Juxtaposing two things to highlight their similarities and differences.
What is compare and contrast?
Refers to telling a story or recounting a series of events.
What is narration?
This is the first step of the classical model and introduces the reader to the subject being discussed.
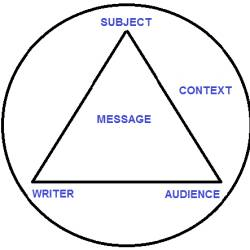 This is the _____.
This is the _____.
What is Rhetorical Triangle?
One's intention or objective in a speech or piece of writing
What is purpose?
Analyzing the things that lead to a certain result or, conversely, the results that stem from a certain thing
What is cause and effect?
Explains how something works, how to do something, or how something was done.
What is process analysis?
This is the last step of the model and brings the essay to a satisfying close.
What is conclusion?
An appeal to logic or reason, this offers clear, rational ideas.
What is logos?
What is audience?
Providing a series of examples, this turns a general idea into a concrete one.
What is exemplification?
Closely allied with narration, this emphasizes the senses by painting a picture of how something looks, sounds, smells, tastes, or feels.
What is description?
What is narration?
An appeal to the emotions of the reader/listener/viewer
Words, events, or circumstances that help determine meaning
What is context?
Being able to sort material or ideas into major categories; what goes together and why
What is classification and division?
The action or fact of ____ someone to do something or of being ____ to believe or do something.
What is persuasion/persuasive?
This is the fourth part of the classical model and addresses the counterargument.
What is refutation?
The author's attempt to establish their credibility and prove why we should be listening to them.
What is ethos?
The speaker's attitude toward the subject or audience.
What is tone?
To ensure that writers and their audiences are speaking the same language, _____ may lay the foundation to establish common ground or identifying areas of conflict.
What is definition?
An ironic, sarcastic, or witty composition that claims to argue for something but actually argues against it.
What is satire?
This is the third part of the classical model, usually the major part of the text, and includes the development/proof needed to make the writer's case.
What is confirmation?
Making a serious or urgent request, typically to the public, but also to the reader/viewer/listener.
What is appeal?
The practice of taking someone else's work or ideas and passing them off as one's own.
What is plagiarism?