AFI greater then 24cm
What is polyhydramnios?
DVP greater then 8cm
Greater the DVP, the greater risk of karytype abnormality
Normal cervical length
3-4cm
Most accurate methods for dates
What is provided LMP or 1st trimester US?
Never change dates based on 3rd trimester US
Measurement of ventricular atrium suggestive of hydrocephalus
What is greater then 10mm?
Appearance of dangling choroid
This structure is flanked be umbilical arteries on color doppler.
What is fetal bladder?
Nonvisualization of bladder is associated by bilateral renal anomalies.
Most accurate measusurement of oligohydramnios
What is DVP of less then 2cm by 1cm?
Earliest gestational age placenta previa can be diagnosed.
What is at 16 weeks?
Recommended follow up at 32 weeks
Gestational age fetal biometry used instead of CRL
What is at 14 weeks?
Important midline structure which is part of fetal anatomic survey
What is the Cavum septum pellicidum?
If absent, can indicate corpus callosum agenisis.
Don’t try to find corpus callosum.
32 week gestation. Name of this sign and association.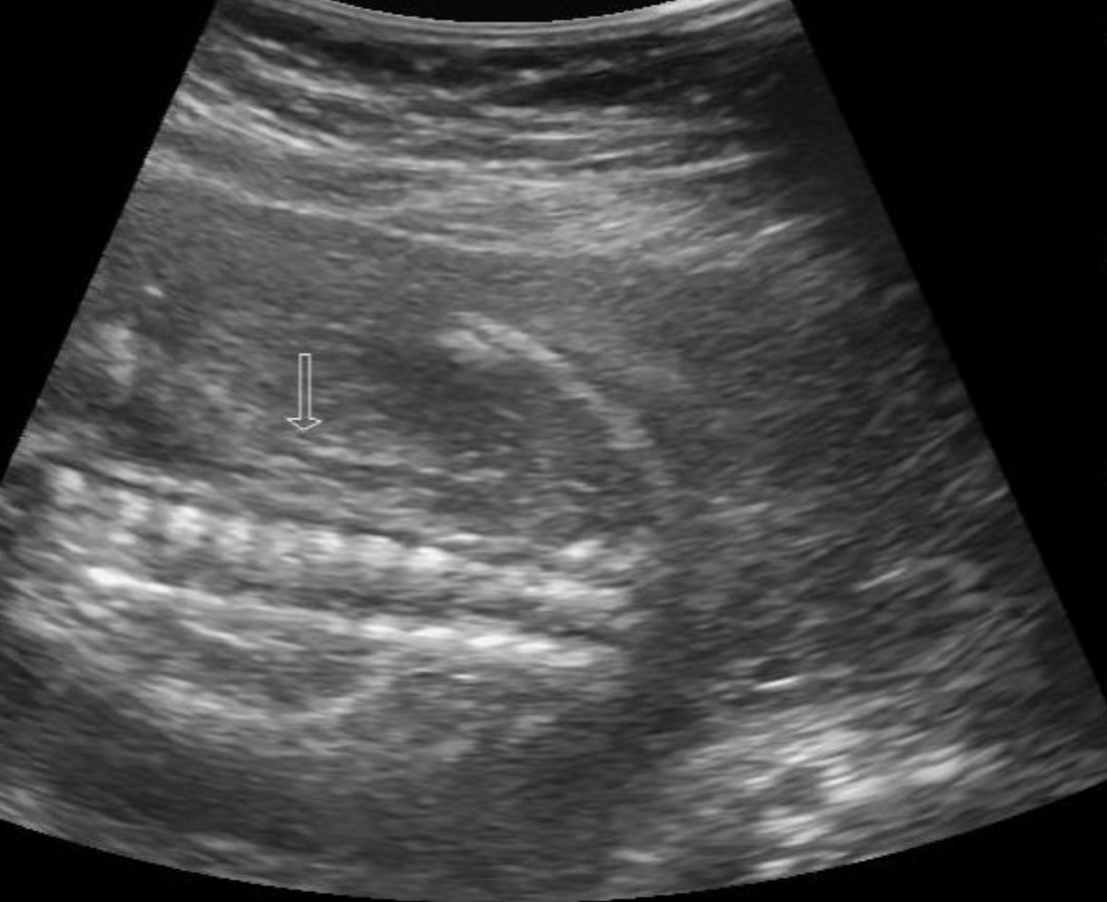
What is the lying down adrenal gland sign in renal a genesis?
