Which of the following are a source of light?
star fire mirror plant torch moon
Star, fire and torch
What is the opening in the eye called that lets in light? It dilates (gets bigger) when it is dark and constricts (gets smaller) when it is bright.

Pupil
What type of wave is a sound wave? Starts with L!
Longitudinal
What are the two functions of the ear?
Hearing and Balance
Draw what the reflection would look like of this word...
REFLECT
REFLECT l TƆƎ⅃ꟻƎЯ
What type of lens is in the eye? What is the place where all of the light meets called (hint: think about the movies)?

Convex lens + focal point is where the light rays meet/converge
Label the parts of the wave

A - Trough, B - Amplitude, C - Crest, D - Wavelength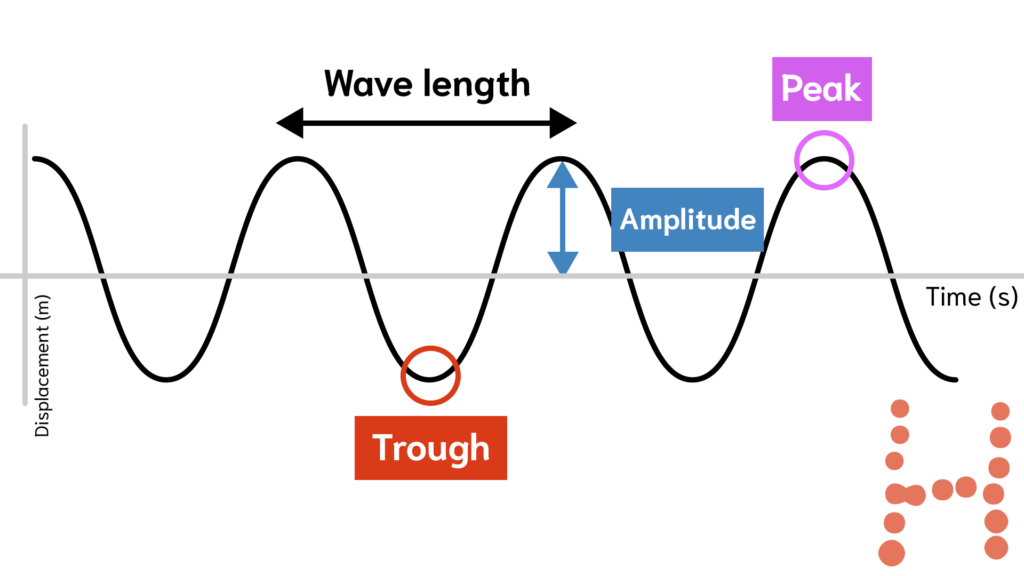
