What is the "powerhouse" of the cell?
The Mitochondria
What are the 4 main types of tissue?
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, and Nervous tissue
What is the long bone structure? (Parts)
Epiphysis, Diaphysis, Articular Cartilage, Periosteum, Medulla/Medullary cavity
What are the types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal, Smooth, and Cardiac
What is the difference between the axons and dendrites?
Axons send away or conduct information away from the cell, while dendrites receive information.
What are the phases of Mitosis?
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase and Cytokinesis
Difference between tendons and ligaments?
Tendons are muscles to bones, and ligaments are bones to bones
What is Articular Cartilage?
Cartilage covering the ends of the bones
What is the difference between actin and myosin?
Actin are thin filaments while myosin are thick filaments.
Which brain lobe has a function of smell, speech, hearing, and core memory on the left; and on the right it has a function of hearing, smell, rhythm, intonation of speech, and interpreting facial expressions.
The Temporal lobe
What is the difference between the cytoplasm and cell membrane?
The cytoplasm contains the organelles and is the area in between the nucleus and the membrane. The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell (it is selectively permeable).
Where is nerve tissue found?
Found in brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Where are the mature bone cells enclosed? (name the chambers and name of the cells)
Osteocytes are enclosed in tiny chambers called Lacunae
What are the three layers of connective tissue in order from the outermost to the one surrounding each muscle fiber?
Epimysium is the outermost layer, Perimysium surrounds the fascicles, and Endomysium surrounds each individual muscle fiber
WHat two ions are important in neural impulse?
Potassium (K-) and Sodium (Na+) ions
In active transport, what is exocytosis and endocytosis?
Exocytosis: secretion; things exit the cell
Endocytosis: things enter the cell
What type of cartilage covers the ends of the joints and which one is found near your ear and larynx?
Hyaline; Elastic
What are the types of joints (articulations) and how movable are each?
Synarthrotic - immovable joint, Amphiarthrotic - slightly movable, Diarthrotic - movable joint
What is Muscular Dystrophy?
A disorder that causes muscle weakness and leads to reduced mobility.
What are the symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis?
Sensory loss: Numbness in limbs, burning or prickly sensations; Spinal cord (motor): muscle cramping, paralysis; Vision: blindness or blurred; Constitutional: fatigue and dizziness; Cognitive difficulties: concentration, memory, and judgment; Mental health: depression, bipolar or dementia
Label the diagram:
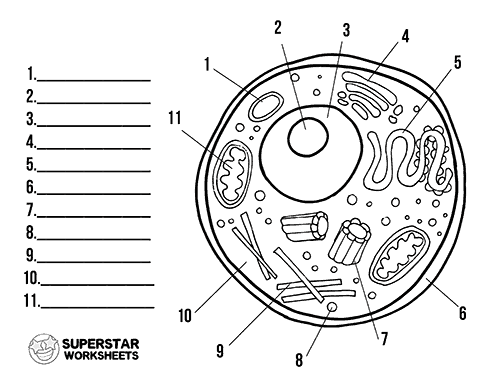
1. Lysosome, 2. Nucleolus, 3. DNA/Nucleus, 4. Golgi apparatus, 5. Smooth ER/Endoplasmic Reticulum, 6. Cell membrane, 7. Centrosomes or centrioles, 8. Ribosomes, 9. Cytoskeleton, 10. Cytoplasm, 11. Mitochondria
Which ones are involuntary or voluntary of the 3 muscle type tissue?
Skeletal is voluntary, Smooth is involuntary, Cardiac is involuntary.
Name the bones/sutures of the skull, starting from the left to bottom and then right to bottom
1. Frontal, 2. Nasal, 3. Sphenoid, 4. Lacrimal, 5. Zygomatic, 6. Vomer, 7. Maxilla, 8. Coronal Suture, 9. Parietal, 10. Temporal, 11. Mandible
Label the diagram.
Sarcomere is G, Sarcolemma D, Synapse is A, Motor end plate is E, Neuron is B, Vesicles are C, and T-tubules are F
Label the diagram.
1. cell body, 2. oligodendrocyte, 3. microglial cell, 4. myelin sheath