2 types of fetal anomalies associated with polyhydramnios
What are fetal GI and CNS anomalies?
other causes:
maternal diabetes, fetal infections, disorders affecting fetal swallowing
What is the next appropriate step?
What is transvaginal, transperineal, or translabial us?
Less then 10% fetal weight
What is IUGR or small for gestational age?
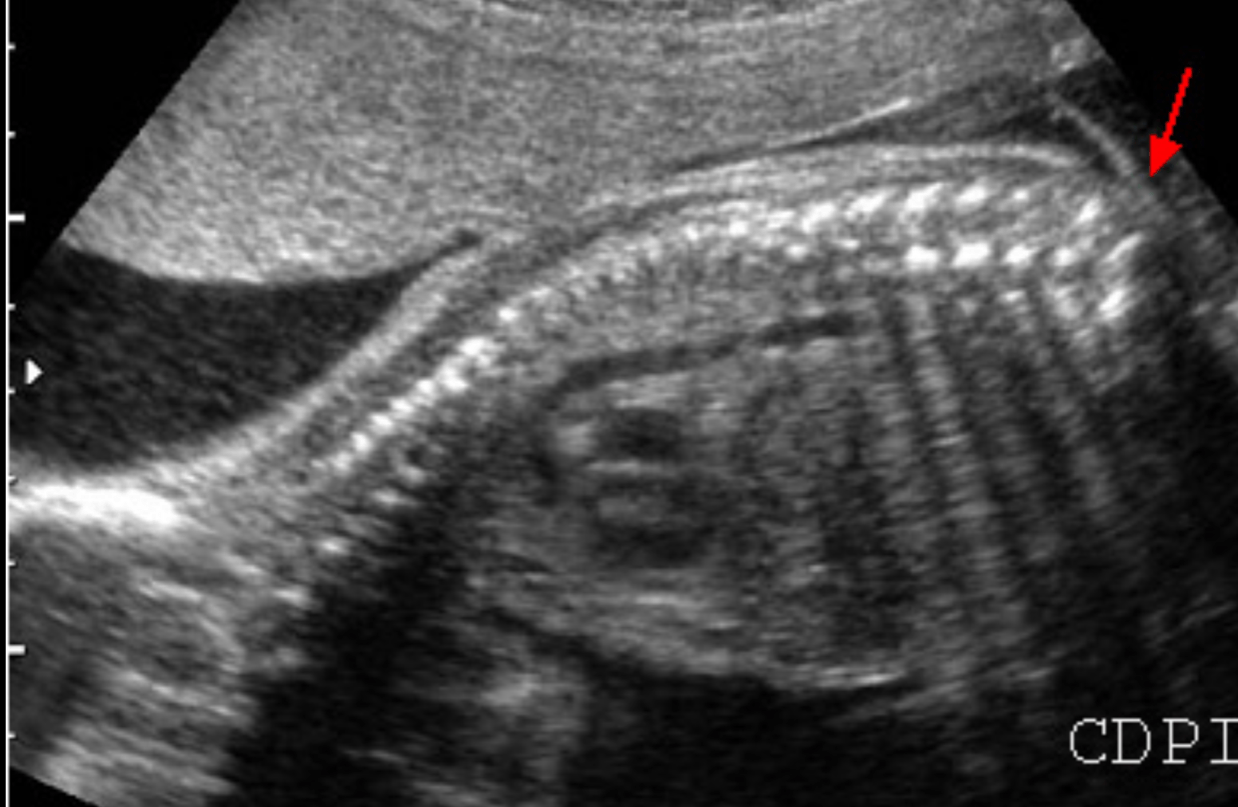
What is caudal regression?
Normal spine should be upturned towards sacrum..
