Level 1
Level 2
Which subatomic particle determines the identity of an element?
Proton
What information can you gather from an element’s atomic number on the periodic table?
It tells the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom.
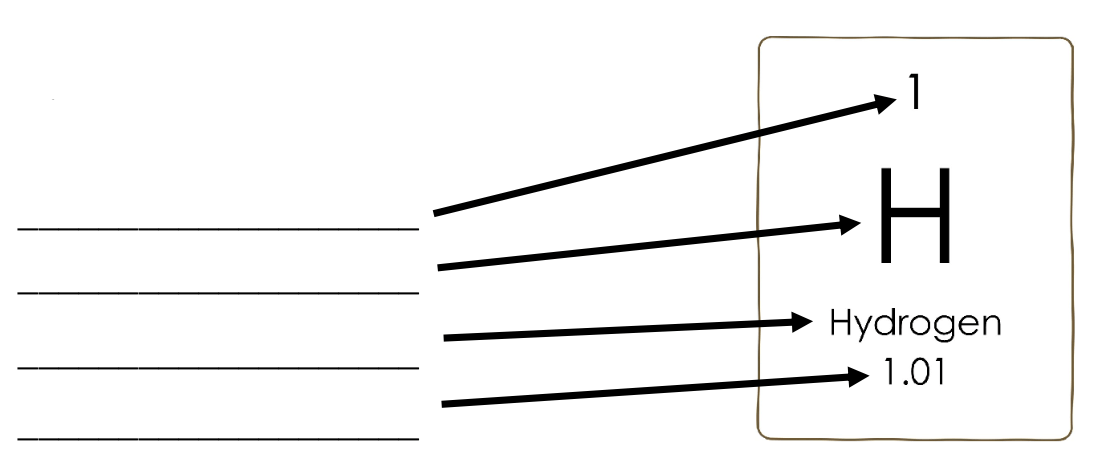
Name each of the parts of an element in the periodic table
Atomic number
Symbol
Name
Atomic weight
What is an isotope?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
What is the process called when an unstable nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation?
Radioactive decay
What force holds the negatively charged electrons in the electron cloud and the positively charged nucleus together?
Electromagnetic force
What's the nuclear notation of these neutral atom?
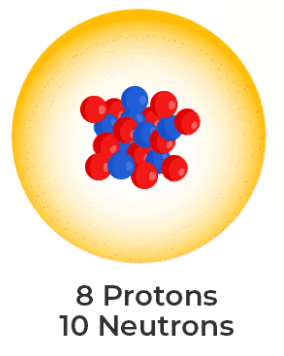
188 O
In which group would you find the most reactive nonmetals? What about the most reactive metals?
Group 1, the Alkali metals
Why do isotopes of the same element have different mass numbers but the same atomic number?
Isotopes have the same atomic number because they have the same number of protons, but they have different mass numbers because they have different numbers of neutrons.
Which type of radiation involves the release of a helium nucleus from an atom?
Alpha radiation
What is the name of the force that keeps the protons inside the nucleus despite their repulsion from each other?
Strong nuclear force
What is the relationship between the atomic number and the number of electrons in a neutral atom?
In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the atomic number (the number of protons).
