A group of the same species that live in the same place at the same time.
Population
Anything that has mass and takes up space.
Matter.
Molecules comprised of carbon and hydrogen only.
Hydrocarbons.
States:
all living things are composed of one or more cells
the cell is the basic unit of life
all new cells arise from existing cells
Cell Theory
DO NOT have Cell wall, chloroplasts, plasmodesmata, and plastids used for storage, or a large central vacuole.
Animal cells
Interconnected directly with the nuclear membrane.
Produces lipids and proteins in different areas.
Sends molecules produced to other organelles via vesicles.
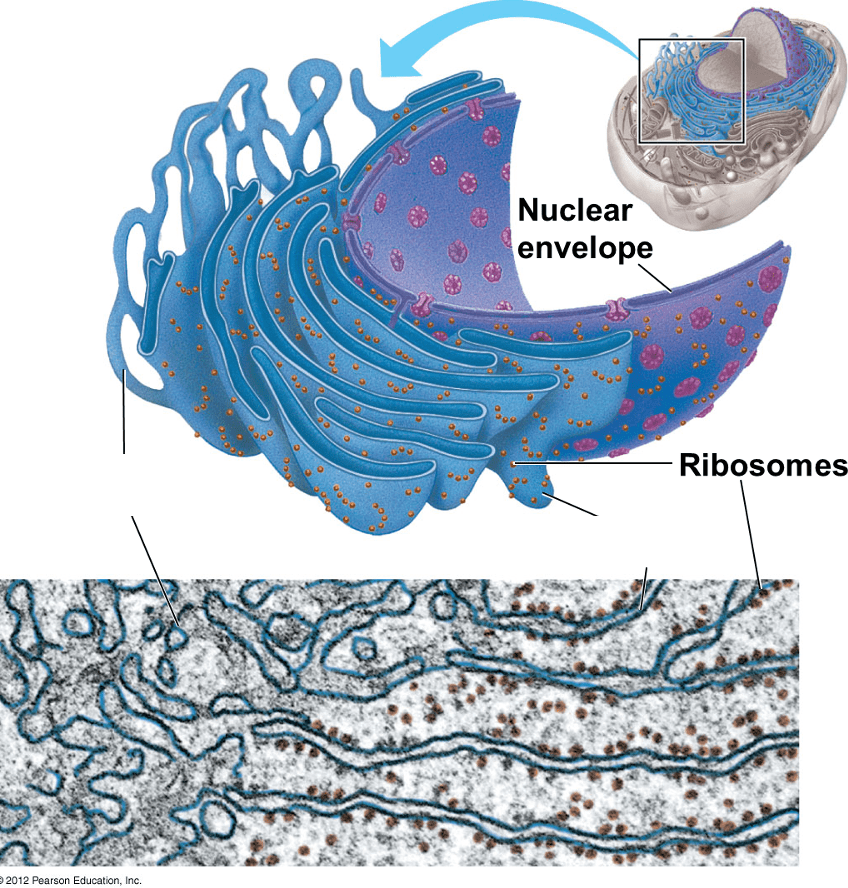
Endoplasmic reticulum. (Smooth and Rough).
Term for a group of cells that bond together to perform a similar function.
Tissue
An element / atom that has the standard number of protons, but more neutrons so it also has a higher atomic mass.
Isotope.
Affects a biological molecule’s function in a characteristic way.