Criteria to be mentioned about umbilical cord in normal fetal anatomic survey of fetal abdomen.
What is number of vessels and cord insertion on fetal abdomen?
At least two of the following list must be present to diagnose what fetal condition?
fetal pleural effusion, fetal pericardial effusion, fetal ascites, skin thickness >5mm, polyhydramnios, hepatomegaly, placental enlargment
What is Hydrops?
heart failure, volume overload, decreased oncotic pressure, increased vascular permeability

What is placenta previa and recommend 32 wk follow up
Placenta previa: placental edge is within 2cm from cervical os
No longer use marginal or partial
Percentile for fetal macrosomia
What is greater then 90%?
Also consider large for gestational age.
Next appropriate step?
What is repeat exam and/or refer for cardiac echo?
Fetal renal pelvic AP diameter considered abnormal.
What is 10mm?
name at least 3 causes of oligohydramnios
What are GU anomalies, ruptured membranes, and IUGR?
two diagnoses on this image.
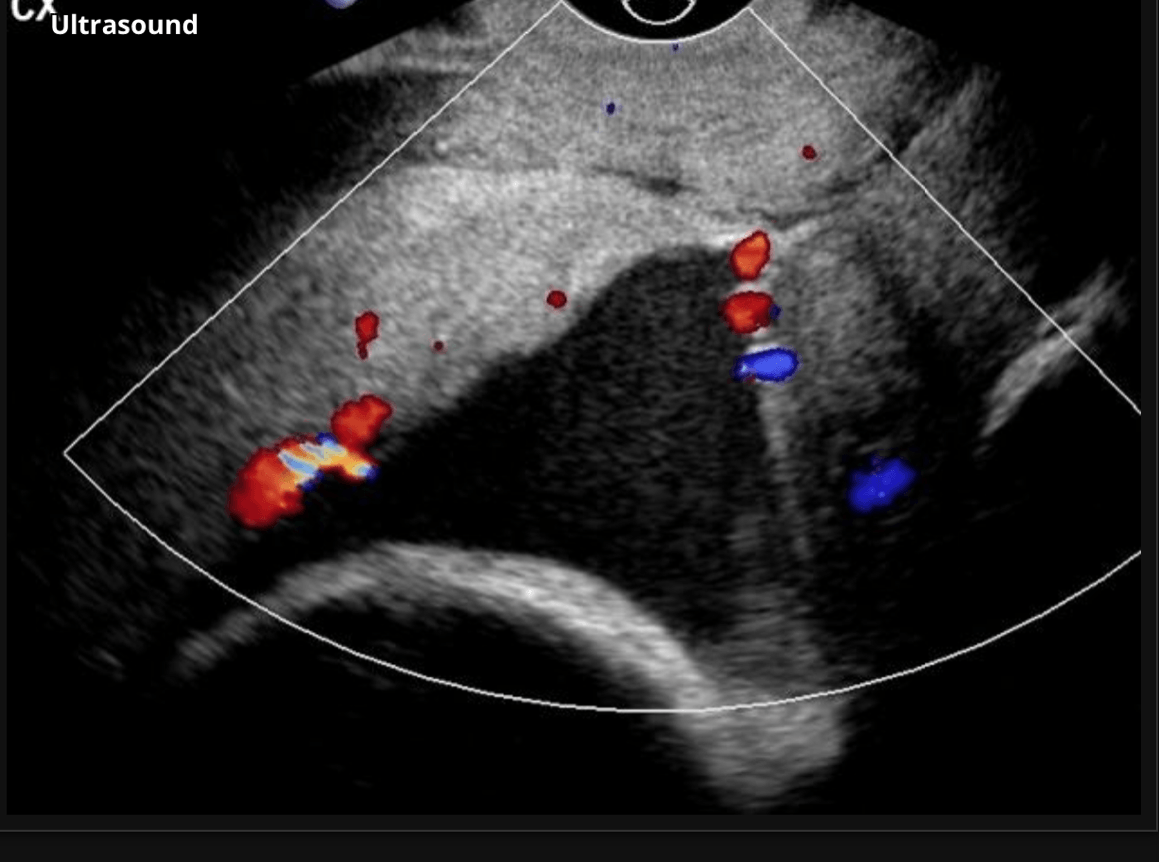
What is vasa previa and velamentous cord insertion?
