Describe 2 properties of water.
Solvent; surface tension; polarity; surface tension; adhesion/cohesion; low density of ice; capillary action; high heat capacity.
What are the four types of macromolecules we studied.
Proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids
What is the job of DNA? What is the job ofRNA?
DNA- Stores the genetic code "Instruction manual"
RNA- Translates the genetic code into proteins "Reads and executes instructions"
What is a chemical agent that selectively speeds up reactions?
Catalyst
What functional group(s) is present in the following image?
Amino group
What is the name of the bond when one side is partially negative and one is partially positive?
Polar Covalent Bonds
Why is carbon crucial in forming all macromolecules?
Allows for complex, and diverse structures because it can bond with up to four different atoms at once.
"Our bond is like a hydrogen bond, weak yet indispensable!"
Add 200 points!

How will raising the temperature slightly affect the rate of the reaction?
Increase the rate of the reaction.
What two groups join together to form the backbone of proteins?
Amino group and carboxyl group.
What are the differences between cohesion and adhesion?
Cohesion: attraction between the SAME molecules, i.e water and water
Adhesion: attraction between two DIFFERENT molecules, i.e water and plant wall
How do you tell the difference between a saturated fatty acid, and an unsaturated fatty acid?
Saturated: Contains NO double bonds
Unsaturated: Contains at least one double bond
What are the structural differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA- double stranded, has deoxyribose, and contains A, G, C, T
RNA- Single stranded, has ribose, and contains A, G, C, U
Uh oh! You forgot to properly label your graph, minus 300 points

What functional group is found in ATP and ADP?
Phosphate group
Explain the reason why water and oil don't mix together
Differences in polarity, water is polar, and oil is non-polar, so their differences in polarity don't allow it. "Like dissolves like"
Nitrogen is crucial for forming what macromolecule(s)?
Proteins and nucleic acids
What are the main components of a DNA strand?
Nitrogenous base, sugar phosphate bone, phosphate end (5') and hydroxyl end (3')
What are the reactants of enzyme-catalyzed reactions?
Substrates
What functional group(s) are present in the following image?
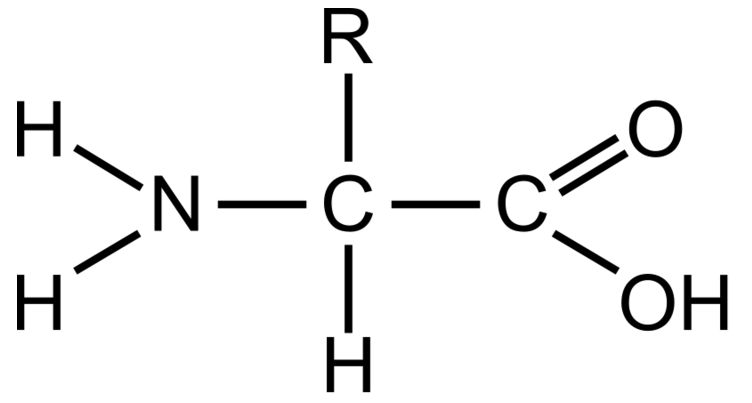
Amine Group and Carboxyl Group
How do ice sheets in the water help/harm the ecosystems they are in? Why do they float?
They help by reflecting the sun rays and helping protect the wildlife below.
They float because the ice is less dense than the liquid form of water, due to its crystalline structure.
Describe each type of protein structure
Primary: A linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
Secondary: Repeating patterns of folding within the chain, (alpha helix or beta pleated cheat)
Tertiary: 3D folding pattern of a protein due to side chain interactions.
Quaternary: Arrangement of multiple polypeptide subunit to form a functional protein complex.
What is the complementary strand of this DNA sequence?
5' ATGGACGATCG 3'
3' TACCTGCTAGC 5'
What is the difference between dehydration and hydrolysis?
Hydrolysis- ADDITION of water to a molecule to break it down into smaller pieces. (polymers to monomers)
Dehydration- REMOVAL of water between two molecules to form one. (monomers to polymers)
Write the abbreviated name for ALL 7 functional groups
COOH
NH2
SH
OH
CO
PO4
CH3