May include 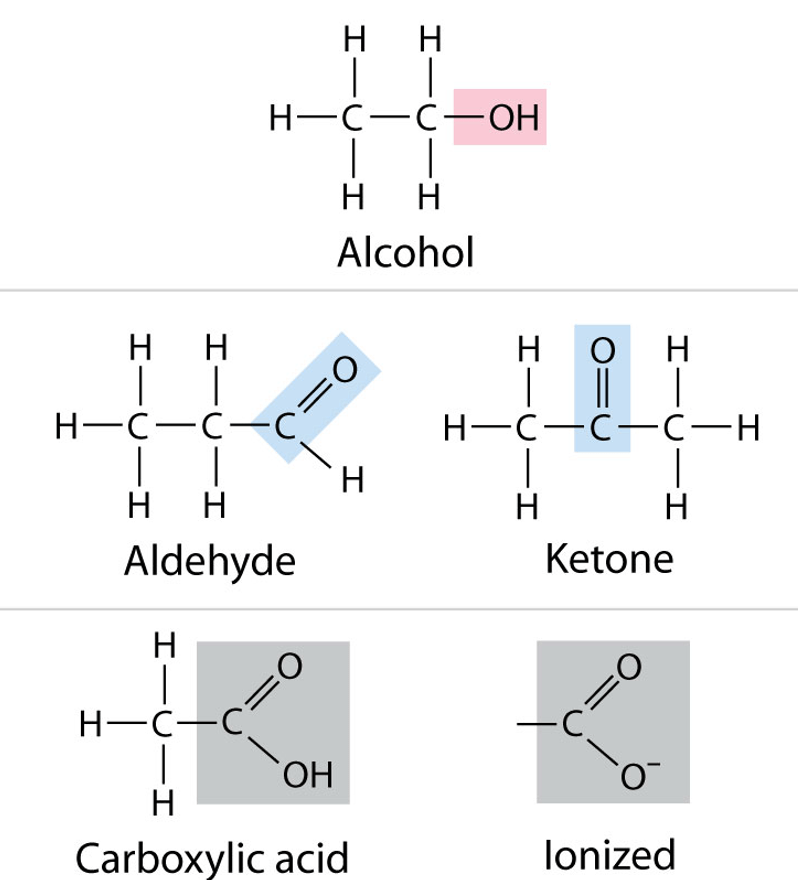
Functional group.
Type of microscopy that:
Has a stage and course focus.
Uses two sets of lenses to magnify the image.
Illuminates the image from below.
Can magnify using an occular lens and objective lenses of various magnifications (e.g., 4x, 10x, 40x)
Compound light microscopy.
Have their own DNA and ribosomes.
Site of photosynthesis.
Contain chlorophyll.
Occur in plant cells and not animal cells.
Chloroplasts.
Used for:
Motility of the cell / propulsion of cell
To clear the area around cells
Fine hair-like structures that "row" in unison to move cells like Paramecium

Cilia
Bacteria
Archeae
Eukarya
Domains of Life
The need for an element to have the maximum number of electrons in its valence shell (often 8).
Rule of Octet.
Called this because of their large size.
Made of multiple monomers bonded together.
Include fatty acids, polysaccharides, and nucleic acids.
Polymers.
Have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan, comprised of sugars and amino acids
DNA is found in nucleoid
Have polysaccharide capsule (protection, attachment)
MAY have flagella, pili, or fimbriae.
Prokaryotic cells
Membrane around cells that:
contains a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins (integral or peripheral)
separates inside of the cell from the environment outside the cell
maintains structure and fluidity of the cell while regulating what enters and leaves the cell
Plasma membrane / Phospolipid bilayer / Fluid mosaic model
Cell structures responsible for protein synthesis
Found in practically every cell.
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts have their own
May be free or attached to the ER
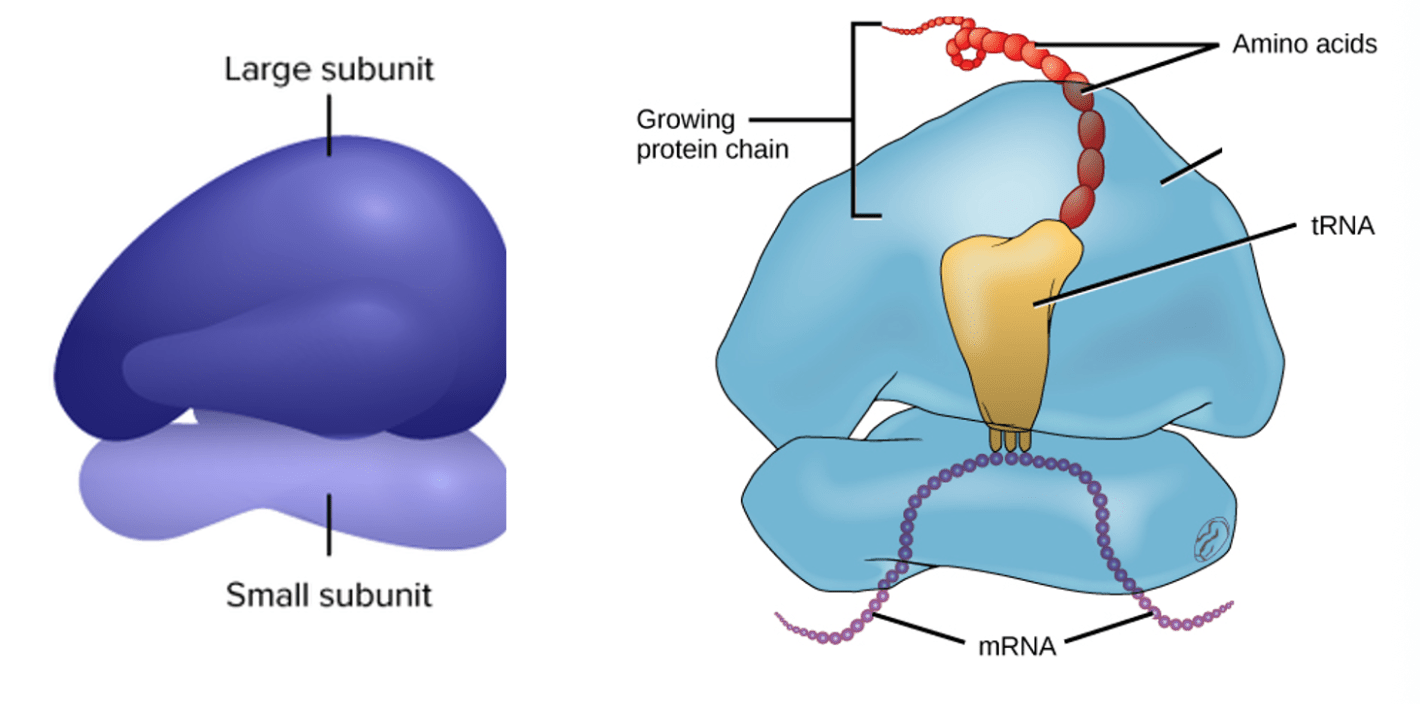
Ribosomes
An educated guess that attempts to answer a scientific question.
Hypothesis