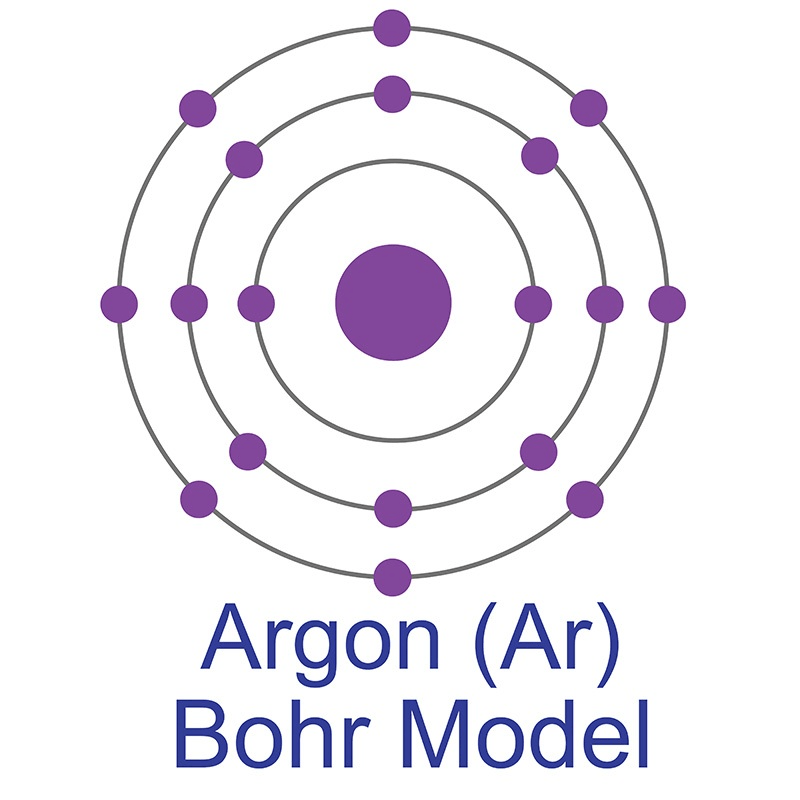
Draw a Bohr Model for the atom Argon on your whiteboards, AS A GROUP.
Is this element reactive yes or no? Why?
If an element has isotopes with mass numbers 35 and 37, and its average atomic mass is 35.5, what does this tell you about the relative abundances of these isotopes?
This indicates that isotope 35 is more abundant than isotope 37, because the average atomic mass is closer to 35.
In beta decay, a neutron splits into what two subatomic particles?
A proton and an electron
Explain how the electrons are organized in the atom and their relation with energy.
Electrons are arranged by their energy; the closest energy level (n = 1) has the least energy.
According to the Bohr Model, how many electrons can the first 3 energy levels hold?
2, 8, 18
Name 2 characteristics for each:
Non metals, Metals, Metalloids
Metals: Almost all are shiny solids with luster + Good conductors of heat and electricity
Non metals: Mostly gases or dull brittle solids + Poor conductors
Metalloids: Solids Semi-conductors
What's the difference between atomic number, atomic mass, and atomic weight?
Atomic number tells you how many protons an atom has.
Atomic mass is the sum of protons and neutrons in a specific isotope.
Atomic weight is the average mass of all isotopes of an element, accounting for their relative abundances.
What is half-life?
the amount of time it takes for half of a radioactive substance to decay
Explain why protons in the nucleus do not fly apart due to their positive charges, and what role do neutrons play in this structure?
The strong nuclear force overcomes the repulsive electromagnetic force between protons. Neutrons contribute to the stability by adding mass without charge, which helps balance the forces.
Which part of the atom is responsible for its mass and how can you calculate it? What about the electrons and how do you know how many electrons an atom have?
The nucleus, and you calculate it by adding the protons and neutrons.
The electron cloud, you calculate it like:
If the atom is neutral, p = e
If the it's an ion, then #protons - x = overall charge of atom
If an atom has 3 energy levels and 8 electrons in its outermost level, what group and period does this element likely belong to, and what's the name of this element?
Group 18 (noble gases) and Period 3.