Vasa previa is very dangerous to fetus. 50% of undiagnosed cases lead to stillbirth
Correctly identified cases increase survival to 97%
This was recently added to this list for fetal anatomic survey for head:
cerebellum, choroid, cisterna magna, lateral ventricles, midline flax, cavum septum pellucidum
What are the lips?
The fetal anatomic survey of chest includes 4 chamber heart and this view was added.
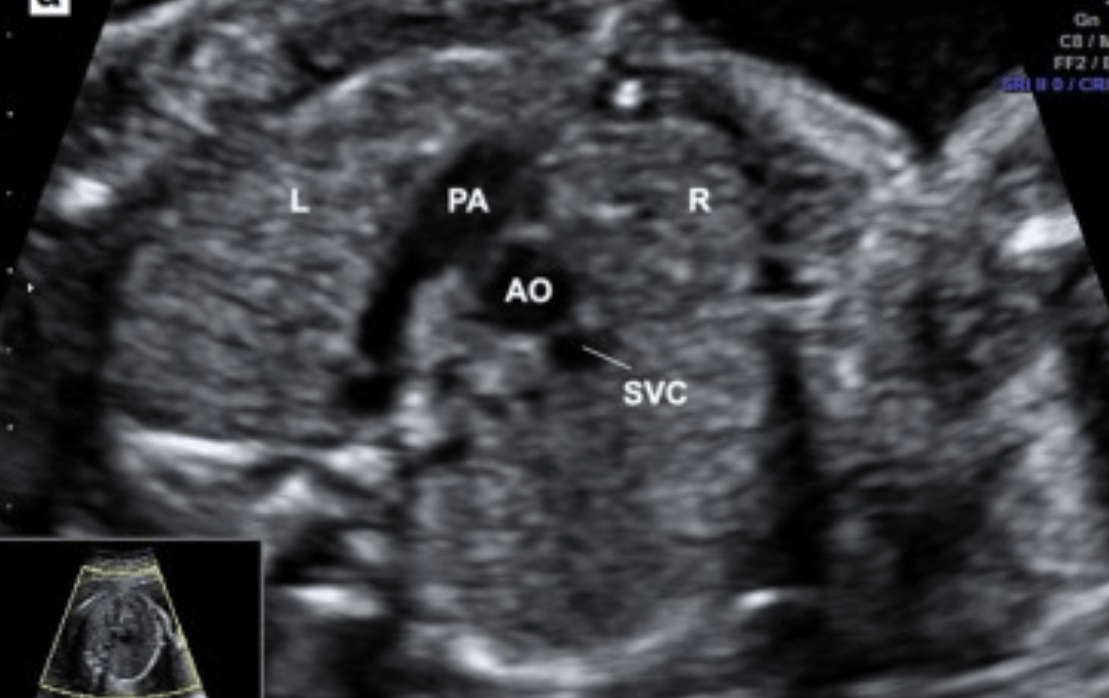
What is cardiac outflow view or 3 vessel view?
What fetal condition is this doppler obtained for?
Is this normal or abnormal?