The type of bond in which electrons are shared to attain the rule of octet.
A strong bond and may be polar or non-polar.
Covalent bond.
The type of reaction used to break macromolecules into individual building blocks.
Requires the addition of water to occur.
Hydrolysis
1.A plasma membrane, an outer covering that separates the cell’s interior from its surrounding environment
2.Cytoplasm, consisting of a jelly-like region within the cell
3.DNA, the genetic material of the cell
4.Ribosomes, particles that synthesize proteins
Common features of all cells.
Occur in both plant and animal cells.
Have their own DNA and ribosomes.
Considered the powerhouse of the cell
Have their own DNA and ribosomes.
Mitochondria
Substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
NO energy being used
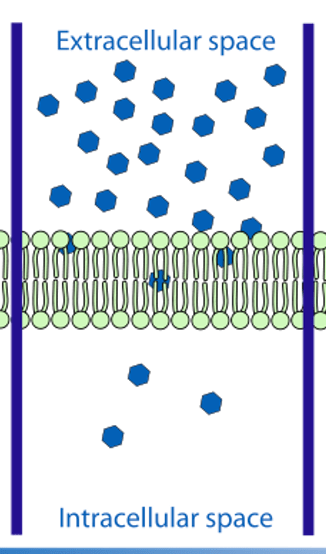
Passive diffusion
Order, Reproduction, Adaptation, Homeostasis, Response to Stimuli
Some properties of life.
Contribute to cohesion and adhesion.
Create surface tension.
Often occur between polar covalent molecules.
Transient and fairly weak bonds.
Hydrogen bonds
Include thousands of variations with different functions including enzymes, transport channels, and receptors.
Formed by peptide bonds.
Made of just 20 building blocks arranged in different, specific orders called primary structures.
Proteins.
Are membrane-bound structures found in eukaryotic cells.
Perform various functions within the cell.
Include mitochondria, centrosomes, and peroxisomes.
Organelles
Most obvious organelle in most animal and plant cells
Contains DNA in chromosomes
Directs protein synthesis by making RNA (mRNA)
Nucleus
Solution such as tap water.
The extracellular fluid (outside the cell) has a lower concentration of solutes than the fluid inside the cell, and water enters the cell.
Cell will tend to swell.
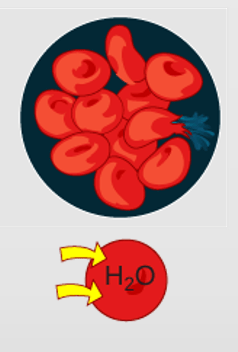
Hypotonic solution