fertile soil and water for farming and survival.
 Who was the god of the afterlife?
Who was the god of the afterlife?
Osiris
Which class grew crops and paid taxes in food?
Farmers.
What natural substance was used to dry the body?
Natron salt.
 Which female Pharaoh ruled successfully but had her monuments destroyed?
Which female Pharaoh ruled successfully but had her monuments destroyed?
Hatshepsut.
What natural barriers protected Egypt from invasion?
Deserts and cataracts.
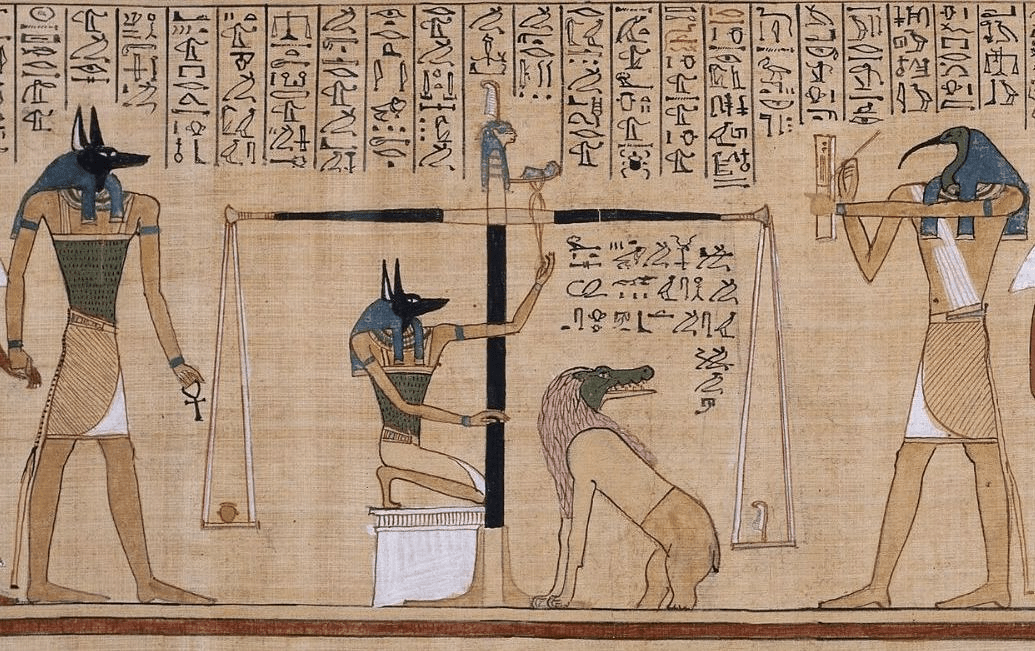 What was the purpose of the Book of the Dead?
What was the purpose of the Book of the Dead?
To guide the dead through the afterlife.
Which group performed rituals and mummification?
Priests.
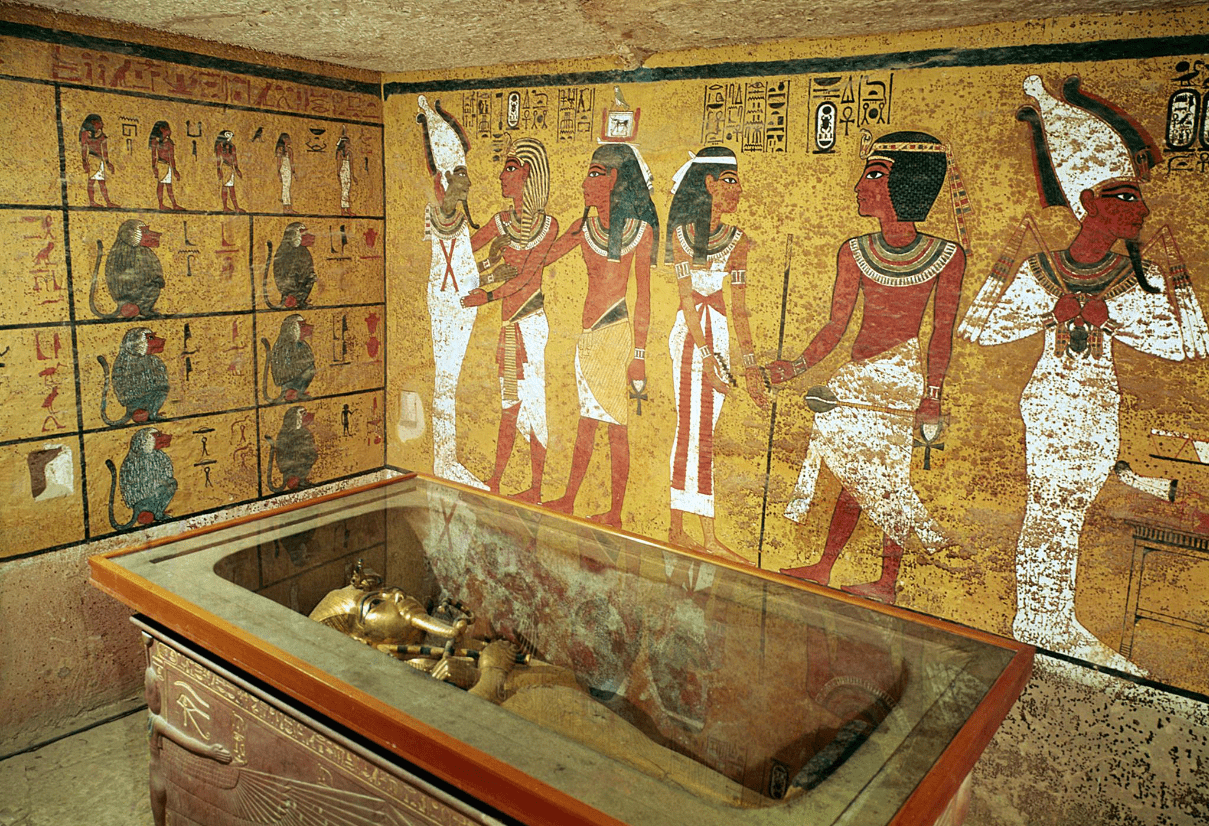 Why were treasures placed in tombs?