What is the part of the ear that is coloured red and helps keep the pressure inside and outside of your ear balanced called?
a) Semi-circular canal b) Ear canal c) Ossicle d) Eustachian tube
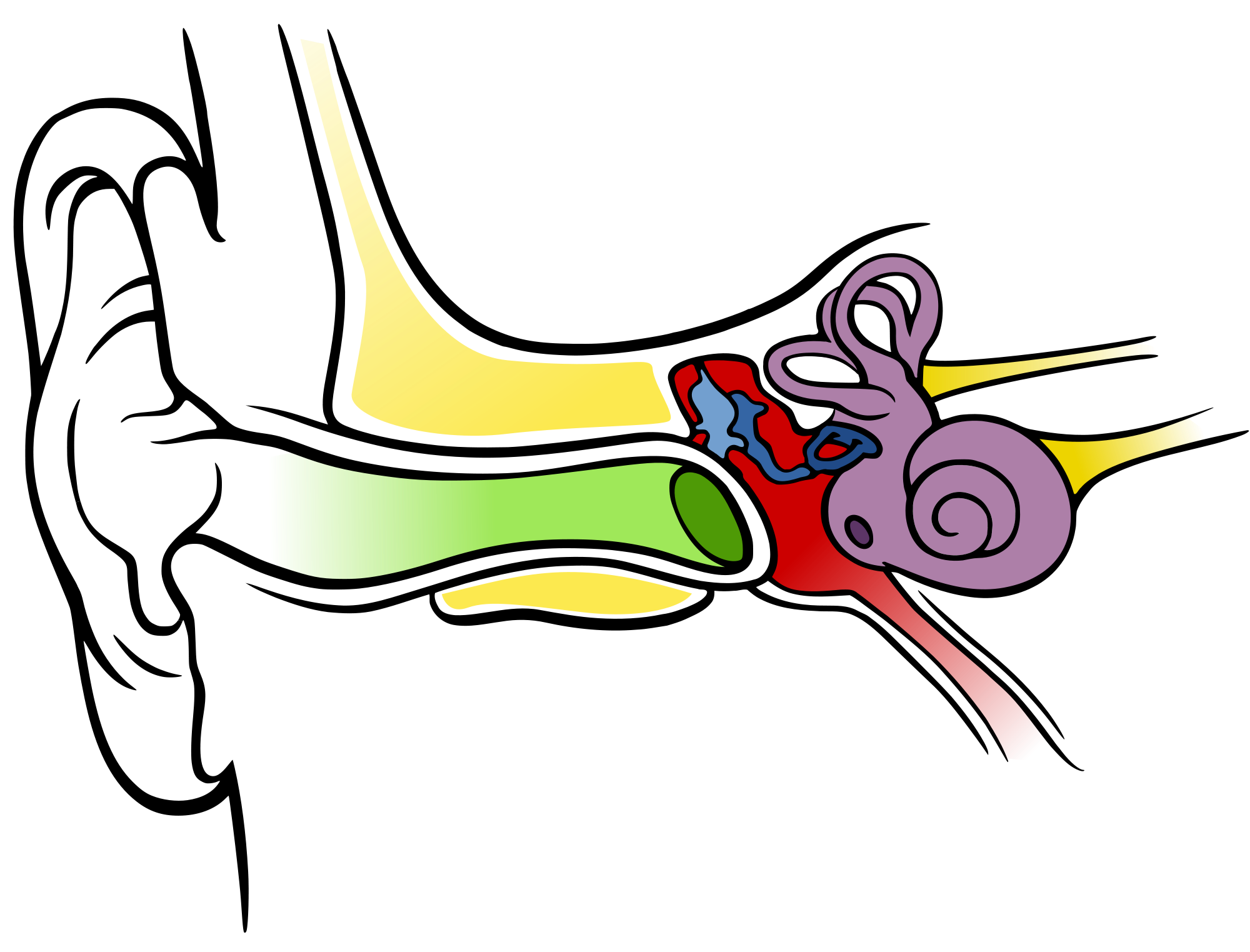
d) Eustachian tube
What is happening to light that hits this basketball?
Main basketball -
Lines -

Main basketball - orange is being reflected, all other colours are being absorbed
Lines - all light wavelengths are being absorbed
In a normal eye, the image is focused onto the back of the retina. The eye below is focusing the image behind the retina, meaning it must be...
Short-sighted or Long-sighted?
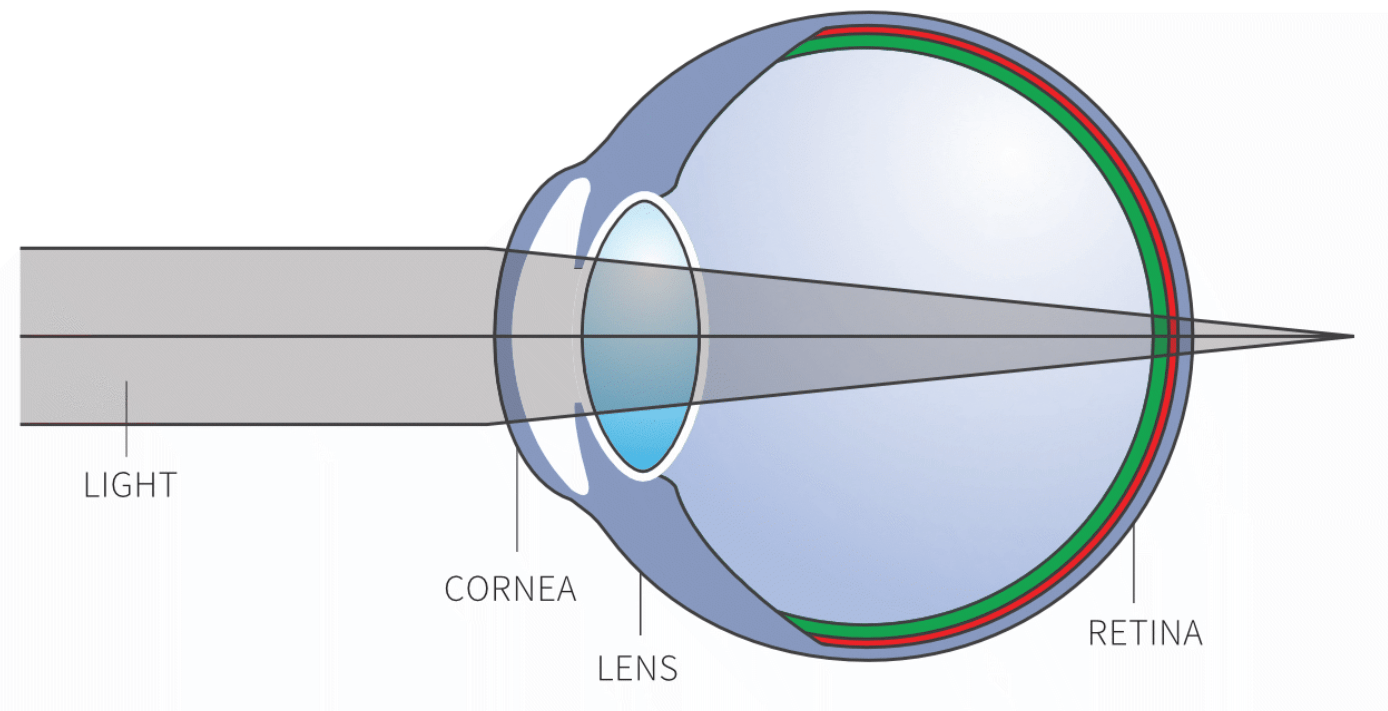
Long-sighted - it can see things far away fine, but things close are not focused onto the back of the retina and are therefore blurry.
