How do you respond to an IDENTIFY Prompt
Simple one sentence answer WITH a B.S. sentence
Identify a Primary Producer
Algae or Seaweed
Describe the critical processes by which nitrogen is cycled through the biotic and abiotic components of Earth’s ecosystems and identify the primary storage sink for nitrogen.
Atmospheric nitrogen is fixed by bacteria in soil and in root nodules to produce ammonia/ammonium (some by lightning).
Ammonia is oxidized in soil by nitrifying bacteria to nitrites and then to nitrates.
Plants take up soluble nitrogen compounds through roots.
In plants, nitrogen compounds are used to produce biochemicals like protein, DNA, chlorophyll.
Denitrifying bacteria break down nitrogen compounds in the process of decomposition and release elemental nitrogen back into the atmosphere; or nitrifying decomposers break down organic nitrogen compounds, making them available to plants again in the form of nitrates.
The atmosphere is the primary storage sink!
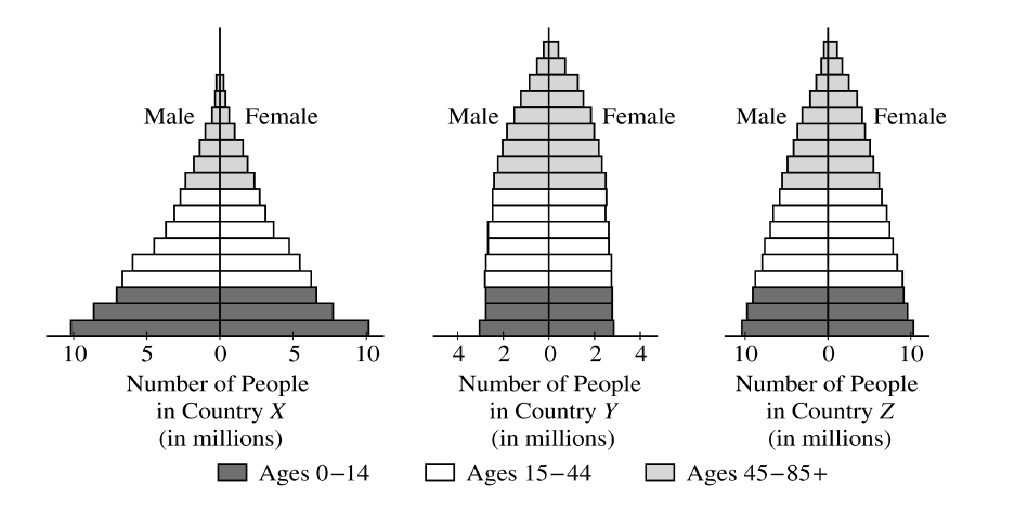 Which of the 3 countries has the largest rate of population growth? Which has the smallest?
Which of the 3 countries has the largest rate of population growth? Which has the smallest?
X has the highest rate of population growth
How do you respond to an DESCRIBE prompt
2 points of detail, basic key facts
Describe the two organisms that compete for the same food source.
that compete for the same food source.
Seal or herring gull
Explain ONE major way in which the phosphorus cycle differs from the nitrogen cycle.
Phosphorus cycle does not involve any gaseous compounds.
Or the major sink in the phosphorus cycle is the lithosphere,
Or that bacteria are not as pivotal in the phosphorous cycle as they are in the nitrogen cycle.
Compare the infant mortality rates that are likely in Countries X and Y. Explain your reasoning.
Country X has a higher infant mortality rate than country Y
How do you respond to a EXPLAIN prompt in an FRQ?
3 layers of detail. Give some connection between a CAUSE and EFFECT
 Explain how primary productivity determines the energy within an ecosystem and how energy changes through trophic levels.
Explain how primary productivity determines the energy within an ecosystem and how energy changes through trophic levels.
Identify EITHER one nitrogen compound OR one phosphorus compound that is considered a pollutant when released by human activity into the environment. For the compound you identified, describe the human activity and a specific environmental problem that results.
One point is earned for identification of one N or one P compound (such as nitrates in commercial fertilizers or phosphates in cleaning agents).
One point is earned for a description of a human activity that results in the release of the compound (such as application of fertilizer in farming and subsequent runoff, or release of gray water from improper wastewater treatment or cleaning operations).
One point is earned for describing a specific environmental problem that results from the release of the identified compound (such as altered DO, cultural eutrophication, dead zones).