Why were treasures placed in tombs?
For use in the afterlife.
Who became Pharaoh at age nine and died at nineteen?
Tutankhamun.
What does the term “Kemet” mean?
Rich, black soil. Also traditional name for the Egyptian people.
What concept represented truth and justice in Egyptian religion?
Ma'at.
Who recorded laws and taxes in Ancient Egypt?
Scribes.
What type of structure served as tombs for Pharaohs?
Pyramids.
In what year was King Tut’s tomb discovered?
1922.
Why did Herodotus call Egypt “The Gift of the Nile”?
Because the Nile made Egyptian civilization possible.
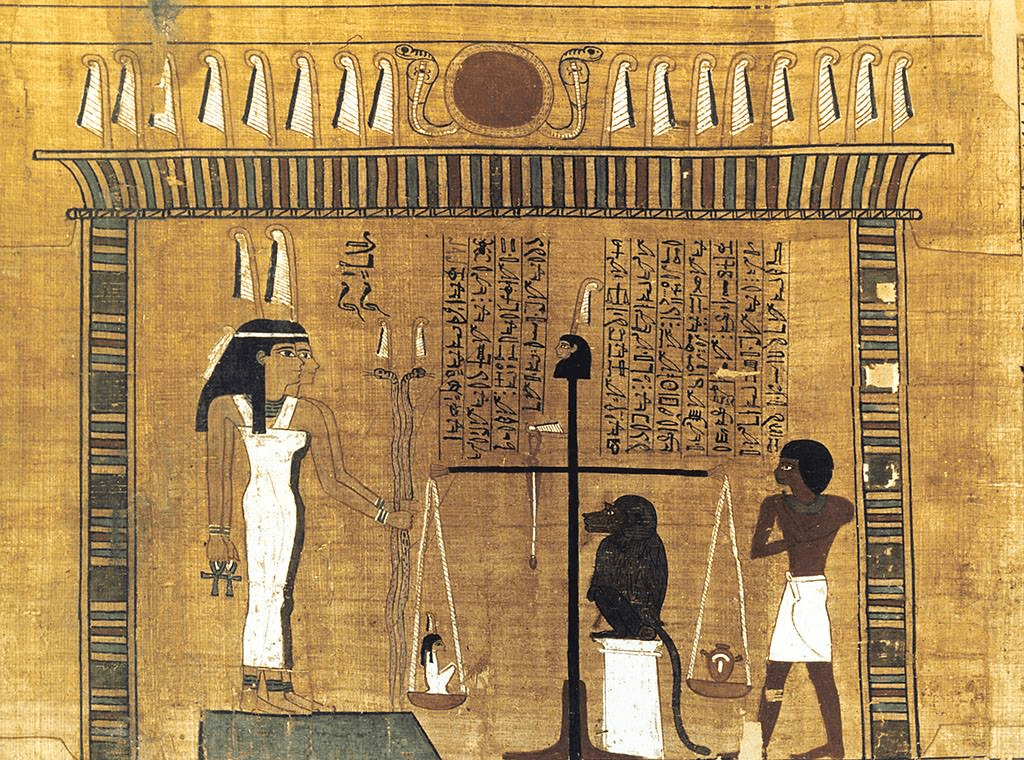 What happened if the heart was heavier than the feather in the final judgment?
What happened if the heart was heavier than the feather in the final judgment?
It was eaten by Ammit and the soul was destroyed.
Name two roles of the Pharaoh.
Maintained Ma’at, led the army, oversaw building projects.
What amulet was placed to prevent the heart from betraying the deceased?
Heart scarab.
 Why were Pharaohs buried with riches?
Why were Pharaohs buried with riches?
They believed they needed them in the afterlife.