time = distance ÷ speed of sound
time = 3,300 ÷ 330 = 10 seconds
It will take 10 seconds for the sound to reach you.
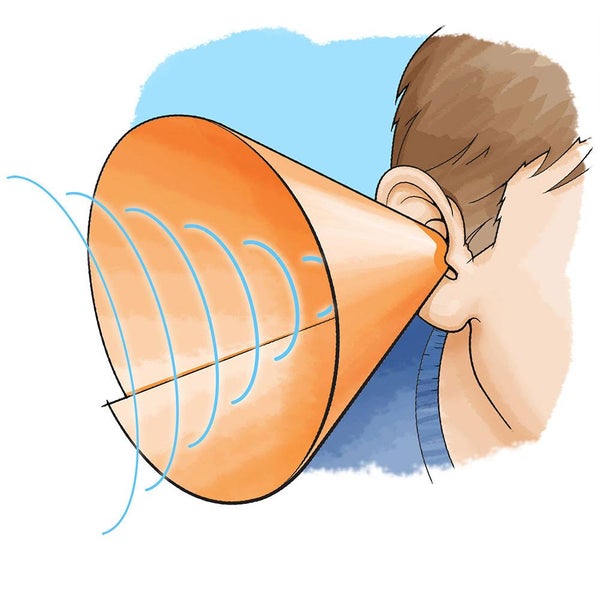
Why does the pinna's shape help it do its job?
It helps to collect and direct the sound waves into the ear canal, like a funnel.
Light going into a prism is ____a____ as it slows down passing into a more ____b____ substance, this makes it bend closer to the ____c____ line. White light is made up of all the ____d____ of light and they all bend different amounts, which makes them separate into the full spectrum of visible light. As the light comes back out of the prism, it ____e____ up again, bending ____f____ the normal.
nomal refracted speeds wavelengths dense away from
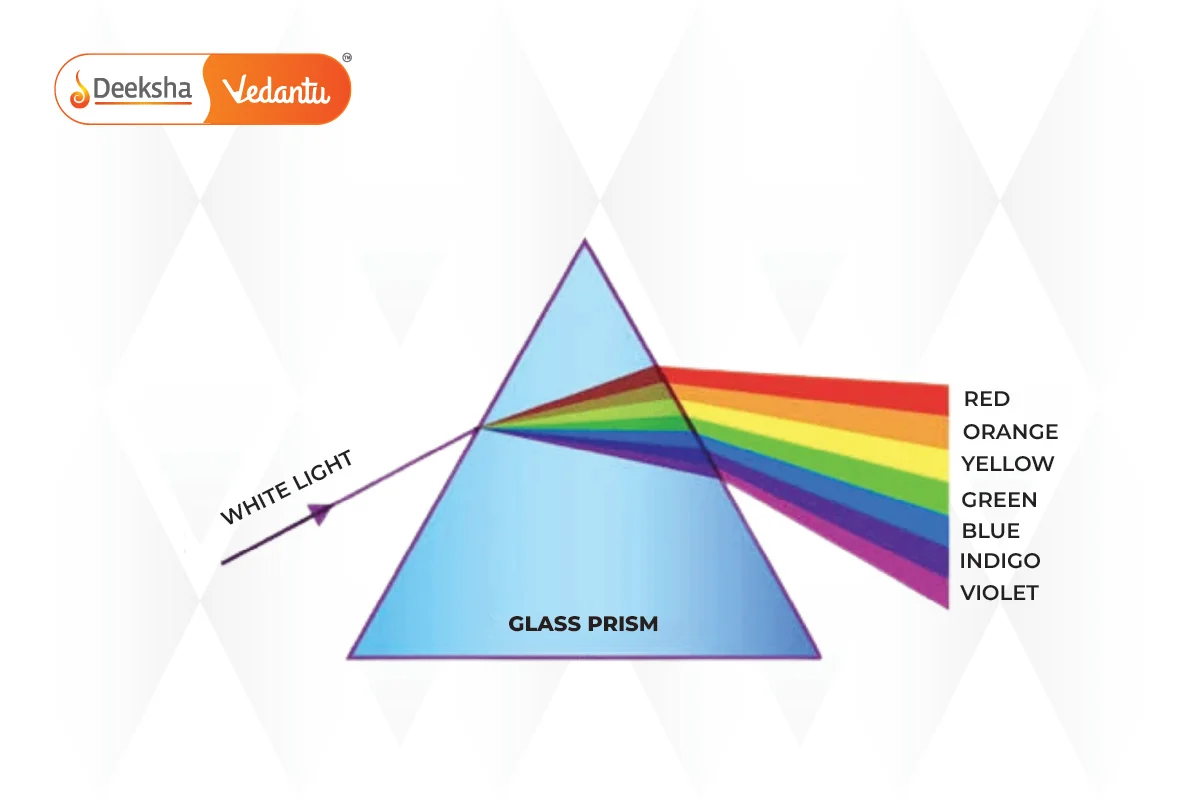
Light going into a prism is a) refracted as it slows down passing into a more b) dense substance, this makes it bend closer to the c) normal line. White light is made up of all the d) wavelenghts of light and they all bend different amounts, which makes them separate into the full spectrum of visible light. As the light comes back out of the prism, it e) speeds up again, bending away from the normal.
Match up the part of the eye to what it is...
a) Blind spot b)Vitreous humour c) Retina d) Cornea
1. The goopy jelly-like liquid in the eye
2. The place where the optic nerve comes out the back of the eye
3. The clear protective layer on the outside of the eye
4. The back of the eye where light is focused onto
1. b) vitreous humour
2. a) blind spot
3. d) cornea
4. c) retina
Out of the things below, which will sound travel fastest through and why?
Air, Soup, Jam, Steel, Cardboard