Describe the changes in both the birth rate and the death rate for a country making the transition from a preindustrial society to an industrial society.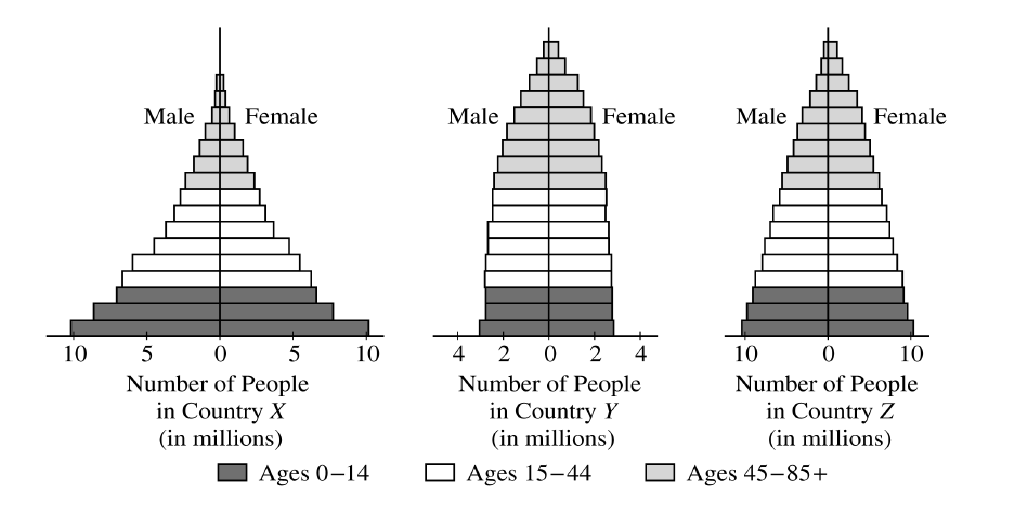
1 point earned for preindustrial phase (term not necessary): initially birth rate and death rate are both high
1 point earned for transition phase: birth rate remains high, death rate declines (because of better health care, etc.)
1 point earned for industrial phase: birth rate declines and approaches death rate (mention of postindustrial phase with explanation is acceptable)
How do you respond to a "Propose a solution" prompt
2 layers of detail. Explain how your proposed solution will solve the problem presented.
 Make a Claim about how the population of crabs can be increased in this aquatic foodweb.
Make a Claim about how the population of crabs can be increased in this aquatic foodweb.
If the population of seaweed is increased through a fertilization program then the crab population will increase due to the increased food availability.
Describe ONE way in which humans have disrupted the natural cycling of carbon and TWO major environmental consequences of that disruption.
One point is earned for identifying one disruption caused by humans (such as burning of fossil fuels, deforestation/slash and burn).
One point each is earned for two environmental consequences of the disruption (such as global warming, increased rates of photosynthesis, ocean acidification, sea-level rise, and weather disruptions resulting from global warming—for example, flooding, drought, heat waves, intensification of storms).
Note: No points are earned for acid rain or any other noncarbon-related environmental problems.
One additional elaboration point may be earned for a more detailed description of a sustainable method.
Describe the changes in both the birth rate and the death rate for a country making the transition from a preindustrial society to an industrial society.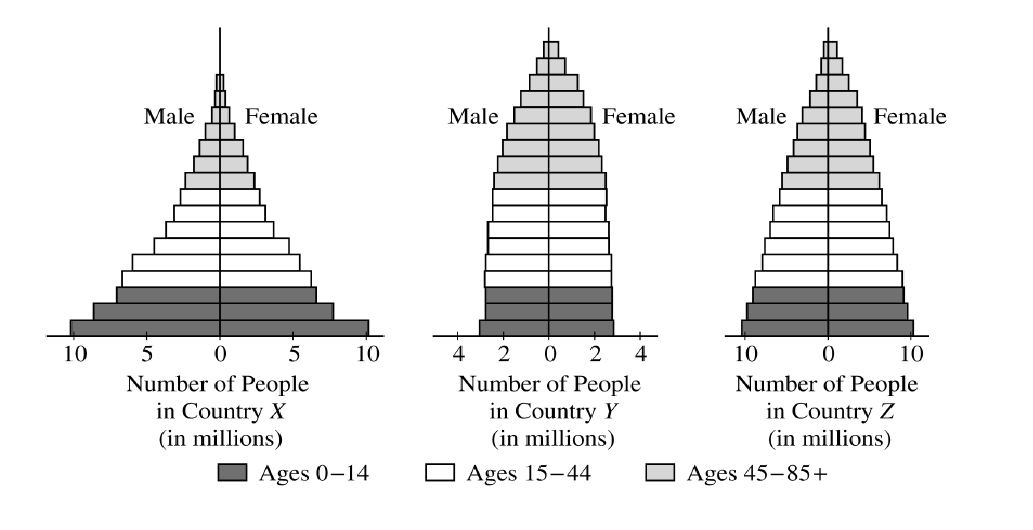
Free/more accessible/government-subsidized family planning -- must be linked to specific example, such as: free clinical services like birth control, free education about birth control, birth spacing, etc.
Economic rewards or penalties -- must be linked to specific example, such as:
payment for sterilization eliminating income tax deductions for more than one child
free health-care benefits for families with 0-1 children
free higher education for women/child of single-child family
increased social security or pension benefits for couples with 0-1 children
better job opportunities for women/couples with 0-1 children
monetary bonus at end of year if only have 0-1 children
giving free counseling to teenagers that have had a child
government subsidized housing if have 0-1 children
bonus at end of year if woman remains under single-child limit
couples pay a tax for each child after the first one
other logical methods of negative economic incentives or rewards.
Raising legal marriage age
Specific examples with explanation (e.g., China)
paid leave to women for fertility operations
monthly subsidy to single-child families
job priorities for only children
housing preferences for single-child families
additional food rations for one-child families
monetary compensation for single-child families
If this occurs, then this will happen!
 Propose a solution that will limit the overharvesting of fish populations in this food web system
Propose a solution that will limit the overharvesting of fish populations in this food web system
Lets see what you got!