ARGON
Fill in the chart AS A GROUP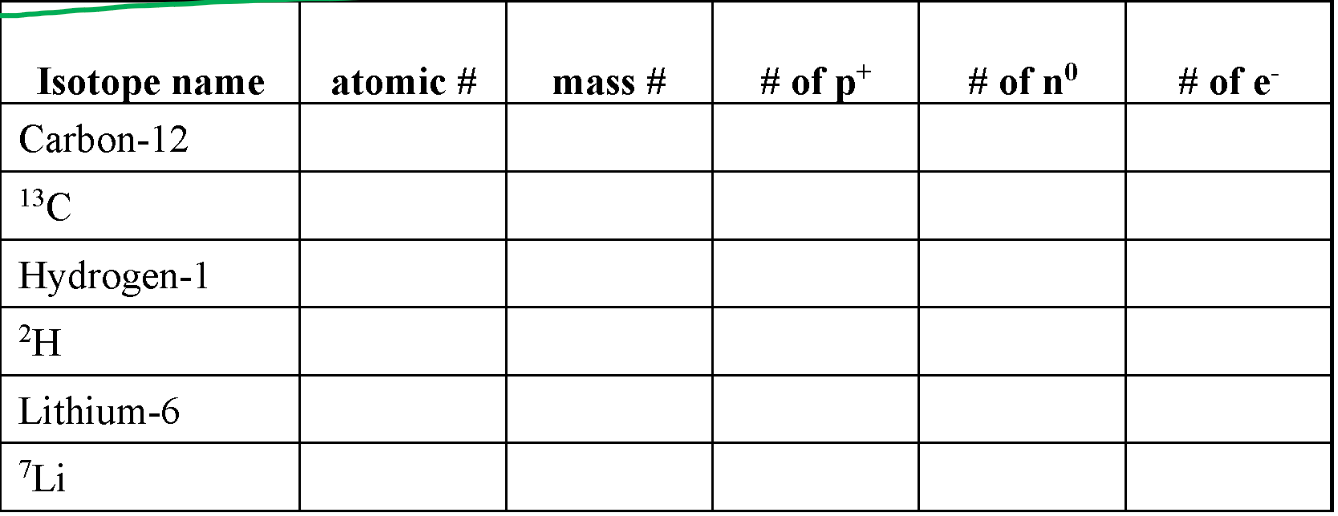
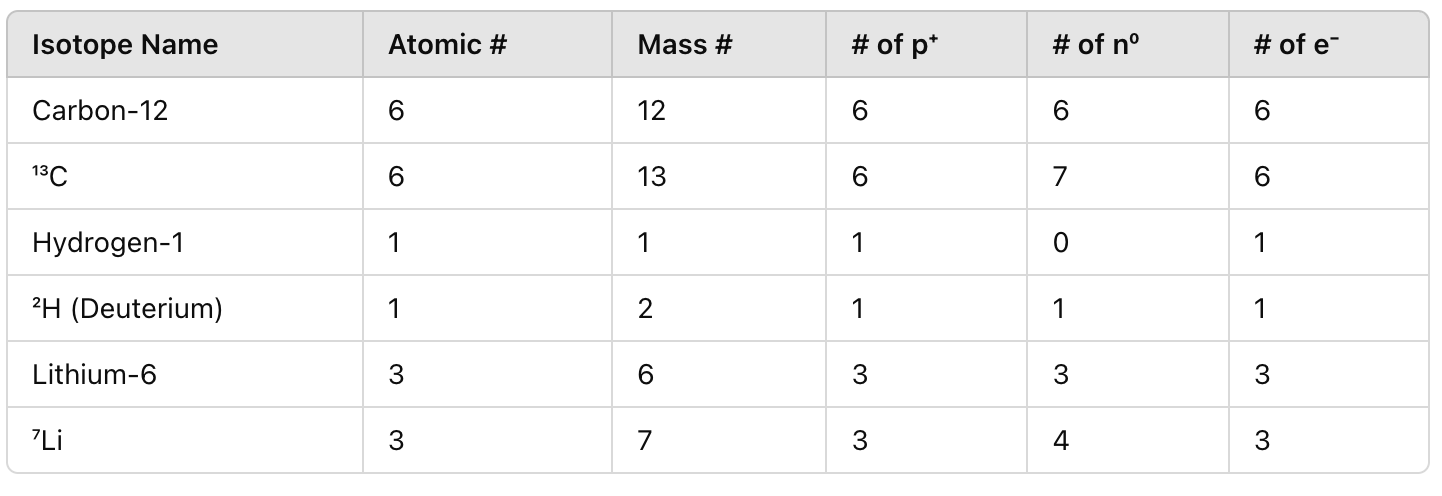
What is the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion?
Nuclear fission is the splitting of a large atom into smaller atoms.
Nuclear fusion is the combining of smaller atoms into a larger atom