Steel, because sound travels fastest in denser substances. Particles in steel are closer together, which means the vibrations are passed on more quickly.

Which number shows the...
a) Hammer b) Cochlea c) Ear canal d) Semi-circular canals e) Stirrup f) Ear drum g) Nerves
a) Hammer - 13 b) Cochlea - 7 c) Ear canal - 2 d) Semi-circular canals - 9
e) Stirrup - 11 f) Ear drum - 3 g) Nerves - 8
Label the diagram and describe how F and B are related.
normal angle of incidence (θi) reflected ray
angle of reflection (θr) incident ray plane mirror
A) Incident ray B) Angle of reflection (θr) c) Reflected ray
d) Normal e) Plane mirror f) Angle of incidence (θi)
The angle of incidence and reflection are equal/the same.
Label each part of the eye (except for 6)

1. Cornea 2. Pupil 3. Iris
4. Lens 5. Retina 7. Optic nerve
Which of these waves has...
a) Highest frequency b) Loudest volume c) Lowest pitch
d) Longest wavelength e) Biggest amplitude
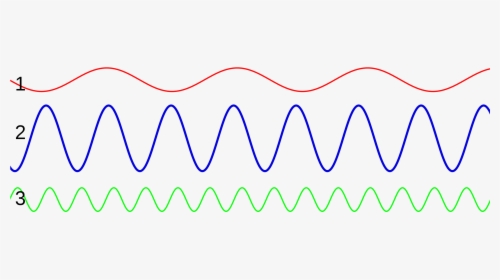
a) 3 b) 2 c) 1 d) 1 e) 2
Fill in the gaps...
Sound waves are collected by the pinna and travel down the _____a_____, the sound vibrates the _____b_____ which then vibrates the hammer, anvil and stirrup (tiny _____c_____ in the middle ear). This passes the vibrations onto the fluid-filled _____d_____ where tiny hairs turn the vibrations into electrical signals which travel down the _____e_____ to the brain to be interpreted.
Sound waves are collected by the pinna and travel down the a) ear canal, the sound vibrates the b) ear drum which then vibrates the hammer, anvil and stirrup (tiny c) bones in the middle ear). This passes the vibrations onto the fluid-filled d) cochlea where tiny hairs turn the vibrations into electrical signals which travel down the e) nerves to the brain to be interpreted.