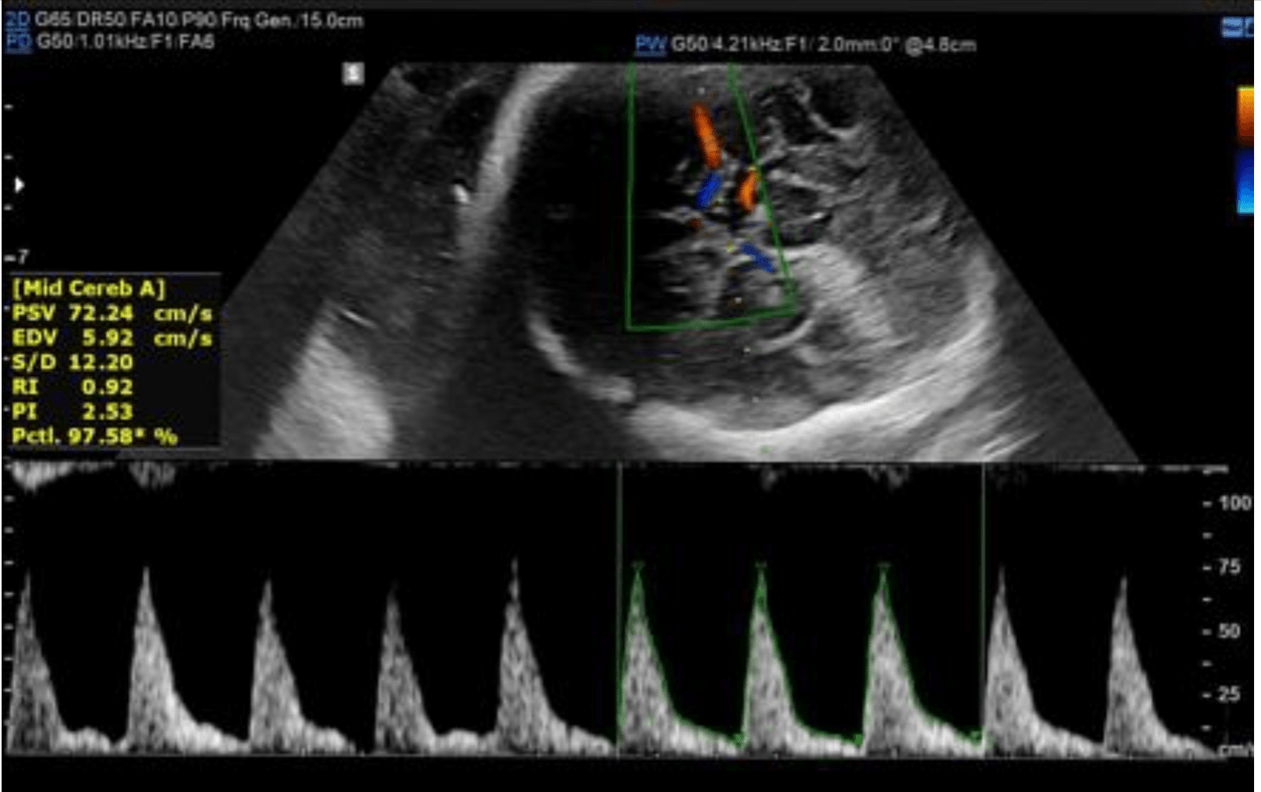
What is fetal anemia? Seen in alloimmunization, viral infections, monochorionic
Done in hydrops.
This is normal high resistance MCA doppler.
cerebroplacental ratio=MCA/umbilical artery
Cause of polyhydramnios in this case
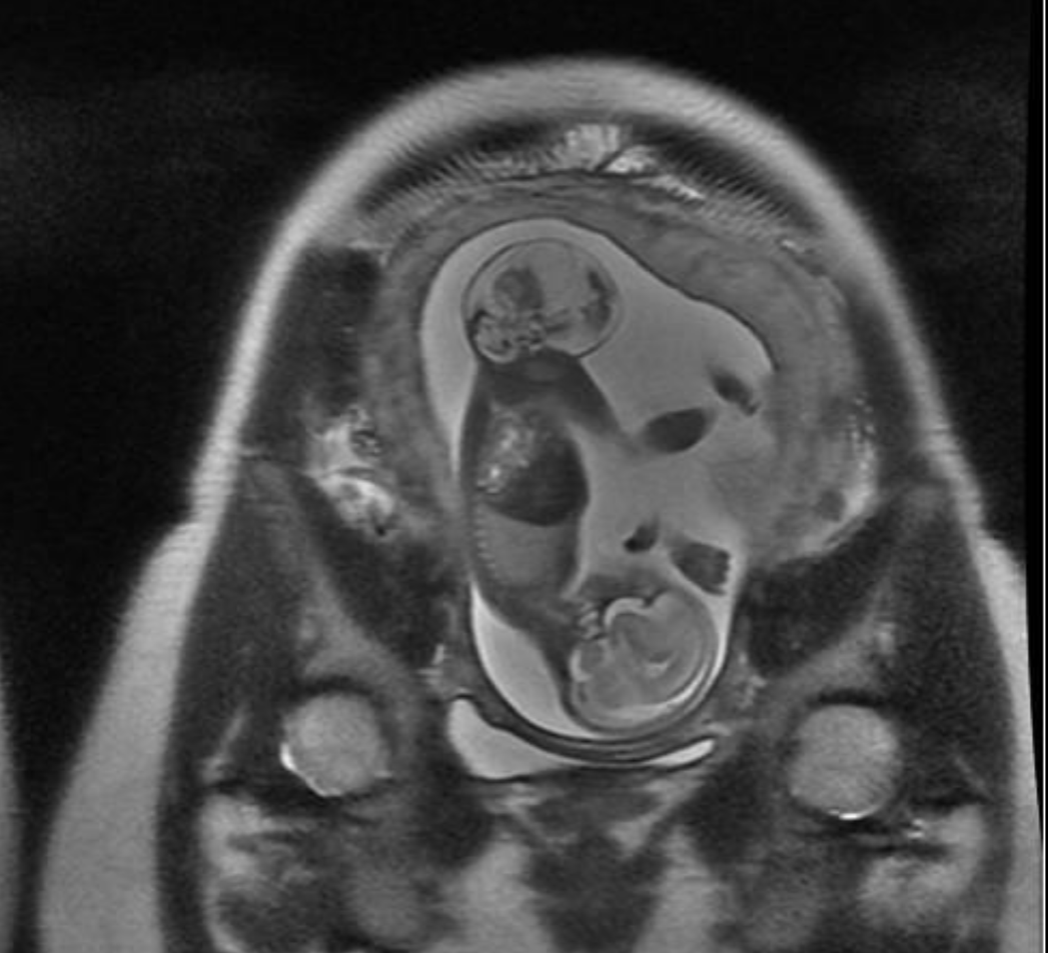
