When water evaporates from a leaf, this process is called

A species on which other species in an ecosystem largely depend, such that if it were removed the ecosystem would change drastically.
Cell walls
The failure of one or more pairs of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate normally during nuclear division, usually resulting in an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the daughter nuclei.

More CO2 is released in the atmosphere today than in the past because of the

Burning of fossil fuels


Only special bacteria can directly use nitrogen in our atmosphere and convert it so other organisms can benefit. These bacteria are called
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria
What is crossing-over? When does it occur?

Crossing-over is the exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes, resulting in a mixture of parental characteristics in offspring. Crossing-over occurs during prophase/metaphase 1 of meiosis.
The __________ principle states that allele and genotype frequencies in a population will remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of other evolutionary influences.
What is runoff? How can runoff have negative impacts on the environment?

Runoff is precipitation that made its way from the ground surface into places that water collect. Runoff causes erosion and carries chemicals on the ground surface to rivers causing water pollution.
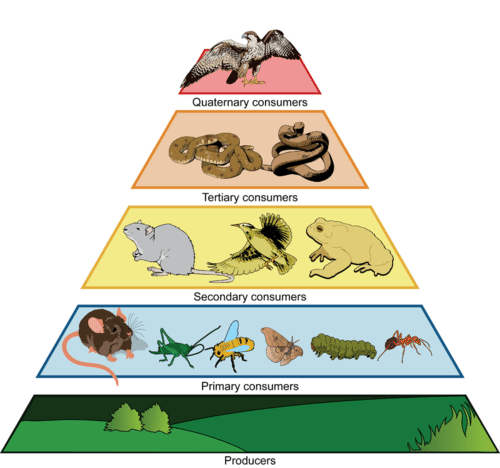
The primary consumers receive 1,000 kcal of energy from the producers. How much energy do the tertiary consumers receive?
Meiosis produces how many cells? Are they identical to each other? Are they haploid/diploid? What type of cells are these?
Meiosis: 4 non-identical haploid gametes
Natural Selection
Why is the use of too many phosphorus-rich fertilizers bad for the environment?
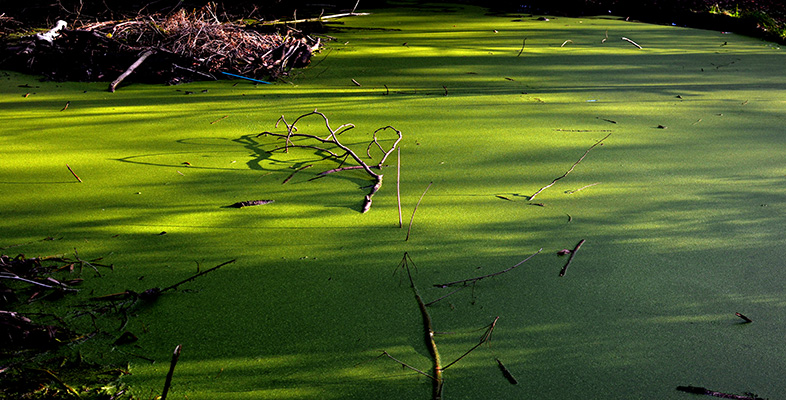

Agriculture runoff goes into aquatic ecosystems which cause plants to grow and overpopulate the water. (Eutrophication)
(VIDEO BONUS) Which form of transport is illustrated in the video?
(VIDEO BONUS) Describe what is happening at each step in the video. What process does this video show?
2) Centrioles align at opposite poles of the cell; nuclear envelope breaks down (prophase)
3) Microtubules attach and align paired chromatids at the center of the cell (metaphase)
4) Chromosomes are pulled apart (anaphase)
5) Nuclear membranes reform (telophase)
6) Cell membrane pinches apart (cytokinesis)