What is a sacral coccygeal Teratoma causing high Output state?
Ultrasound findings of this entity and associations?
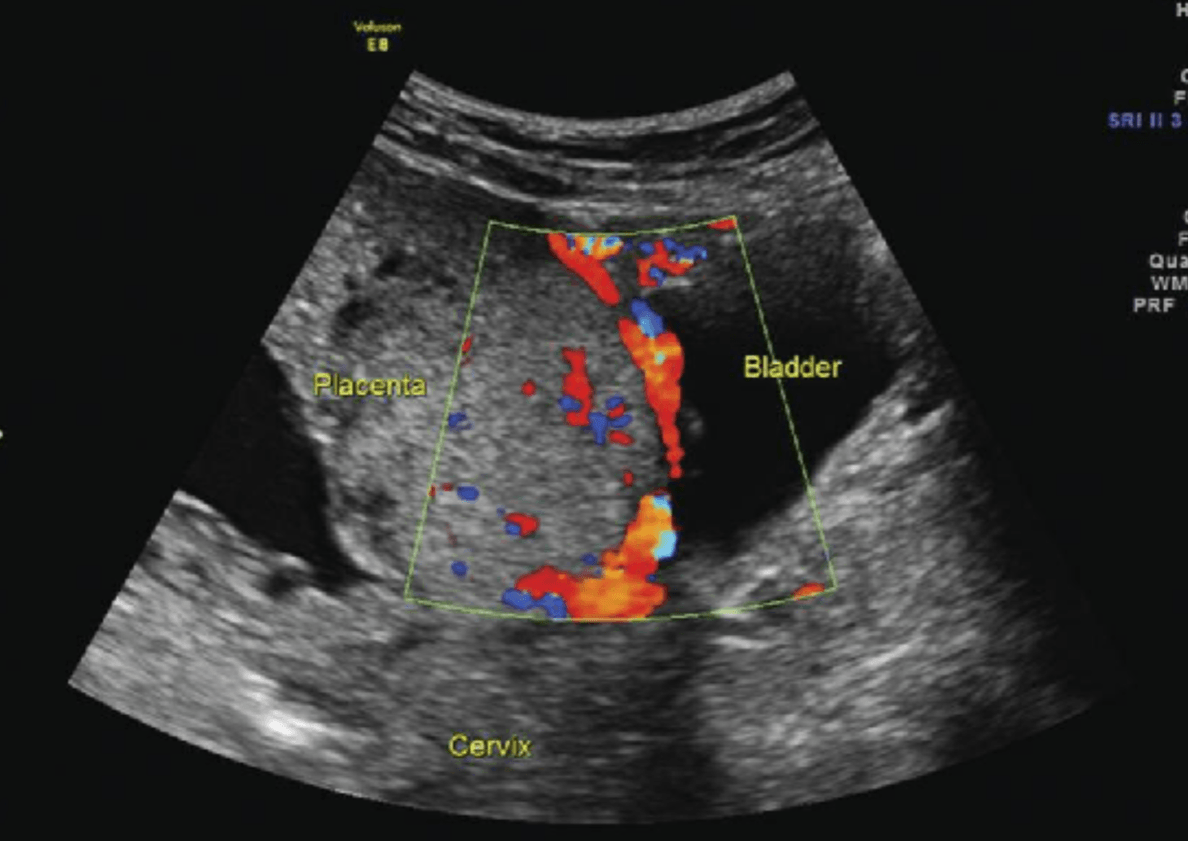
What are placental lacune and loss of retroplacental clear space?
What is prior C-section and placenta previa?
Placenta Accreta, increta, and percreta
What are these lines used to determine?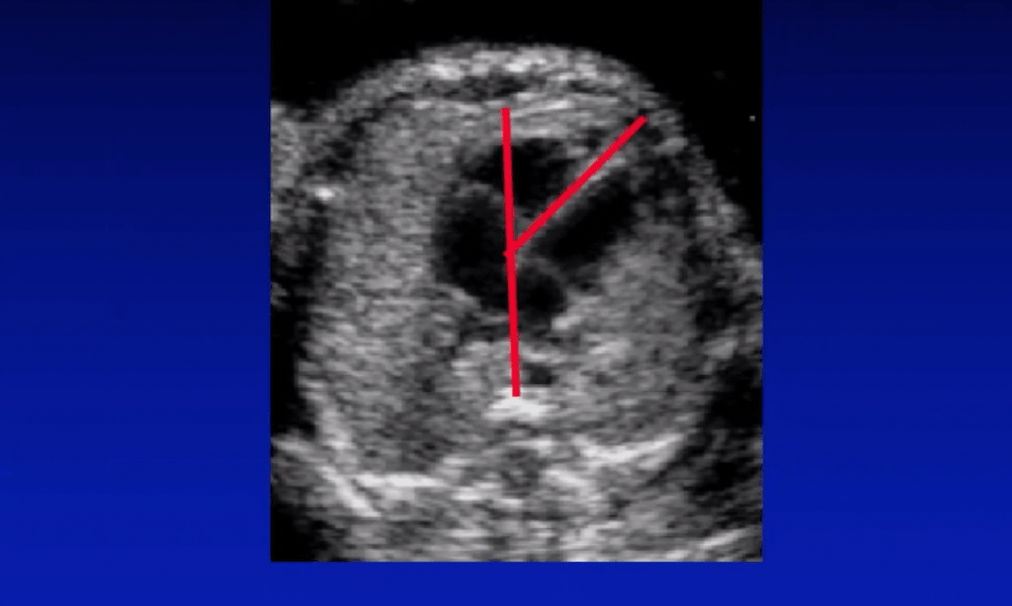
What is cardiac axis?
This is associated with IUGR, vasa previa, and twin -twin transfusion.
What is a velamentous cord insertion?
1. What is the stomach bubble?
2. What is the duodenum?
Absent stomach bubble with polyhydramnios, suspect esophageal atresia
Duodenal atresia assoc with Trisomy21